Measurements and Sources of Errors
300 likes | 1.53k Vues
Islamic University of Gaza Industrial Engineering Department EIND3102: Measurements Lab. Eng. Ibrahim Kuhail. Measurements and Sources of Errors. Metrology.

Measurements and Sources of Errors
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Islamic University of Gaza Industrial Engineering Department EIND3102: Measurements Lab Eng. Ibrahim Kuhail Measurements and Sources of Errors
Metrology • Metrology is the science of measurement, embracing both experimental and theoretical determinations at any level of uncertainty in any field of science and technology. ”International Bureau of Weights and measurements (BIPM)” Measurements and Sources of Errors
Measurement • Measurement is the process of determining or finding the size, quantity or degree of something . • The principle dimensional measurement is length; secondary measurement is angle and curvature. You can describe shape without describing size, but not the reverse. Measurements and Sources of Errors
Measurement Methods • Four methods of measurement: • Direct method. • Indirect method. • Comparison method: the comparison of an unknown quantity to a known quantity called a standard using Dial Indicator. • Coincidence method. Measurements and Sources of Errors
Measuring Instruments • Measuring instruments are measuring devices that transform the measured quantity into an information, either analog or digital. Measurements and Sources of Errors
Measuring Instruments (Cont.) • The functions of the measuring instruments are: • Indicating function • Recording function • Controlling function • The applications of the measuring instruments are: • Monitoring of processes and operations • Control of process • Experimental engineering analysis Measurements and Sources of Errors
Measuring Instruments Types • Measuring Instruments Types: • Angle measuring Instruments: e.g. Angle gauges; Divided scales; Sine bar with slip gauges; Autocollimator; and Tool Maker Microscope. • Length measuring Instruments: ex: steel rule; Caliper; Micrometer; and comparators. • Instruments for surface finish: surface roughness measurements. • Instruments for deviations: Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM). Measurements and Sources of Errors
Measurement Applications • Measurement Applications • Plate Work: The layout and inspection performed from a surface plate. The primary purpose of a surface plate is to provide a reference plane. • Coordinate Measurement • Statistical Quality Control • Inspection: Verification of conformity to a standard. Measurements and Sources of Errors
Important Terms in Measurements • Resolution: It is the minimum value that can be measured when the instrument is gradually increased from non-zero value. • Repeatability: The ability of the measuring instrument to repeat the same results • Reproducibility: It is defined as the degree of closeness with which a given value may be repeatedly measured under same loading conditions. Perfect reproducibility means that the instrument has no drift. • Gaging: Itis not measurement, but a form of inspection and sorting. • Tolerance: The two extremes within which an actual part dimension must lie. Measurements and Sources of Errors
Calibration • Calibration of a measuring instrument The process of determining the values of the quality being measured corresponding to a pre-established arbitrary scale. • Advantages of calibration: • Increases production yields. • Optimizes resources. • Assures consistency. • Ensures measurements (and perhaps products) are compatible with those made elsewhere. • Eliminate or reduce bias in the user's measurement system relative to the reference base. Measurements and Sources of Errors
Accuracy and Precision • Accuracy is the overall closeness of agreement between a measured value and the true value. • Precision also called reproducibility or repeatability, the degree to which further measurements or calculations show the same or similar results. • Instrument precision is usually associated with the number of digits displayed on the output, i.e., its resolution. Measurements and Sources of Errors
Accuracy and Precision (Cont.) • Accuracy indicates proximity to the true value, precision to the repeatability or reproducibility of the measurement Measurements and Sources of Errors
Accuracy and Precision (Cont.) High precision, but low accuracy High accuracy, but low precision Measurements and Sources of Errors
Accuracy and Precision Errors • Accuracy Error is Inaccuracy or Uncertainty. • Accuracy error is the measured value minus the true value. • Precision error is the random error. • Precision error is the reading minus the average of readings. Measurements and Sources of Errors
Measurements Errors • Measurements Errors : Is the difference between the true value of the size and the value found by measurement. • Errors pertains to measurement not to an instrument. Error = True Size – Actual Size • True Size: is the theoretical size obtained through measurement. This type of size is free from any type of error. It is the guide for measuring many properties such as accuracy of an instrument. • Actual Size: is a measured size with permissible error. It refers to the minimum acceptable size of a sample. Measurements and Sources of Errors
