Chapter 14 Blood
370 likes | 471 Vues
Explore the functions of blood connective tissue including transport, maintaining homeostasis, and immunity. Learn about red and white blood cells, plasma, clotting, and more. Test your knowledge on leukocytes and plasma proteins.

Chapter 14 Blood
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Connective tissue • Functions: transport, maintains fluid/solid homeostasis, distributes heat, immunity • 8% of body weight ~ 5 liters Hematocrit: = packed cell volume 55% plasma 45% RBC <1% WBC, platelets
Cells Hematopeietic stem cells Myeloid (rbc, wbc, platelets, macrophages Lymphoid (lymphocytes cells, macrophages)
Red Blood Cells = Erythrocytes • Small • Biconcave – increases surface area for gas attachment • No nucleus • No mitochondria (Use glycolysis to make only 2 ATPs) http://www.popsci.com/science/article/2011-11/first-transfusion-lab-grown-blood-success
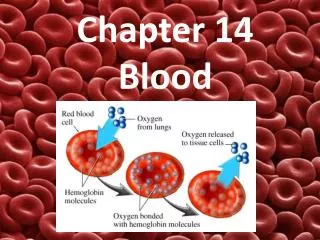
Hemoglobin • 1/3 of cell is hemoglobin • Hemoglobin (Hb) + O2 = oxyhemoglobin = red color • Hb – O2 = deoxyhemoglobin = dark red/purple • Cyanosis = low O2 = increased oxyHb and looks blue • Cold temperatures make you look blue from decreased blood flow (more oxyHb)
Carbon Monoxide • Binds to RBC better than oxygen. • Not good • Kills us silently • Cant smell it or taste it.
Erythropoiesis – RBC production Erythropoietin hormone – negative feedback mechanism
Diet and Blood Cell Production B12 and folic acid needed for DNA synthesis, and intrinsic factor in stomach needed for absorption Iron (heme) – need vitamin C for Fe absorption Anemia= low rbc or low Hb (especially during pregnancy due to increased blood volume that decreases hematocrit levels)
White Blood Cells Hormones: interleukin and colony-stimulating factor (CSF) stimulate development Granulocytes vs. Agranulocytes (cytoplasmic granules) a) neutrophils – phagocytosis of bacteria cells a) monocytes – lysosomes for phagocytosis b)eosinophils – kills parasites, allergies b) lymphocytes – T cells and B cells c) basophils – releases chemicals like histimine to increase blod vessel size (inflammation), heparin to thin blood
Neutrophils(nucleus has several lobes) Active phagocytes 60% of WBC Found in pus of wounds
Eosinophils Mainly attack parasites 2% of WBC
Basophils Produces heparin and histamines Important in inflammatory response 1% of WBC
Monocytes(large, horeshoe-shaped nucleus, agranular) Become macrophages 6% of WBC
Lymphocytes(dark nucleus takes up most of cell, very little cytoplasm) Make antibodies 30% of WBC
Test Yourself! When you are ready, click the mouse to see the answers. A = red blood cell B= lymphocyte C = neutrophil D= eosinophil E = neutrophil F = monocyte G = platelet H = lymphocyte I = eosinophil J = basophil
Chemotaxis Damaged cells release chemical signals (CAMs) that attract more leukocytes. Diapediesis= movement of wbc PUS
Platelets = thrombocytes • Cell fragments • Developed in response to thrombopoietin • Amoebic movements • ½ size of rbc • Sticky and release serotonin to contract blood vessel walls to decrease blood flow
Plasma • Functions: • 92% water • Transport nutrients, gases, vitamins, proteins, etc. • Regulate fluids and electrolytes • Maintain pH levels
This machine removes the plasma from the blood and returns the RBC’s to the donor.
Proteins • Albumins • Smallest, 60% of proteins in plasma • Synthesized in liver • Help transport bilirubin, fatty acids, hormones • Helps maintain osmotic pressure (proteins too large to cross membrane therefore holds fluid in vessels) – regulates fluid and blood pressure • Especially important in pregnancy KWASHIORKOR EDEMA
2. Globulins – 36% of plasma • α alpha – from liver • β beta- from liver • γ gamma – from lymph, type of antibody (immunoglobulins) • 3. Fibrinogen: 4% of plasma, converted to fibrin • largest • blood coagulation
Gases and Nutrients • O2, CO2, N2 • Amino acids • Monosaccharides • Nucleotides • Lipids – because plasma is mostly water, lipids must be bound to proteins (lipoprotein complexes)
Nonprotein Nitrogenous Substances (NPN) Excreted in Urine • Amino acids- from protein digestion • Urea- from protein digestion • Uric acid – from nucleic acid digestion
Creatine • Creatinine • Found as creatine phosphate in muscle, brain, and blood. • Stores energy in bonds like ATP does • A high level indicates kidney disorder
Plasma Electrolytes Na – muscle and neurons Cl – muscle and neuron HCO3 – maintains pH and osmotic pressure K – muscles and neurons Ca – nerve and blood clotting Mg – muscle, bone, teeth, enzyme action PO4 – ATP and DNA synthesis
Clotting Blood Vessel Spasm (vasospasm) – contracts bv to decrease blood loss Platelet Plug = platelets and collagen Blood coagulation – blood clot cascade (vitamin K is necessary), uses fibrin (converted from fibrinogen by “thrombin” enzyme)
Thrombus – clot in a blood vessel (Ex – Deep Vein Thrombosis) Embolus – dslodged clot or fragment that breaks loose and carried in blood **Atherosclerosis can cause this by changing arterial lining
Blood Groups and Transfusions 31+ different genes and over 29 different blood groups
See a list of all the rare blood groups: More Info About Bombay Blood Type: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hh_antigen_system http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_blood_group_systems
Blood chip – new way to diagnose disease http://newscenter.berkeley.edu/2011/03/16/standalone-lab-on-a-chip/