MEIOSIS
230 likes | 480 Vues
MEIOSIS. VOCABULARY BACKGROUND. Gamete - sex cell ( egg or sperm) Somatic Cell – Body cells except egg or sperm. Ex: Heart, liver, eye…… Zygote – a cell produced by the union of 2 gametes before it starts to divide. VOCABULARY BACKGROUND.

MEIOSIS
E N D
Presentation Transcript
VOCABULARY BACKGROUND • Gamete- sex cell ( egg or sperm) • Somatic Cell – Body cells except egg or sperm. • Ex: Heart, liver, eye…… • Zygote – a cell produced by the union of 2 gametes before it starts to divide
VOCABULARY BACKGROUND • Asexual Reproduction – DNA contributed by one parent. • No genetic recombination Sexual Reproduction – DNA contributed by both parents. • Genetic recombination
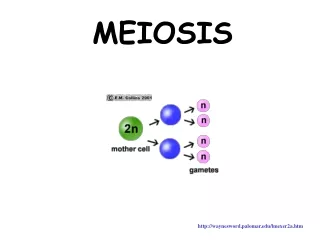
WHAT IS MEIOSIS? • Cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes in a cell in half. • Purpose: for sexual reproductive organisms to produce GAMETES = sex cells=egg/sperm
What we first must understand!! • Humans have 46 chromosomes (2 sets of 23) in every somatic cell • Ex. If a fish has 30 chromosomes, then it will have 15 pairs. • Cells containing two complete sets of chromosomes are called diploid cells (2N) • Diploid cells= Body cells= liver, blood…..etc
Chromosome numbers Do all organisms have the same number of chromosomes?
What we first must understandCont’d • First 22 pairs are called autosomes. They are homologouspairs – corresponding chromosomes (not identical) • one from mom, one from dad • The 23rd pair are the sex chromosomes • XX—female • XY—male
KARYOTYPE: Human Chromosomes Autosomes Sex Chromosomes
What we first must understand Cont’d • Human gametes contain 1 set of chromosomes (23). • Cells with only one complete set of chromosomes are called haploidcells (N). • When egg and sperm combine, this produces offspring with 46 chromosomes, diploid cells.
from mom from dad child too much! meiosis reduces genetic content MEIOSIS: cell division forming gametes Goal: to reduce genetic material by half – ( 23 chromosomes from dad’s sperm), 23 chromosomes from mom’s egg =‘s 46) Location – Female ovaries & male testes
2 STAGES OF MEIOSIS • Meiosis I – • homologous chromosomes separate • Goes through Pro, Meta, Ana, Telo (I) • Crossing over of chromosomes leads to genetic diversity • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hYatQBr2uyU&feature=related&safety_mode=true&persist_safety_mode=1
Mom DAD
2 STAGES OF MEIOSIS • Meiosis II – • sister chromatids separate • Goes through Pro, Meta, Ana, Telo (II)
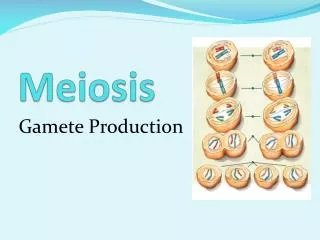
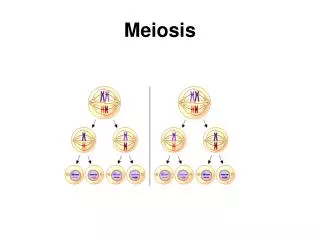
Sister chromatids separate MEIOSIS I MEIOSIS II DIPLOID HAPLOID HAPLOID MEIOSIS: 2 PART CELL DIVISION Homologues separate RESULT: one copy of each chromosome in each gamete.
MEIOSIS II Prophase II Metaphase II Anaphase II Chromosomes line up in a similar way to the metaphase stage of mitosis. Haploid cells from Meiosis I go through Meiosis II without stopping in Interphase. Telophase II The sister chromatids separate and move toward opposite ends of the cell. Meiosis II results in four haploid daughter cells.
RESULTS OF MEIOSIS • Gametes • Four haploid cells • One copy of each chromosome • One allele per gene • Different allele combinations