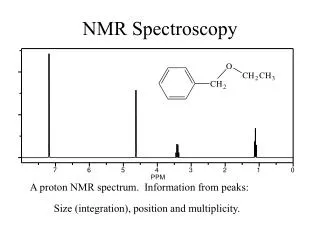
NMR spectroscopy
410 likes | 1.47k Vues
NMR spectroscopy. L.O.: State that NMR spectroscopy involves interaction of materials with low-energy radio frequency radiation. Describe the use of tetramethylsilane , TMS, as the standard for chemical shift measurement.

NMR spectroscopy
E N D
Presentation Transcript
NMR spectroscopy L.O.: State that NMR spectroscopy involves interaction of materials with low-energy radio frequency radiation. Describe the use of tetramethylsilane, TMS, as the standard for chemical shift measurement. State the need for deuterated solvents, e.g. CDCl3, when running an NMR spectrum.
Some nuclei have a magnetic spin: 1H, 13C, 19F In a strong magnetic field they can line up either with the field or opposed the field.
Excitation: a nucleus in its low –energy spin state can be promoted to an upper energy level. This energy is provided by a radio-frequency radiation. Relaxation: The excited nucleus will drop back to the lower energy level. Resonance: the energy provided by the radiation is the same as the energy gap between the tow spin states.
The magnetic field felt by each nucleus depends on: • the applied magnetic field • Chemical environment. Electrons surrounding the nucleus generate a magnetic field.
Nuclear shielding – electrons modify the magnetic field experienced by the nucleus
Chemical shift, d, is a scale that compares the frequency of an NMR absorption with the frequency of the reference peak of TMS at d=0.
Carbon-13 NMR spectroscopy • L.O.: • Analyse carbon-13 NMR spectra to make predictions about the different types of carbon atoms present. • Predict the chemical shifts of carbons in a given molecule.
Electron withdrawing groups (O, CO, F, N) are less shielding. The less shielding, the higher the chemical shift.
Carbon-13 NMR spectra of propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol showing peak assignments
13C NMR TASK 1 For each of these compounds indicate the number of signals in the 13C NMR spectrum predict the approximate chemical shift of each signal using the data sheet a)methylpropene b)propene c)2-chloropropane d)Propanone e)methylamine f)ethyl propanoate g) 1,2-dibromopropane h)dimethylethyl propanoate i)but-2-ene
L.O.: • Analyse carbon-13 NMR spectra to make predictions about possible structures for an unknown compound.
Structural isomers of the carbonyl isomers of C3H6O showing different carbon environments
Carbon-13 NMR spectra of an aromatic compound with molecular formula C8 H8