Six Sigma An Introduction
310 likes | 1.62k Vues
Six Sigma An Introduction. History of Six Sigma. Motorola (1987) Texas Instruments (1988) IBM (1990) ABB (1993) Allied Signal (now Honeywell) and Kodak (1994) GE (1995) Whirlpool, PACCAR, Siebe, Iomega, Polaroid, Sony, Home Depot, Penske (1996/99). What Is Six Sigma?.

Six Sigma An Introduction
E N D
Presentation Transcript
History of Six Sigma • Motorola (1987) • Texas Instruments (1988) • IBM (1990) • ABB (1993) • Allied Signal (now Honeywell) and Kodak (1994) • GE (1995) • Whirlpool, PACCAR, Siebe, Iomega, Polaroid, Sony, Home Depot, Penske (1996/99)
What Is Six Sigma? Basically it is a statistically based methodology for process improvement.
Continuous improvement Virtually defect-free New way of doing business Innovation and creativity Reduce variability with the process. Based on precision and accuracy-leading to data driven decisions Six Sigma: A Philosophy
Currently used in: Manufacturing Military Sales Transactional services Six Sigma: Where and What Can It Be Used For?
L o w e r S p e c 3 Sigma Level Process:No Mean Shift U p p e r S p e c 3 5 4 5 5 5 6 5 Process +3s Tolerance +3s
Six Sigma Level Process:No Mean Shift Lower Spec Upper Spec +3s 2 0 3 0 4 0 5 0 6 0 7 0 8 0 Process Tolerance +6s
99% versus 99.99966% Pretty much the same. Right?
Practical Meaning 99% Good 99.99966% Good U.S. Postal System 20,000 lost articles / hr 7 lost articles / hr
Practical Meaning 99% Good 99.99966% Good Medical Profession 200,000 Wrong Drug Prescriptions/Year 68 Wrong/Year
Practical Meaning 99% Good 99.99966% Good Airline System 2 short/long landings / day 1 short/long / 5 years
The Goal of Six Sigma • The Reduction of VARIATION!
Sources of Variation • Machines • Materials • Methods • Manpower • Measurement • Mother Nature
The Funneling Effect Define 30+ Inputs All X’s Measure 10 - 15 1st “Hit List” Analyze 8 - 10 Screened List Improve 4 - 8 Found Critical X’s 3 - 6 Control Controlling Critical X’s Optimized Process
Six Sigma Breakthrough BAD 3 Sigma Level Six Sigma Breakthrough Performance 6 Sigma Level GOOD Time
What’s The Most Important Thing At The Drive Thru? THE WAIT TIME!
What Does The Data Show Us? The average wait time for the drive thru is over 6 minutes!
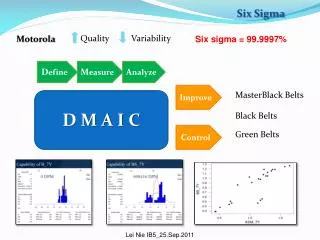
Lean Six Sigma: A Powerful Methodology (DMAIC) Define Measure Analyze Improve Control the process: Analyze Data Identify Root Causes the process gains: Ensure Solution is Sustained what is important to the customer: Project Selection Team Formation Establish Goal the process performance measures: Prioritize root causes Innovate pilot solutions Validate the improvement how well we are doing: Collect Data Construct Process Flow Validate Measurement System
Six Sigma: A Powerful Methodology (DMAIC) Define Measure Analyze Improve Control the process: Analyze Data Identify Root Causes the process gains: Ensure Solution is Sustained what is important to the customer: Project Selection Team Formation Establish Goal the process performance measures: Prioritize root causes Innovate pilot solutions Validate the improvement how well we are doing: Collect Data Construct Process Flow Validate Measurement System
Summary of Key Points • Six Sigma is a philosophy of continuous improvement. • Six Sigma measures defects in a process. • One can expect 3.4 defects per million opportunities in a six sigma level process. • Six Sigma is a methodology that includes defining, measuring, analyzing, improving, and controlling a process.