Weather forecasting
250 likes | 877 Vues
Weather forecasting. EG1204 Earth Systems Dr Jonathan Lageard. Weather. ‘Overall state of the atmosphere on a time-scale of minutes to months’ Thomas & Goudie, 2000 p527 Weather describes specific conditions rain, temperatures, dew-point, wind speed and direction, visibility…

Weather forecasting
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Weather forecasting EG1204 Earth Systems Dr Jonathan Lageard
Weather • ‘Overall state of the atmosphere on a time-scale of minutes to months’ Thomas & Goudie, 2000 p527 • Weather describes specific conditions rain, temperatures, dew-point, wind speed and direction, visibility… Weather forecasting • ‘The science of predicting the future state of the atmosphere from very short periods of less than one hour up to 7-10 days ahead’ Thomas & Goudie, 2000 p527
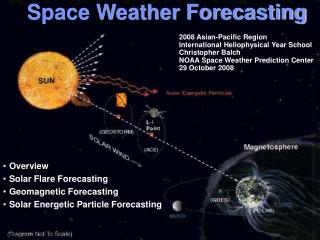
content • Climatic regions / climate graphs • Mid-latitude weather (UK) • Weather monitoring / forecasting • Weather & climate practical
Hadley cell regimeThompson 1998, p Holden 2005, p30 Global rainfall patterns Holden, 2005 p39 Global temperature patterns (Jan) Barry & Chorley 2003 p43
Climate graphs Landes-Pyrenees Properties, 2007 London climate graph Cool Antarctica, 2007
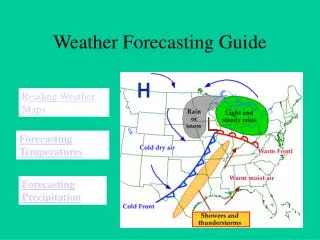
Weather maps Stirling, 1997 p25 Synoptic weather chart, Met Office 2000 Air Ministry 1941. The Weather Map. London, HMSO
Weather systems Stirling, 1997 p28
Aerospace Technology, 2007 Jetstreams Air masses: Source regions Fronts
Mid-latitude weather (UK) Model of N hemisphere atmospheric circulation Thompson 1998 p107 based on Hanwell 1980
Depressions (cyclonic systems) b) plan form / synoptic chart a) cross-sectional model Mature: Pressure falls warm air rises in warm sector winds inward blowing anticlockwise Coriolis force STAGES: Embryo: Tm & Pm air mix warm air less dense rises in spiral Low Pressure Decay: Cold front catches warm front = Occlusion
What does a depression look like? Met Office, 2007
Weather associated with the passage of a depression Cloud patterns associated with a depression Thompson, 1998 p151 Waugh 1995, p215
Depression tracks (courses) Stirling, 1997 p30 North Sea storm surge 31st January to 1st February 1953 Impacts: coastal areas UK, Belgium & Netherlands Economic damage and community disruption 2,000+ people died across the three countries. Jonkman SN & Kelman I, 2005
Anticylcones Stirling, 1997 p28 Large masses of subsiding warm dry air (settled weather) winds outward-blowing, clockwise Associated weather Summer: hot days (heatwave), rapidly cooling night, land-sea breezes, temperature inversions Winter: similar, but cold / snow, fog / frost
Weather system terminology Musk, 1988
Weather forecasting: tools / data Met Office, 2007 Met station, Muckross House, Killarney NP
Met Office, 2007 Satellite images http://www.metoffice.co.uk/ UK observations regional map (Met Office, 2007)
‘We interrupt TMS to bring you the following gale warning issued by the Met office at 17.25 GMT Wedesday 14th March…’ Met Office, 2007
Directed reading: • Mountain weather / local climates – Holden 2005 pp80-96 • UK weather system variants Met Office 2007 – Learning – Weather resources – Higher - weather systems • Hurricanes (storm of 1987 – Met Office, 2007, Barry & Chorley 2003 pp269-275)
Suggested reading • Barry RG & Chorley RJ 2003. Atmosphere, Weather and Climate (8th Edition). London, Routledge. • Earth Science and Geography, Keele University 2007. The Weather at Keele (Keele Weather station). http://www.esci.keele.ac.uk/weather/ (accessed 13.3.07) • Holden J (Ed) 2005. An Introduction to Physical Geography and the Environment. Harlow, Pearson. (Atmospheric processes, global climates, local & regional climates pp27-96). • Met Office 2007. Met Office homepage. http://www.metoffice.gov.uk/index.html (accessed 12.3.07) Folllow links to Learning – Weather resources - Higher • O’Hare G, Sweeney J & Wilby R 2005. Weather, Climate and Climate Change. Harlow, Pearson. • Stirling R 1997. The Weather of Britain. Routledge. • Thomas DSG and Goudie A 2000. The Dictionary of Physical Geography. Oxford, Blackwell. • Thompson RD 1998. Atmospheric Processes and Systems. London, Routledge.