LIVER HYDATID CYST
160 likes | 1.11k Vues
LIVER HYDATID CYST. CLASSIFICATION OF HYDATID CYSTS. PRIMARY CYSTS MULTIVESICULAR OR SECONDARY CYSTS SECONDARY ABDOMINAL IMPLANTATION. Natural history of liver hydatid. 1 - Development of cyst – biliary communications 2 - Intrabiliary rupture 3 - Intraabdominal rupture

LIVER HYDATID CYST
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CLASSIFICATION OF HYDATID CYSTS • PRIMARY CYSTS • MULTIVESICULAR OR SECONDARY CYSTS • SECONDARY ABDOMINAL IMPLANTATION
Natural history of liver hydatid • 1 - Development of cyst – biliary communications • 2 -Intrabiliary rupture • 3 - Intraabdominal rupture • 4 - Intrathoracic rupture • 5 - Intrathoracic rupture • 6 - Cyst death
CLINICAL FEATURES • 1 – Symptomless • 2 –Painful or painless hepatomegaly • 3- Abdominal mass • 4-Jaundice • 5 - Intraperitoneal rupture
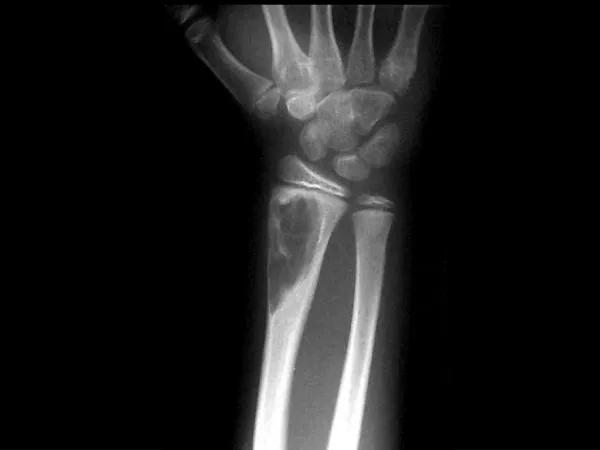
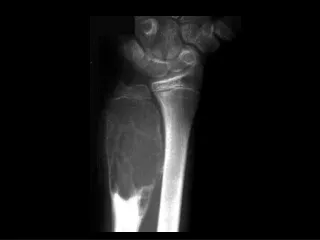
DIAGNOSTIC STUDIES • Serological tests • Imaging techniques 1 Ultrasonography 2 CT scan 3 MRI 4 ERCP
TREATMENT • Medical treatment bebzimidazole group Praziquantel
Indications of medical treatment 1 Inoperable cases - Site - Multiple cysts 2 Concomitant diseases
Contraindications 1 Pregnancy or lactation . 2 Heavily calcified cysts . 3 large cysts . 4 Obstructive jaundice .
Surgical treatment • Objectives Remove all living cyst elements . Prevent spillage . Close biliary communications . Sterilize cavity .
Scolicidal agents 1- Hypertonic saline ( 3 % ) . 2- Hydrogen peroxide 6% . 3- Citeramide . 4- Silver nitrate 0.5% . 5- Rectified spirit ( 96% ) . 6- Formalin
Intrabiliary rupture • Operative cholangiogram . • Bile duct exploration . • T tube insertion . • Choledochoscopy .
Residual cavity management • (1) Suture any obvious small bile duct openings • (2) Fill it with ordinary 0.9% saline • (3) Saucerize it by excising the protruding portion • (4) Fill it with a graft of omentum. • (5) Stitch the walls of the cyst