Reynolds Unwrapped: Fantastic Cartoons, Gifts & More!
2.16k likes | 2.21k Vues
Discover daily hilarious cartoons, funny greeting cards, and beautiful paintings at Reynolds Unwrapped. Perfect for gifts or personal enjoyment. Get reprints, originals, and more. Learn about the artist's work in this YouTube video.

Reynolds Unwrapped: Fantastic Cartoons, Gifts & More!
E N D
Presentation Transcript
BRAIN ReynoldsUnwrapped.com offers FANTASTIC, inexpensive daily email subscriptions, where you can receive a HILARIOUS new cartoon every day, and it is a MARVELOUS idea for a UNIQUE gift for your family and friends as well. That is how I learned about this...one of my fellow teachers gave me a subscription as a birthday present. He also has FUNNY greeting cards and BEAUTIFUL paintings for sale as well. You can also get reprints suitable for framing, or originals. Here is more info about his work and a YOUTUBE video. https://nccnews.expressions.syr.edu/?p=11515
MENTAL HOSPITAL PHONE MENU • Hello and thank you for calling The State Mental Hospital. Please select from the following options menu: • If you are obsessive-compulsive, press 1 repeatedly. If you are co-dependent, please ask someone to press 2 for you. If you have multiple personalities, press 3, 4, 5 and 6. If you are paranoid, we know who you are and what you want, stay on the line so we can trace your call. If you are delusional, press 7 and your call will be forwarded to the Mother Ship. If you are schizophrenic, listen carefully and a little voice will tell You which number to press. If you are manic-depressive, hang up. It doesn't matter which number you press, nothing will make you happy anyway. If you are dyslexic, press 9-6-9-6. If you are bipolar, please leave a message after the beep or before the beep or after the beep. • But Please wait for the beep. If you have short-term memory loss, press 9. If you have short-term memory loss, press 9. If you have short-term memory loss, press 9. If you have low self-esteem, please hang up. Our operators are too busy to talk with you. If you are menopausal, put the gun down, hang up, turn on the fan, lie down and cry. You won't be crazy forever.
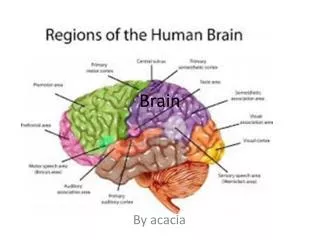
THE BRAIN • ANATOMICAL REGIONS • A. Cerebrum • B. Diencephalon • Thalamus • Hypothalamus • C. Brain Stem • Midbrain • Pons • Medulla oblongata • D. Cerebellum
THE BRAIN • FUNCTIONAL REGIONS • A. MOTOR AREAS • B. SENSORY AREAS • C. HIGHER FUNCTIONS
MAJOR ANATOMICAL REGIONS OF THE BRAIN • Cerebrum • Diencephalon • Brain Stem • Cerebellum
The Brain • Since the brain is so important, it is protected by the skull, cerebrospinal fluid which cushions it, and meninges which are membranes that surround the brain and only let certain substances cross through to the brain. • The brain is one of the few organs that can only use glucose to get ATP as its energy source. Therefore, without some sugar in our bloodstream, the brain will die. That’s one reason why proper nutrition is so important.
The Brain • By the way, geniuses have the same size brain as everyone else; they are just more efficient at forming synapses. They also have more synapses because they have more dendrites. You can develop more dendrites and synapses by keeping your brain active by learning and reading new things. • Six weeks after this class started, you will have more dendrites and will be able to remember things better. Fun Fact: -Scientists say the higher your I.Q. The more you dream.
CEREBRUM • The brain is divided into parts, and is bilaterally symmetrical. • In general, the left side controls the right half of the body, and the right side of the brain controls the left half of the body. • The largest portion is the CEREBRUM, which makes up 80% of the brain. • The cerebrum controls logical thought and conscious awareness of the environment, and the sensory and motor activity. • The cerebrum is made up mostly of grey matter (cell bodies, dendrites, and unmyelinated axons).
GYRUS AND SULCUS • The superficial region of the brain (and all other organs) is called the cortex. • The surface is not smooth, it’s convoluted. Each bump on the surface of the cerebrum is called a GYRUS, and each shallow groove on the surface of the cerebrum is called a SULCUS. • This up and down formation increases the surface area, and the surface (cortex) is where the information processing is.
