Chapter 12: The Digestive System
800 likes | 1.44k Vues
Chapter 12: The Digestive System. Chapter Objectives. Function of the digestive system. Digestive tract, functions of each part. Accessory organs and their role in digestion. Roots pertaining to the digestive system. Major disorders of the digestive system.

Chapter 12: The Digestive System
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chapter Objectives • Function of the digestive system. • Digestive tract, functions of each part. • Accessory organs and their role in digestion. • Roots pertaining to the digestive system. • Major disorders of the digestive system. • Medical terms used in reference to the digestive system. • Abbreviations used in referring to the gastrointestinal system.
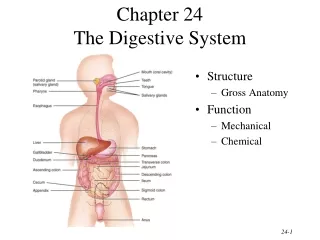
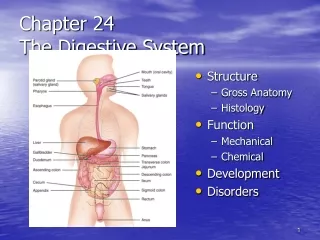
Digestion • Prepares food for cellular intake • Nutrients must be small enough to be absorbed • Nutrients broken down by mechanical and chemical means • Occurs in digestive tract • Food moved by peristalsis
The Mouth to the Stomach • Digestion begins in mouth • Mastication breaks up food • Tongue, lips, cheek, and palate break up food and mix in saliva • Moistened food passed: • Into pharynx → through esophagus →into stomach • Churning of stomach further breaks down food by: • Mixing with enzyme pepsin and HCl
The Small Intestine • Partially digested food passes through pylorus into duodenum • Digestion completed after passing through other parts of small intestine (jejunum and ileum) • Digested nutrients absorbed into circulation • Aided by villi
The Large Intestine • Undigested food, water, digestive juices • Begins with cecum • Colon twists and turns: • Ascending colon • Transverse colon • Descending colon • Water reabsorbed, feces formed • Waste material passes into sigmoid colon • Waste stored in rectum; eliminated through anus
Accessory Organs • Salivary glands • Secretes enzyme that begins digestion of starch • Liver • Secretes bile to break down fats • Gallbladder • Bile stored here until needed • Pancreas • Produces mixture of digestive enzymes
Clinical Aspects of the Digestive System • Infection • Can be caused by variety of organisms • Ulcers • Lesion of skin or mucous membrane • Marked by inflammation or tissue damage • Can be diagnosed by: • Endoscopy • Barium study (Radiography with contrast medium)
Cancer • Colon and rectum most likely affected area • Risk factors: • Diet low in fiber, high in fat • Heredity • Chronic inflammation of colon (colitis) • Polyps often become cancerous • Symptom: bleeding into intestine
Cancer (cont’d) • Internal observations performed with endoscopes • Treatment may require surgical removal of portion of GI tract • May create a stoma for waste elimination • Surgery is called –ostomy, with root named for involved organ (e.g. colostomy)
Obstructions • Hernia • Protrusion of organ through abnormal opening • Pyloric stenosis • Opening between stomach and small intestine too narrow • Intussusception • Slipping of part of intestine into part below
Obstructions (cont’d) • Volvulus • Intestinal twisting • Ileus • Intestinal obstruction caused by lack of peristalsis • Hemorrhoids • Varicose veins in the rectum
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease • Reflux of gastric juices caused by weakness at gastroesophageal junction • Heartburn likely to occur after meals, when lying down, with hiatal hernia, and pregnancy • Treatment: • Weight loss • Elevate head • Avoidance of irritating foods • Drugs • Surgery
Inflammatory Intestinal Disease • Crohn disease • Chronic inflammation of intestinal wall segments, usually ileum • May causes, pain, diarrhea, abscess, formation of fistula • Ulcerative colitis • Continuous inflammation of colon lining, usually rectum
Inflammatory Intestinal Disease (cont’d) • Celiac disease • Inability to absorb gluten • Diverticulitis • Many small pouches in wall of intestine • Attributed to diet low in fiber • If pouches collect waste and bacteria, leads to diverticulitis • Treated with diet improvement, stool softeners, drugs to reduce motility
Hepatitis • Inflammation of the liver • More than six types of viral infections • Hepatitis A • Spread by fecal-oral contamination • Hepatitis B • Spread by blood and other body fluids • Hepatitis C • Spread through blood or close contact to infected person
Hepatitis (cont’d) • Hepatitis D • Highly pathogenic, only affects those with Hepatitis B • Hepatitis E • Spread by contaminated food and water • Hepatitis G • Spread through contact with blood of infected person • Vaccines available for Hepatitis A and B