Corynebacterium spp
170 likes | 353 Vues
Corynebacterium diphtheriae is a Gram-positive, non-motile bacillus responsible for diphtheria, primarily affecting children’s upper respiratory tracts. Laboratory diagnosis involves several methods: culture on Blood Tellurite Agar (BTA), Gram staining to reveal the characteristic Chinese letter arrangement, and a positive catalase test. The Elek’s test detects toxigenicity via a reaction with diphtheria antitoxin. This test showcases radiating lines of precipitation on serum agar, confirming the presence of the toxigenic strain. Accurate diagnosis is essential for managing diphtheria.

Corynebacterium spp
E N D
Presentation Transcript
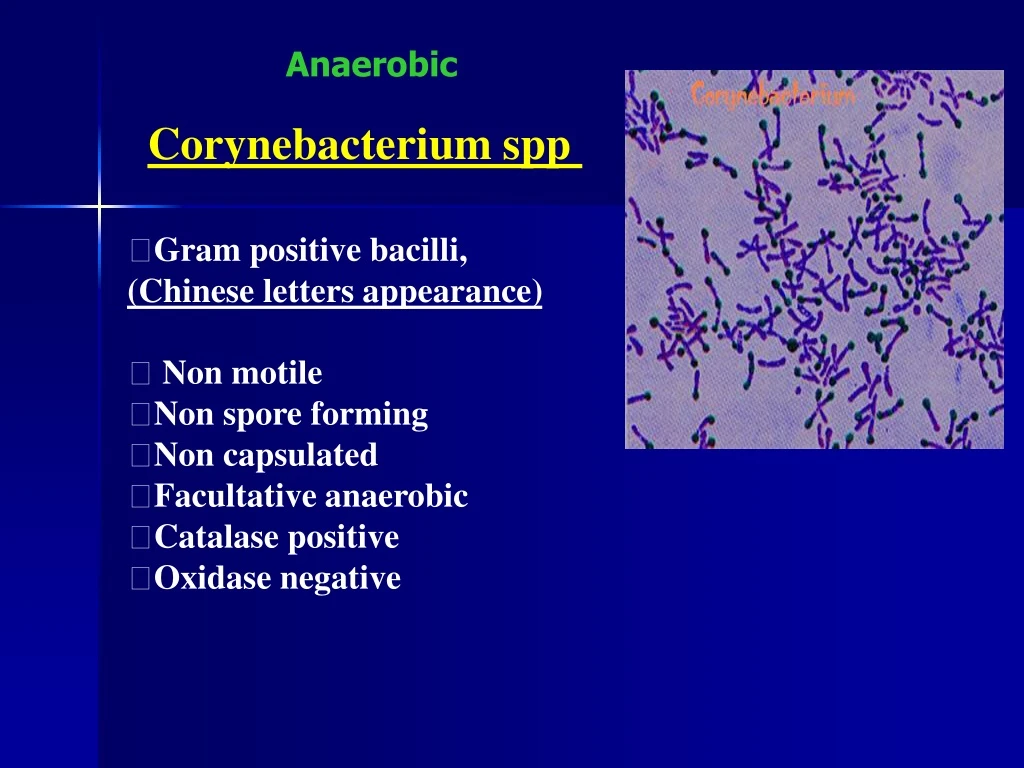
Anaerobic Corynebacterium spp Gram positive bacilli, (Chinese letters appearance) Non motile Non spore forming Non capsulated Facultative anaerobic Catalase positive Oxidase negative
Corynebacterium diphtheriae - Diphtheria is a childhood disease affecting the upper respiratory tract Laboratory diagnosis of case 1- Cultural characteristics : On BTA 2- Gram Stain 3-Catalase (+) 4- Elek’s Test
Laboratory diagnosis Specimen: throat swab Cultural characteristics : On Blood Tellurite Agar BTA –It is selective medium for isolation of C. diphtheriae (containing potassium tellurite ) which inhibiting most other pathogenic The colonies of C. diphtheriae are small, granular, grey, and creamy with irregular edges
Stain: gram stain: Gram +ve, nonspore forming - bacilli (Chinese letters appearance)
Elek’s Test Principle: –It is toxin/antitoxin reaction Procedure: A strip of filter paper saturated with diphtheria antitoxin is placed on the surface of serum agar The organism is streaked at right angels to the filter paper Incubate the plate at 37C for 24 hrs
Result: After 48 hrs incubation, the antitoxin diffusing from filter paper strip and the toxigenic strains produce exotoxin, which diffuses and resulted in lines four precipitation lines radiating from intersection of the strip and the growth of organism Lines of precipitations Filter paper saturated with diphtheria antitoxin Inoculated M.O.