Cladistic Systematics
240 likes | 787 Vues
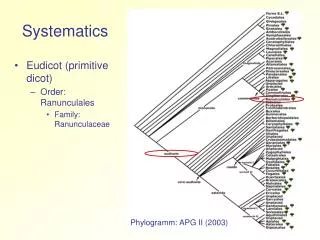
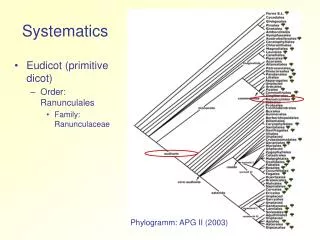
Cladistic Systematics. Now that we know how to read phylogenetic trees….how are they made? Based on shared anatomical characteristics Cladogram : a branching diagram that shows the relationship among species in regard to their shared derived characteristics

Cladistic Systematics
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Cladistic Systematics • Now that we know how to read phylogenetic trees….how are they made? • Based on shared anatomical characteristics • Cladogram:a branching diagram that shows the relationship among species in regard to their shared derived characteristics A cladogram is a special type of phylogenetic tree
Cladistic Systematics • Cladogram: Traces evolutionary history of the group under study • Uses shared derived characters to: • Classify organisms, and • Arrange taxa into a cladogram • A clade is an evolutionary branch that includes: • A common ancestor, together with • All its descendent species
Constructing a Cladogram When constructing a cladogram, the first step is to make a chart with the characteristics to be compared. Notice in the chart on the right all of the organisms have a notochord, but not all of them are vertebrates.
Constructing a Cladogram Only the newt, snake and lizard have lungs and a 3-chambered heart. Snakes and lizards have internalization fertilization and amniotic membranes in their eggs. Reptiles (snakes and lizards) are a clade Clade: an evolutionary branch that includes a common ancestor together with all its descendant species
Constructing a Cladogram The newt (an amphibian) and the eel (fish) are all evolutionary descendants of reptiles The next step is to draw a cladogram showing these relationships The goal is to have the simplest drawing possible What is the deal then with bony limbs and long cylindrical body?
Constructing a Cladogram parsimony: the fewest number of assumptions is the most logical. results in the simplest cladogram possible
Parsimony • Cladists are always guided by the principle of parsimony • The arrangement requiring the fewest assumptions is preferred • This would: • Leave the fewest number of shared derived characters unexplained • Minimize the number of assumed evolutionary changes • The reliability of a cladogram is dependent on the knowledge and skill of the investigator
Alternate, Simplified Cladograms • X, Y and Z share the same characteristics. • b. & c. b. and c. are unlikely examples as the shared characteristics in Y and Z would have had to evolve independently
Phenetic Systematics • Assumes it will never be possible to construct a truly phylogenetic classification system • Species are classified according to the total number of shared similarities • Disregards assumed phylogenetic considerations • Ignores issues of convergent or parallel evolution
Traditional Systematics • Mainly uses anatomical data • Classify organisms using assumed phylogeny with emphasis on phenotype • Stress both common ancestry and degree of structural difference among divergent groups • Construct phylogenetic trees by applying evolutionary principles to categories • Not strict in making sure all taxa are monophyletic