Atomic Physics
250 likes | 351 Vues
Explore the atomic world with Dimitri Mendeleev in Lecture 15, delving into the periodic table of elements, Schroedinger’s Equation, energy shells, and quantum states. Learn about atomic properties, electron configurations, chemical bonding, molecular formation, and atomic spectra. Discover the principles behind electron states, quantum energies, quantum jumps, and the conservation of parity in quantum mechanics. Dive into the fascinating realm of atomic redshifts, laser technology, and applications of stimulated emission of radiation. Gain a deeper understanding of atomic structure and behavior through Mendeleev's insightful lecture.

Atomic Physics
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Atomic Physics Micro-world Macro-world Lecture 15 Dimitri Mendeleev
Periodic table of elements Elements in vertical rows have similar chemical properties Inert gases
Schroedinger’s Equation for multi-electron Atoms - - - + - -
Solutions give energy levels that are clustered in “shells” n # of states - - - - 1 2 - - 2 8 - - - 3a 8 + 3b 10 - - - - - - 4a 8 - 4b 10 4c 14 - -
Pauli exclusion principle Wolfgang Pauli Only one electron per quantum state Once a quantum state is occupied additional electrons are excluded
Light elements - +2 +1 - - outermost shell is full 1 electron in outermost shell Helium Hydrogen - - - - - - - +3 +10 - - - - - - Neon Lithium
Periodic table of elements Elements in vertical rows have similar chemical properties 1 e- in outer shell Filled outer shell
Chemical properties depend upon the outermost shell configuration - - - - - - - - - - - +8 - - - - +16 - - - - - - - Oxygen Outermost shells Have 2 vacancies - - Sulfur
Periodic table of elements 2 vacancies in outer shell
Atoms combine to form molecules by filling outer shells +1 Hydrogen - - - Water=H2O - - +8 - - - - - Hydrogen +1 Oxygen
Atoms combine to form molecules by filling outer shells Hydrogen Hydrogen +1 - - +1 - - - Methane=CH4 +6 - - - - - +1 +1 Carbon Hydrogen Hydrogen
Elements with full outer shells don’t form molecules - - - - - - - - - - - - - - +2 - +10 +18 - - - - - - - - - - Helium - - - Neon - - Noble gasses Argon
Periodic table revisited Elements in vertical rows have same outer shell configurations 1 elec in outer shell 2 vacancies in outer shell 4 e- in outer shell Outer shell is full
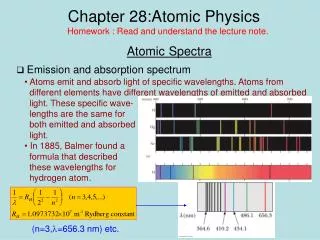
Spectra are atomic “signatures” Hydrogen Mercury Neon
Decoding atomic spectra Mercury spectrum “quantum jump” photon Ephoton=E2-E1 quantum energies quantum orbits Mercury energy levels
1924 Otto Laporte Allowed quantum states are either even or odd Laport rule odd Otto Laporte 1902-1971 even even even even odd odd odd even odd OK odd even not allowed even X even odd X odd
Laporte rule is a consequence ofLeft-Right symmetry of Nature Left Right symmetry = “Parity” symmetry Eugene Wigner 1902-1995 Eugene Wigner 1902-1995 1963 Nobel Physics prize “for the discovery and application of fundamental symmetry principles”
P = Parity = L R/R L Field (& rules) of football are parity symmetric Rules of baseball are not parity symmetric
Even & Odd quantum functions Even Function Odd Function LR RL LR RL Does not change Changes sign Parity = +1 Parity = -1
Parity Conservation in QM Left Right symmetry of Nature Conservation of Parity photon has P=-1 even state initially: even state (Peven=+1) finally: odd state+ (Podd=-1) Photon (Pphot=-1) odd state Pinitial=+1 Pfinal=(-1)(-1)=+1 Parity is conserved
Atomic red shifts V=0.25c=75,000km/s l shift = 25% V=0.05c=15,000km/s l shift= 5% V=0.01c=3,000km/s l shift = 1%
Laser – Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation – Example: Helium-Neon Laser Cartoon: sealed container I I I Helium-Neon gas mixture mirror “partial” mirror + - Helium-Neon Laser in real life Power source
Laser – Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation – “Pump” → Ne* → → “meta-stable” states Ne* → → → Ne* → → Ne* → → → Stimulates emission Ne* → Exactly in phase → → Ne* → Exactly in phase Exactly in phase