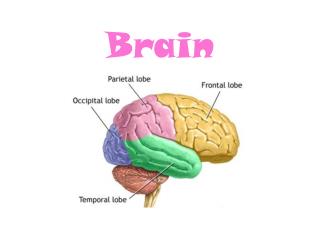
CEREBRUM • The cerebrum is divided into 2 halves called CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES, which are separated by the longitudinal fissure. • Each hemisphere is divided into lobes, named for the bones on top of them.
The Cerebral Hemispheres and lobes Figure 13.7b, c
The Cerebral Hemispheres and lobes Central sulcus • The FRONTAL LOBE and PARIETAL LOBE are separated by the CENTRAL SULCUS. • The TEMPORAL LOBE is between the parietal and frontal lobe, separated by the LATERAL SULCUS. • The OCCIPITAL LOBE does not have a real border; it’s just a region. • These are the anatomical areas, but the functional areas are more important. Lateral sulcus
CORPUS CALLOSUM • If you slice the brain down the center in a mid-sagittal section, you will slice through a white colored tissue called the CORPUS CALLOSUM, which is the area that connects the right and left halves of the brain.
CORPUS CALLOSUM • The CORPUS CALLOSUM is the area that connects the right and left halves of the brain. • The fact that it is white means that there are myelinated axons there.
Sheep brain Corpus callosum
CORPUS CALLOSUM • This is the area that is responsible for the right half of the brain communicating with the left half of the brain. • If the corpus callosum was cut, there would be no communication between the right and left halves of the brain. • Autism is a neurological disease that includes problems with communication between the right and left cerebral hemispheres. • Music therapy for autism: • http://ezinearticles.com/?The-Benefits-of-Music-Therapy-for-Autism&id=432566
Phineas Gage • Phineas was a railroad construction foreman who survived an accident in which a large iron rod was driven completely through his head, severing connections between his left and right frontal lobe. • It changed his personality; he became emotional and had frequent outbursts. He used to be quiet and calm. • This was the first case suggesting that damage to specific regions of the brain might affect personality and behavior.
Phineas Gage • The left side of the brain is responsible for critical thinking, and the right side is responsible for emotion. • Since his left frontal lobe was damaged, his emotions went unchecked.
CORPUS CALLOSUM: Fun Fact • Women have a wider corpus callosum than men. • They tend to use both sides of their brain more than men do. • That’s why they like to talk more. • Give a little girl a doll, and she will hold it like a baby. • Give a little boy a doll, and he will take the head off to see what it looks like inside. • This is a difference between using both sides of the brain vs. just one side. • There is a new book out in paperback called “How to Understand Women”
WHY WOMEN CAN'T SLEEP In a woman’s brain, every one of those little balls is a thought about something thatneeds to be done, a decision that has to be made, or a problem that needs to be solved.A man has only 2 balls. They consume all his thoughts, and he sleeps like a baby.
Diencephalon Consists of two parts: • Thalamus • The superior portion of the diencephalon • Processes sensory information according to importance • Major relay station for sensory impulses to the cerebrum • Hypothalamus • The inferior portion of the diencephalon • Makes hormones which maintains the homeostasis of the body
THALAMUS • The THALAMUS functions to sort out all the sensory information. • It compares the input and determines what information is worth sending to the cortex. • Your body ignores most sensory information. • Up until now, have you noticed the sound of the air conditioner? It’s not important, so it goes unnoticed. • This area also compares information from the right and left eyes for stereoscopic vision, and the right and left ear to determine direction of sound.
Thalamus Hypothalamus Pituitary gland
Thalamus Hypothalamus Pituitary gland
HYPOTHALAMUS • This small area exerts more control over autonomic functioning than any other part. • Makes hormones which provide homeostatic control over the body • It maintains homeostasis by controlling the autonomic nervous reflexes, glucose and hormone levels. • It is also the main visceral (organ) control center, so it controls body temperature, hunger and thirst, and blood pressure by using hormones. • Functionally, the hypothalamus is part of the limbic system (which is involved in memories and emotions), so that’s why a painful memory can increase blood pressure, and a good memory can lower blood pressure.
HYPOTHALAMUS • The hypothalamus synthesizes and secretes hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones. • By secreting hormones, the hypothalamus controls blood pressure, body temperature, hunger, thirst, fatigue, sleep, autonomic nervous reflexes, and circadian cycles.
BRAIN STEM • MIDBRAIN • PONS • MEDULLA OBLONGATA
Midbrain • The top of the brain stem is the MIDBRAIN. • It controls automatic behaviors (fight or flight) • The midbrain also contains a pigmented area called the substantia nigra. • The Substantia nigra is involved in addictions and in initiating body movement. • The substantia nigra secretes the neurotransmitter dopamine. • When the neurons in the substantia nigra become damaged, dopamine levels decrease, causing Parkinson's Disease. • Treatment is to replace the dopamine
Dopamine • Remember that acetylcholine is the neurotransmitter that functions to contract skeletal muscles? • There are many other types of neurotransmitters as well. One is called dopamine. • Dopamine is the neurotransmitter that controls the flow of information between various areas of the brain. • Dopamine is lacking in Parkinson's Disease, in which the person has muscular rigidity and tremors, so they lose the ability to start movements. They need a service dog to help them get out of a chair or to take a first step. They also have a pill-rolling tremor at rest.
VIDEOS • Parkinson’s gait • Parkinson’s patient
Dopamine • Dopamine plays a major role in the brain system that is responsible for reward-driven learning. Every type of reward that has been studied increases the level of dopamine transmission in the brain, and a variety of highly addictive drugs, including stimulants such as cocaine and methamphetamine, act directly on the dopamine system. • There is evidence that people with extraverted (reward-seeking) personality types tend to show higher levels of dopamine activity than people with introverted personalities.
Dopamine • Several important diseases of the nervous system are associated with dysfunctions of the dopamine system. Parkinson's disease, an age-related degenerative condition causing tremor and motor impairment, is caused by loss of dopamine-secreting neurons in the substantia nigra. • Schizophrenia has been shown to involve elevated levels of dopamine activity in regions of the brain and decreased levels of dopamine in other regions. • Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is also believed to be associated with decreased dopamine activity.
Dopamine • Because dopamine cannot cross the blood–brain barrier, patients with diseases such as Parkinson's disease are given L-DOPA (the precursor of dopamine) because it crosses the blood-brain barrier relatively easily. • It is then converted by the body to dopamine.
VIDEOS • Huntington’s disease is the opposite of Parkinson’s disease. They have increased dopamine, and a hyperkinetic gait, with writhing, dance-like movements called chorea. • Huntington’s chorea gait • Huntington’s chorea patient
Endorphins • From the Greek: word endo meaning "within" and morphine, from Morpheus, the god of sleep. • Endorphins are neurotransmitters made within our body that are produced by the pituitary gland during exercise, excitement, pain, acupuncture, consumption of spicy food, love and orgasm, and they resemble opiates in their abilities to produce analgesia (pain suppression) and a feeling of well-being. • They cause more dopamine to be released. • How drugs cause dopamine release: Mouse Party • http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/addiction/mouse/
Corpora Quadrigemina “Quadruplet bodies” • They control visual and audio (hearing) reflexes. • Throw something at your face, you blink = visual reflex. Loud noise (BANG!) causing a startle, is the audio reflex. • The two superior bodies are for eye blinking and fast eye movements. • The two inferior bodies are for sound reflexes • The corpora quadrigemina are linked to the midbrain.
Corpora quadrigemina Midbrain
Pons Farther down the brainstem is the PONS, which relays sensory information between the cerebellum (for balance) and cerebrum (conscious awareness).
Spinal cord Midbrain Medulla Oblongata Pons
Midbrain Pons Medulla Oblongata
Medulla Oblongata • At the base of the brainstem is the MEDULLA OBLONGATA, which contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor (blood vessel constriction) centers. • It controls the nerves that effect the heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing. • Damage here causes coma. Swelling from an injury causes pressure, which can damage this area, which can cause a coma. • Concussions cause nausea and a decrease in blood pressure; patients with these symptoms need an MRI to see if this is early signs of damage to medulla oblongata • Boxers who are knocked out can recover, but repeated knock-outs can cause permanent brain damage.
What’s the difference in function between the medulla oblongata and the hypothalamus? • The medulla oblongata controls blood pressure directly (using nerves), and the hypothalamus controls it indirectly (using hormones).