Measurements Errors (cont.) • There are two general categories of error: systematic (or bias) errors and random (or precision) errors. Measurements and Sources of Errors
Systematic Errors • Systematic errors (also called bias errors) Theyare consistent, repeatable errors. For example, suppose the first two millimeters of a ruler are worn off, and the user is not aware of it. Everything he or she measures will be too short by two millimeters – a systematic error. Measurements and Sources of Errors
Systematic Errors Sources Systematic errors arise for many reasons. Here are just a few: • Calibration Errors: due to nonlinearity or errors in the calibration method. • Loading or Intrusion Errors: the sensor may actually change the very thing it is trying to measure. • Spatial Errors: arise when a quantity varies in space, but a measurement is taken only at one location (e.g. temperature in a room - usually the top of a room is warmer than the bottom). • Human Errors: arise if a person consistently reads a scale on the low side, for example. • Defective Equipment Errors: arise if the instrument consistently reads too high or too low due to some internal problem or damage. Measurements and Sources of Errors
Random Errors • Random errors Theyare unrepeatable, inconsistent errors, resulting in scatter in the output data. The random error of one data point is defined as the reading minus the average of readings. Measurements and Sources of Errors
Other Sources of Errors There are many other errors, which all have technical names, as defined here: • Zero Error: The instrument does not read zero when the input is zero. Zero error is a type of bias error that offsets all measurements taken by the instrument, but can usually be corrected by some kind of zero offset adjustment. • Linearity Error: The output deviates from the calibrated linear relationship between the input and the output. Linearity error is a type of bias error, but unlike zero error, the degree of error varies with the magnitude of the reading. Measurements and Sources of Errors
Other Sources of Errors (Cont.) • Sensitivity Error: The slope of the output vs. input curve is not calibrated exactly in the first place. Since this affects all readings by the instrument, this is a type of systematic or bias error. • Resolution Error: The output precision is limited to discrete steps (e.g., if one reads to the nearest millimeter on a ruler, the resolution error is around +/- 1 mm). Resolution error is a type of random or precision error. Measurements and Sources of Errors
Other Sources of Errors (Cont.) • Hysteresis Error: The output is different, depending on whether the input is increasing or decreasing at the time of measurement. This is a separate error from instrument repeatability error. • Instrument Repeatability Error: The instrument gives a different output, when the input returns to the same value, is the same. The reasons for the differences and the procedure to get to that value are usually random, so instrument repeatability error is a type of random error. Measurements and Sources of Errors
Other Sources of Errors (Cont.) • Drift Error: The output changes (drifts) from its correct value, even though the input remains constant. Drift error can often be seen in the zero reading, which may fluctuate randomly due to electrical noise and other random causes, or it can drift higher or lower (zero drift) due to nonrandom causes, such as a slow increase in air temperature in the room. Thus, drift error can be either random or systematic. • Parallax: This error can occur whenever there is some distance between the measuring scale and the indicator used to obtain a measurement. If the observer's eye is not squarely aligned with the pointer and scale, the reading may be too high or low (some analog meters have mirrors to help with this alignment). Measurements and Sources of Errors
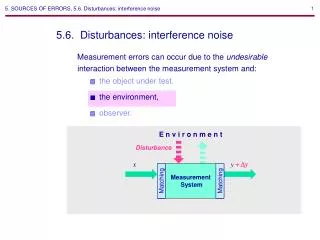
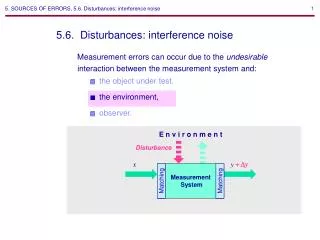
Other Sources of Errors (Cont.) • Environmental factors: Be aware of errors introduced by your immediate working environment. You may need to take account for or protect your experiment from vibrations, drafts, changes in temperature, electronic noise or other effects from nearby apparatus. • Reading Error: describes such factors as parallax, interpolation, or optical resolution. • Loading Error: results from the change of the measurement instrument when it is being used. • Effect of support. • Effect of alignment. • Dirt. Measurements and Sources of Errors
Other Sources of Errors (Cont.) • Errors due to Vibrations. • Metallurgical Effects. • Contact Point Penetration. • Errors due to Deflection. • Errors due to Looseness. • Errors due to Wear in Gauges. • Errors due to Location. • Error due to Poor Contact. • Errors due to Impression of Measuring Stylus. Measurements and Sources of Errors
Grading Policy Measurements and Sources of Errors
Any Questions ? Measurements and Sources of Errors