Scientific Method Overview
750 likes | 1.9k Vues
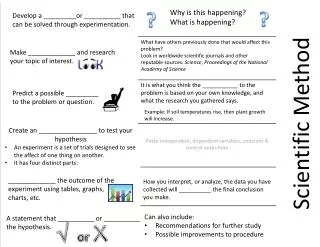
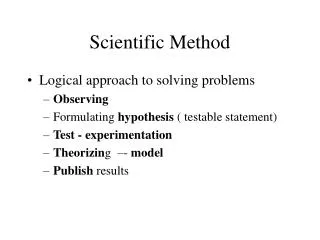
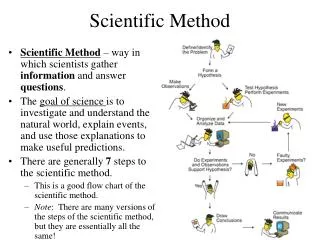
Scientific Method Overview. Seven steps: Choose problem Research problem Develop hypothesis Write procedures Test hypothesis Organize data State conclusions. Choose a Problem. What do you want to learn more about? Ask a specific question Ex 1: Do plants need water to grow? Ex: 2:

Scientific Method Overview
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Scientific Method Overview • Seven steps: • Choose problem • Research problem • Develop hypothesis • Write procedures • Test hypothesis • Organize data • State conclusions
Choose a Problem • What do you want to learn more about? • Ask a specific question • Ex 1: • Do plants need water to grow? • Ex: 2: • Is Mr. Decker the best teacher of all time?
Research Your Problem • How can you find the answer to your question? • Research! • Library • Internet • Adults • Your own background knowledge!
What do you think the answer to your question will be? Hypothesis- A statement that tries to explain a relationship between two variables THE Develop a Hypothesis They’re sisters…
Use the words IF and THEN Ex 1: IF you water a plant more, THEN it will grow taller Ex 2: IF Mrs. Jayne is your teacher, THEN you will become a genius! IF IF IF IFIF IF IF IFTHEN THEN THEN Still Developing Hypothesis…
What is a variable again? Variable: Anything that can be changed or manipulated during an experiment Ex 1: Type of plant, amount of water, sun exposure, etc. Ex 2: Time of day with Mr. Decker, how much time spent, etc 2A + 3 = 7 2B + 3 = 7 2C + 3 = 7 2D + 3 = 7 2E + 3 = 7 Still Developing Hypothesis…
Write Procedures • How will you test your hypothesis? • List materials • List each thing that you will do • Number each step • Write down EVERYTHING you will do • Anyone should be able to replicate your experiment
Test Your Hypothesis • Obtain materials • Conduct experiment • Follow your procedure… exactly • Be sure to control your variables • Variable- • Anything that can change or vary during an experiment
Controlling Variables • You need to know exactly what you are testing… • …You have to control EVERYTHING • Three different types: • Independent variable • Dependant variable • Control variables
Independent Variable • Independent variable- • The variable that you are changing or testing • Example hypothesis: • IF you water a plant more, THEN it will grow taller • Water is the independent variable • It will always be the IF portion of your hypothesis
Dependent Variable • Dependent variable- • Changes in response to the independent variable • The variable you are measuring • Example hypothesis: • IF you water a plant more, THEN it will grow taller • Plant height is the dependent variable • It will always be the THEN portion of your hypothesis
Control Variables • Control variables- • Variables that are unchanged throughout the experiment • Example hypothesis: • IF you water a plant more, THEN it will grow taller • Controlled variables: • Soil, age of plant, type of plant, amount of sunlight, etc..
Organize Data • Organize data into the following: • Tables • Charts • Graphs • Draw pictures • Take photos
State Conclusions • What did you see, hear, smell, taste, etc? • Qualitative data • Data that can’t be measured • This baby has perfect teeth • What does your numerical data show you? • Quantitative data • Data that can be measured • This baby is 86 cm long
State Conclusions • Decide what your data tells you about your hypothesis • Decide how your hypothesis might change based on your results • Communicate your results with others!