Biology
250 likes | 507 Vues
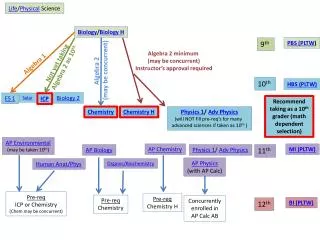
Biology. 35–5 Drugs and the Nervous System. Drugs. A drug is any substance, other than food, that changes the structure or function of the body.

Biology
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Biology Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
35–5 Drugs and the Nervous System Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Drugs • A drug is any substance, other than food, that changes the structure or function of the body. • Some drugs, such as cocaine and heroin are illegal. Other drugs, such as penicillin and codeine are prescribed by doctors. Still other drugs, including cough medicines can be purchased over the counter. • All drugs can be harmful if used improperly or abused. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Drugs • Drugs differ in the ways in which they affect the body. • Some kill bacteria and are useful in treating disease. • Others affect a particular system of the body. • Others cause changes to the brain and synapses. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Drugs That Affect the Synapse • What are the different classes of drugs that directly affect the central nervous system? Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Drugs That Affect the Synapse • Stimulants • Stimulants increase heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing rate. In addition, stimulants increase the release of neurotransmitters at some synapses in the brain. • Common stimulants include amphetamines, cocaine, nicotine, and caffeine. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Drugs That Affect the Synapse • Depressants • Depressants slow down heart rate and breathing rate, lower blood pressure, relax muscles, and relieve tension. • Barbiturates, tranquilizers, and alcohol are some examples of depressants. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Drugs That Affect the Synapse • Cocaine • Cocaine causes the sudden release in the brain of a neurotransmitter called dopamine. • Cocaine also acts as a powerful stimulant. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Drugs That Affect the Synapse • Opiates • Opiates mimic endorphins which normally help to overcome sensations of pain. • Common opiates include morphine and codeine. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Drugs That Affect the Synapse • Marijuana • The most widely abused illegal drug is marijuana. • Marijuana comes from Cannabis sativa, a hemp plant. • Hashish, or hash, is a potent form of marijuana. • The active ingredient in marijuana is THC. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Drugs That Affect the Synapse • Long-term use of marijuana can result in: • loss of memory • inability to concentrate • in males, reduced levels of the hormone testosterone in males Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Drugs That Affect the Synapse • Alcohol • What is the effect of alcohol on the body? Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Drugs That Affect the Synapse • Alcohol is a depressant that slows down the rate at which the central nervous system functions. • Alcohol slows down reflexes, disrupts coordination, and impairs judgment. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Drugs That Affect the Synapse • Heavy drinking fills the blood with so much alcohol that the central nervous system cannot function properly. • People who drink a lot of alcohol usually cannot walk or talk properly, and they are not able to safely control an automobile. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Drugs That Affect the Synapse • Pregnant women who drink alcohol risk having a child with FAS. • Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) is a group of birth defects caused by the effects of alcohol on the fetus. • FAS can cause minor to serious brain damage, heart defects, malformed faces, delayed growth, and poor motor development. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Drugs That Affect the Synapse • Alcohol and Disease • People who have become addicted to alcohol suffer from a disease called alcoholism. • If a person cannot function properly without satisfying the craving for alcohol, that person has an alcohol-abuse problem. • Long-term alcohol use destroys liver cells. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Drug Abuse • Drug Abuse • Drug abuse is the intentional misuse of any drug for nonmedical purposes. • Drug abuse can cause psychological dependence or serious physical damage to the body. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Drug Abuse • Uncontrollable dependence on a drug is called an addiction. • Some drugs cause a strong psychological dependence, or mental craving. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
35–5 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
35–5 • A drug that increases the heart rate and breathing rate is a • depressant. • opiate. • stimulant. • barbiturate. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
35–5 • A powerful stimulant that increases blood pressure and heart rate that can lead to a heart attack is • cocaine. • opium. • marijuana. • caffeine. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
35–5 • Many drugs that affect the brain and behavior do so because they • affect organ systems and those changes are detected by the brain. • interfere with the normal functioning of neurotransmitters. • cause the brain to release endorphins. • enter the cell bodies of brain neurons causing them to behave differently. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
35–5 • True or False? Medically prescribed drugs cannot cause addiction. • True • False Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
35–5 • Alcohol acts on the brain as a • general stimulant of the nervous system. • general depressant of the nervous system. • pain reliever acting in the cerebrum. • stimulant of the brain stem and cerebellum. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall