DNA Form and Function
150 likes | 313 Vues
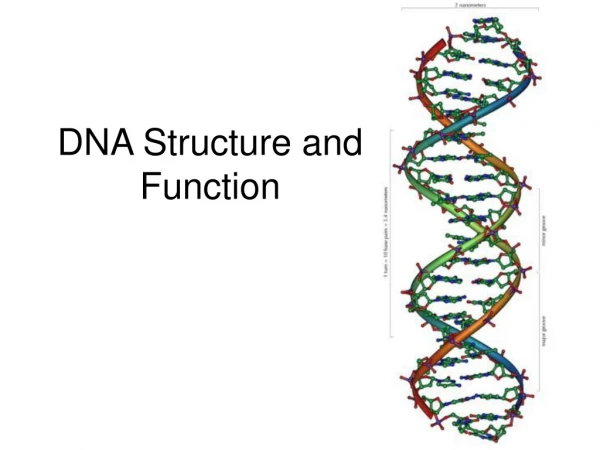
DNA Form and Function. Prokaryote Cell. Eukaryotic Cell. What is DNA?. Deoxyribonucleic acid –DNA There are 3 parts to DNA Phosphate groups Sugar ( deoxyribose ) Nitrogenous base (A,T,C,G) The bases form the rungs of a ladder when they base pair (chemically bond with Hydrogen bonds).

DNA Form and Function
E N D
Presentation Transcript
What is DNA? • Deoxyribonucleic acid –DNA • There are 3 parts to DNA • Phosphate groups • Sugar (deoxyribose) • Nitrogenous base (A,T,C,G) • The bases form the rungs of a ladder when they base pair (chemically bond with Hydrogen bonds)
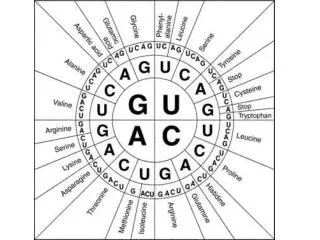
Nucleotides Make up Nucleic Acid • nucleotide= nitrogenous base + phosphate group + sugar • Bases DNA= A,T, G, C (Adenine, Thymine, Guanine and Cytosine) • Bases RNA= A, U, G, C (Same except Uracil) • Pairs A-T(U), G-C
What Does DNA Do? DNA in humans contain about 3 billion base pairs, and more than 99 percent of those bases are the same in all people. Why? If you unwound all the DNA is one cell and placed it end to end, it would measure about 6 feet long. Humans have 20,000- 25,000 different genes among these 3 billion base pairs. What is a gene and what does it ultimately do?
Central Dogma Theory DNA replication- DNA to DNA DNA transcription- DNA to RNA (transcribe genes into RNA, junk DNA does not need to transcribe or gets deleted after transcription) Translation- RNA into protein (uses 3 types of RNA to get proteins made!)
Replication DNA is copied before cells divide, so that the new cell has all of the DNA as it’s parent cell. This allows organisms to grow (if you are a multicellular, eukaryotic organism) or reproduce if you are an asexual prokaryotic or eukaryotic organism.
DNA Replication is semi-conservative When DNA is copied, 1 of the old strands is the template for the new strand. Therefore, each new double helix of DNA has 1 old and 1 new strand of DNA.
DNA Genes are the Template for Transcription (DNA to RNA) DNA is unzippered at the site of a gene and 1 strand is copied into messenger RNA (so mRNA is a single strand and contains the base U instead of T). mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes to a ribosome in order to make a protein
mRNA is the template for amino acids and protein building mRNA is organized so that every 3 base pairs codes for a different amino acids. Amino acids combine in a chain and eventually fold and combine to make complex proteins! Those proteins is what makes us what we are! The genes that code for these proteins, whether they conserved among all humans, or different among individuals can be inherited.
DNA Mutations can be detrimental, neutral or occasionally beneficial • Detrimental-cancers, birth defects • Neutral-mutations in non-coding DNA has no effect • Beneficial- gives organisms the ability to adapt • Think Evolution and Natural Selection- DNA mutations are necessary for this to occur!