The Clash of Northern Industry and Southern Agriculture During Sectionalism
110 likes | 138 Vues
Explore the reasons behind the industrialization shift in New England and the surge in cotton production in the South. Discover the economic, cultural, and social consequences as industry and agriculture clash.

The Clash of Northern Industry and Southern Agriculture During Sectionalism
E N D
Presentation Transcript
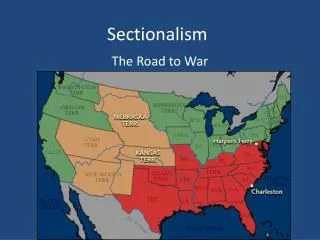
Sectionalism Northern Industry vs. Southern Agriculture
Northern Industry Main Points(Left Column) Leave 3 lines of space between each 1. Why did industrialization spread in New England? 2. Workers Organize 3. Middle Class Emerges 4. Immigrants
Southern Agriculture Main Points (Right Column) Leave 3 lines of space between each 1. Cotton Production Surges 2. Need for slave labor 3. Economic Consequences 4. Cultural Consequences
Northern Industry 1. Why did industrialization spread in New England? • Rivers • Investors • Cheap Labor (immigrants)
Northern Industry 2. Workers Organize • Form unions to seek better wages and working conditions • Hold strikes • Courts are not on their side
Northern Industry 3. Middle Class Emerges • Stood above working class • Men work in offices • Move to outskirts of cities • Why?
Northern Industry 4. Immigrants • Irish & Germans • Nativism Emerges (3rd Type of Division) – favoring native born over immigrants • Do you see that today?
Southern Agriculture 1.Cotton Production Surges • Due to cotton gin (increase demand for cotton and increased slave numbers) • Filled new demand from textile mills • South becomes Cotton Kingdom
Southern Agriculture 2. Need for slave labor • 1808 illegal slave trade started • Slavery becomes more vital than ever • “Necessary Evil”-What does this mean?
Southern Agriculture 3. Economic Consequences • Cotton prices go up and down • No urban growth • No immigrants = less representation in House
Southern Agriculture 4.Cultural Consequences • Lack of education • Focus was primarily on farming • Racial superiority • White over Black