Addition and subtraction
140 likes | 365 Vues
Addition and subtraction. Math 123. Washington standards. http://www.k12.wa.us/mathematics/Strands/k8-operations.pdf. Definitions. Addition of whole numbers:

Addition and subtraction
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Addition and subtraction Math 123
Washington standards • http://www.k12.wa.us/mathematics/Strands/k8-operations.pdf
Definitions • Addition of whole numbers: • Let a and b be any two whole numbers. If A and B are disjoint sets with a = n(A) and b = n(B), then a+b = n(A B). • This seems very complicated. But in reality, this is how children learn to count: if you have 3 apples, and I have 4 apples, to find out how much we have together, we will join your set of 3 and my set of 4 to see how many there are in the union of the two. • Think of direct modeling in a JRU problem.
Subtraction of whole numbers: • Let a and b be any two whole numbers (a>b) and A and B be sets such that a = n(A) and b = n(B), and B A. Then a-b = n(A- B). • Again, this looks complicated, but think about it. I have 5 apples, and you take 3 away from me. I had a set of 5 apples, and you took a subset of 3 from it. What is left is the number of apples I have left. • Think of direct modeling with a SRU problem.
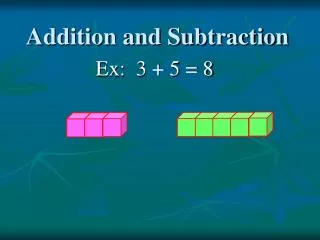
Models • Set model • Number line model Think about how you would represent problems 3+5 and 8 – 3 using sets and the number line.
Contexts for subtraction • Take-away • Missing addend • Comparison Think about a word problem that would represent each of the three contexts. How is this related to the types of problems we saw in CGI? Now solve each of the problems using blocks.
Properties of addition • Closure: the sum of any two whole numbers is a whole number • Commutative property: the order in which numbers are added does not matter: a+b = b+a. • Associative property: numbers can be grouped differently: (a+b)+c = a+(b+c). • Identity property: a+0 = a = 0+a .
The closure property does not hold. • The commutative property does not hold. • The associative property does not hold. • The identity property holds only somewhat: a – 0 = a, but 0 – a = -a.
What do children do wrong? • Look at some examples of children’s strategies. • What were the mistakes that the students were making? • How many of the mistakes you encountered are related to place value?
Terminology • What do you think about terms “carry” and “borrow?” Do they accurately portray what you are doing when you add and subtract? • Are there terms you would rather use?
In math education a term more commonly used these days is “regroup.”