Understanding Real-world Applications of Normal Distributions
110 likes | 205 Vues
Explore practical uses of normal distributions in air crashes, ergonomics, door design, and birth weight analysis, with formulas and examples for real-life scenarios.

Understanding Real-world Applications of Normal Distributions
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Section 6.3 Applications of Normal Distribution
Air Midwest 5481 crashed in Charlotte, North Carolina. All of the 21 people on board were killed. • What was the reason for this crash? What Do The Following Have in Common?
A water taxi sank in Baltimore’s Inner Harbor. Among the 25 people on board, 5 died and 16 were injured. • What was the reason for this crash? What Do The Following Have in Common?
20 passengers were killed when the Ethan Allen tour boat capsized on New York’s Lake George. • What was the reason for this crash? What Do The Following Have in Common?
First, they all were preventable. • Each were working off an old standard – that the mean weight of a person is 140lbs. • This was no longer the case and based on passenger loads, the mean weight of the passengers was so heavy it resulted in the crashes. • Normal distributions are essential for understanding what to expect. • In particular, this area of study is called Ergonomics – the study of how people fit into their environment. Real World Uses For Normal Distributions
In Section 6.2 we considered the standard normal distribution. However, this is an ideal situation and not always relatable to the real world. • What do we use when we have a real life situation with some mean and some standard deviation? Let’s Get REAL
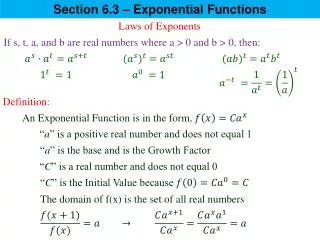
To convert values to standardz-scores use the formula below then following the procedures for working with all normal distributions discussed in Section 6.2. How To Convert Z-Scores
The typical home doorway has a height of 6 ft 8 in. Given that heights of men are normally distributed with a mean of 69 in. and a standard deviation of 2.8 in., find the percentage of men who can fit through the standard doorway without bending or bumping their head. Will a doorway of height 6 ft 8 in. be sufficient in future years? Why Do Doorways Have a Height of 6 ft 8 in. ?
What if we wanted to design a doorway that 95% of men will fit through without bending or bumping their heads. How high should that doorway be assuming heights of men are normally distributed with a mean of 69 in. and a standard deviation of 2.8 in? Designing Doorway Heights
Birth weights in the U.S are normally distributed with a mean of 3420 g and a standard deviation of 495 g. Hospitals require special treatment for babies that are less than 2450 g (unusually light) or more than 4390 g (unusually heavy). What percentage of babies do not require special treatment? Birth Weights
Pg. 272 • #5-7, 9-11, #25 OR #26 Practice