ORAL ANATOMY & ORAL HISTOLOGY
1.9k likes | 2.74k Vues
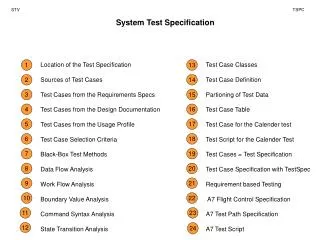
ORAL ANATOMY & ORAL HISTOLOGY. Diphyodont Polyphyodont. Hetero dont Homodont. MAN Diphyodont - Heterodont. “Deciduous” Latin means “FALL OFF” “Milk teeth” – “Temporary teeth” – “Baby tooth”. 6 months – 2 years Mixed dentition period 6 – 12 years

ORAL ANATOMY & ORAL HISTOLOGY
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Diphyodont Polyphyodont
Hetero dont Homodont MAN Diphyodont - Heterodont
“Deciduous” Latin means “FALL OFF” “Milk teeth” – “Temporary teeth” – “Baby tooth”
6 months – 2 years Mixed dentition period 6 – 12 years Permanent teeth – 6 yrs to 21yrs
Maxillary – upper jaw Mandibular – lower jaw
Functions of teeth Mastication (Chewing) Phonation (Speech) Esthetics (Appearance) Self protection
Parts of a Tooth Crown Root Cervix / neck R O O T CROWN
MOLAR TOOTH CROWN R O O T R O O T
Anatomical Crown – covered by enamel Clinical Crown – visible in the oral cavity
Anatomical Root – covered by Cementum Clinical Root – Covered by gingiva
Types of Teeth: Incisors: Have a sharp thin edge cutting. Canines: cutting and tearing. Premolars:have two cusps tearing and crushing. Molars: Have 4 to 5 cusps and a broad surface grinding and chewing
Enamel Outermost covering Hardest Yellowish - grayish white Non-living tissue
Dentin Hard – connective tissue Bulk of the tooth Covered by Enamel – Crown Cementum - Root
Cementum Covers Root Yellowish Anchorage
Pulp Soft connective tissue Central portion Nerves and blood vessels Cells, fibers, intercellular substance
Supporting structures of teeth Alveolar sockets Periodontal ligament (collagen fibers)
Junctions Cemento – Enamel Junction Dentino – Enamel Junction Cemento – Dentinal Junction
Types of Dentition Deciduous Teeth Permanent Teeth
Deciduous teeth Primary teeth Baby teeth Milk teeth Lacteal dentition
Dental formula 2 1 2 2 1 2
Permanent teeth Secondary dentition Successor / Succedaneous teeth Non-successor / Non-succedaneous teeth
Formulae for teeth I – Incisor , C – Canine , P – Premolar , M – Molar
2 1 2 3 I C P M
Dental formula 2 1 2 3 2 1 2 3
Dental formula for Deciduous teeth I 2 / 2 C 1/ 1 M 2 / 2 = 10 2 x 10 = 20 Dental formula for Permanent teeth I 2/2 , C 1/1 , P 2/2 , M 3/3 = 16 2 x 16 = 32
Position of teeth Anterior Teeth Posterior Teeth
Facial Surface 1.Labial 2.Buccal
Lingual / Palatal 1.Palatal 2.Lingual
Incisal / Occlusal 1.Incisal 2.Occlusal
Proximal surface 1. Mesial 2. Distal
Tooth numbering system Recording data Communication
1. Zsigmondy / Palmer notation 2. Universal system 3. FDI ( Federation Dentaire Internationale)
Zsigmondy - Palmer notation / Grid system Adolph Zsigmondy in 1861 Arches are divided quadrants Deciduous teeth A B C D E E D C B A Left Right A B C D E E D C B A
Permanent teeth Central incisor numbered 1 through 8 in each arch left Right 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Advantages Many countries use this system Simple Disadvantage More Chances of error in noting sides