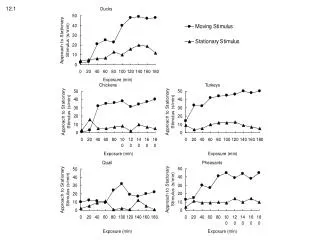
Chapter 12.1
110 likes | 346 Vues
Chapter 12.1. Human Chromosomes . AP Biology Fall 2010. Chapter12.1 Objectives. Differentiate between sex chromosomes and autosomes . Chromosomes. Genes : are units of information about heritable traits

Chapter 12.1
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chapter 12.1 Human Chromosomes AP Biology Fall 2010
Chapter12.1 Objectives • Differentiate between sex chromosomes and autosomes
Chromosomes • Genes: are units of information about heritable traits • Diploid organisms possess pairs of homologous chromosomes, which are alike in length, shape, and gene sequence • Alleles: are slightly different molecular forms of the same gene, which are shuffled during meiosis • A wild-type allele: is a gene’s most common form • A less common form of the gene is the mutant allele
Chromosomes • Genes on the same chromosome are physically connected, but genes from one homolog may exchange places with those on the other homolog in crossing over, which produces genetic recombination • A chromosome’s structure may change during mitosis or meiosis, as can the parental chromosome number (quantity)
Autosomes and Sex Chromosomes • Sex chromosomes determine gender • Human females have 2 X chromosomes • Human males have one X and one Y • 2 present in humans • Do you think all mammals have similar sex chromosomes?
Autosomes and Sex Chromosomes • Most of the chromosomes are of the same quantity and type in both sexes and are called autosomes • 44 present in humans • Total human chromosome number is 46
Sex Determination in Humans • Each human egg with contain 22 autosomes, plus one X • Sperm will carry 22 autosomes, plus either one X or one Y • An X-bearing egg plus a X-bearing sperm produces female offspring • An X-bearing egg plus a Y-bearing sperm produces male offspring
Sex Determination in Humans • The Y chromosome carries a male-determining (SRY) gene, which leads to the formation of the testes, which secrete testosterone • Absence of the male gene in females leads to the formation of ovaries • The X chromosome obviously codes for sexual traits, but it also carries many genes for nonsexual traits • Which genes do you think are sex linked?
Review • What is the difference between sex chromosomes and autosomes? • What chromosomes code for the different sexes in humans?
Answers • Autosomes are pairs of chromosomes that are the same in males and females of a species. Sex chromosomes differ between males and females of a species. • In humans XX codes for females, and XY codes for males.