Sea Floor
140 likes | 314 Vues
Sea Floor . Part 2. Discovery of Mid-Ocean Ridge. After WWII sonar allowed first detailed surveys of large areas of the sea floor Found underwater Mnt range: Mid ocean ridge system Largest geological feature on the planet Can become displaced, can even break the surface .

Sea Floor
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Sea Floor Part 2
Discovery of Mid-Ocean Ridge • After WWII sonar allowed first detailed surveys of large areas of the sea floor • Found underwater Mnt range: Mid ocean ridge system • Largest geological feature on the planet • Can become displaced, can even break the surface
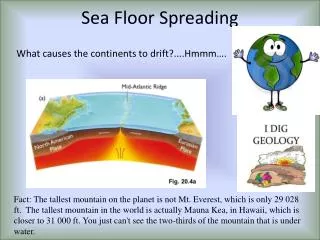
Mid ocean ridge system • Continuous chain of submarine volcanic Mnts • Like the seam on a base ball (encircle the globe)
Mid Atlantic Ridge • Runs down the center of the Atlantic ocean and follows the curves of the opposing coastlines • Inverted Y in Indian Ocean • Runs up eastern side of the Pacific (east pacific rise)
Trenches • Deep depressions in the sea floor • Common in the Pacific
Geological Activity • Earthquakes cluster at the ridge and volcanoes are concentrated near the trenches • Hmmmmm……
What else are we discovering? • Drilling samples of the sea floor • Sea floor is getting older the farther away from the ridge • More importantly – study of magnetism of rocks on the sea floor
Magnetic Field • The magnetic field reverses direction a few times every million years • Present orientation is where magnetic compass points north “normal” orientation • Magnetic reversal – compass would point to the south pole.
Magnetic Bands • Rocks contain magnetic particles • When molten, particles can move • Particles will point in opposite directions during times of normal and reversed magnetic fields • Rocks cool • Particals become frozen (even when the magnetic field changes)
Sea Floor Banding • Geologists found magnetic banding patterns in the sea floor running parallel to mid ocean ridge. • Bands represent the zones in which rocks on the sea floor alternate between normal and reversed magnetization. • The banding is symmetric around the ridge • Magnetic anomalies • Sea Floor was formed at different times
Ridge vs. Trench • Ridge – new oceanic lithosphere is made • Trench – old lithosphere is destroyed • 2 plates collide. 1 plate sinks below the other, weakens under the pressure, breaks up, melts, volcanoes or back to mantle • Trenches are subduction zones
Popsicle Review • Largest geological feature on the planet • Know as a subduction zone • Volcanoes are concentrated around… • What happened to the magnetic pieces in the molten rock once the rock cooled • What type of plate boundary occurs at trenches • How do we know the sea floor was not all formed at the same time • Why do we see a magnetic banding pattern in rocks around ridge sites • Earthquakes are concentrated around… • Why does our planet not expand if new oceanic crust forms at ridges? • How can we tell from the ocean floor that magnetic north reverses?