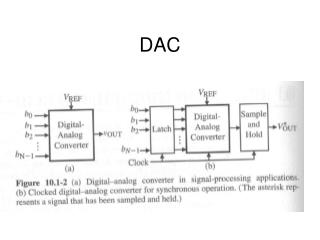
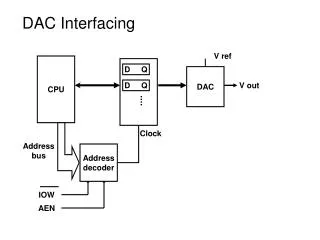
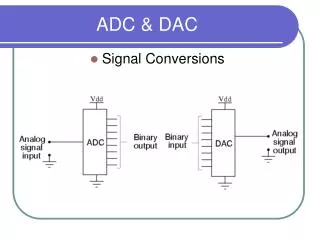
DAC
170 likes | 364 Vues
DAC. Zvi Wiener 02-588-3049 http://pluto.mscc.huji.ac.il/~mswiener/zvi.html. Life Insurance. yearly contribution 10,000 NIS yearly risk premium 2,000 NIS first year agent’s commission 3,000 NIS promised accumulation rate 8,000 NIS/yr

DAC
E N D
Presentation Transcript
DAC Zvi Wiener 02-588-3049 http://pluto.mscc.huji.ac.il/~mswiener/zvi.html http://pluto.mscc.huji.ac.il/~mswiener/zvi.html
Life Insurance • yearly contribution 10,000 NIS • yearly risk premium 2,000 NIS • first year agent’s commission 3,000 NIS • promised accumulation rate 8,000 NIS/yr • After the first payment there is a problem of insufficient funds. 8,000 NIS are promised (with all profits) and only 5,000 NIS arrived. DAC
Client’s 8,000 NIS Agent 3,000 NIS Risk 2,000 NIS 10,000 NIS • insufficient funds if the client leaves • insufficient profits DAC
Risk measurement • The reason to enter this transaction is because of the expected future profits. • Assume that the program is for 15 years and the probability of leaving such a program is . • Fees are • 0.6% of the portfolio value each year • 15% real profit participation DAC
Obligations • The most important question is what are the obligations? • The Ministry of Finance should decide • Transparent to a client • Accounted as a loan DAC
One year example Assume that the program is for one year only and there is no possibility to stop payments before the end. Initial payment P0, fees lost L0, fixed fee a% of the final value P1, participation fee b% of real profits (we ignore real). Investment policy TA-25 (MAOF). DAC
Liabilities (no actual loan) Assets (no actual loan) DAC
Total=Assets-Liabilities Fair value DAC
Liabilities (actual loan) Assets (actual loan) DAC
2 years liabilities (no actual loan) 2 years assets (no actual loan) In reality the situation is even better for the insurer, since profit participation fees once taken are never returned (path dependence). DAC
2 years liabilities (with a loan) 2 years assets (with a loan) DAC
10 years, L0=7% With a loan No loan Profit Stock index DAC
Partial loan - portion q Theoretically q can be negative. DAC
Mixed portfolio When the investment portfolio is a mix one should analyze it in a similar manner. Important: an option on a portfolio is less valuable than a portfolio of options. Another risk factor - leaving rate should be accounted for by taking actuarial tables as leaving rate. DAC
Conclusions It is a reasonable risk management policy not to take a loan against DAC. Up to some optimal point it creates a useful hedge to other assets (call options and shares) of the firm. Intuitively DAC is good when the stock market performs badly and profit participation is valueless. DAC performs bad when the market performs well. DAC