Gene Regulation
60 likes | 196 Vues
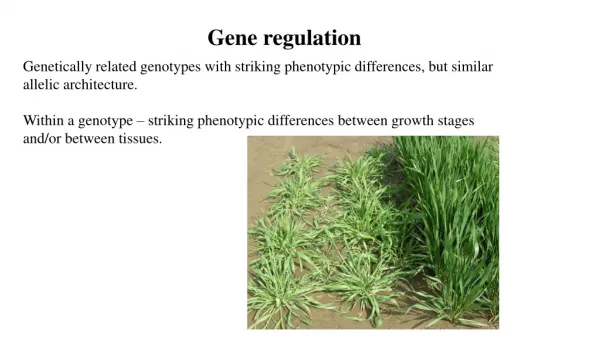
This overview explores key concepts in gene regulation, focusing on the Lac operon's function under varying glucose and lactose levels. It highlights how lactose interacts with the repressor to enable RNA polymerase to transcribe the lactase gene. Additionally, we delve into RNA interference (RNAi) and its mechanism involving microRNA (miRNA) to degrade mRNA, with applications in disease treatment, including cancer and viral infections. Lastly, we touch on Hox genes and their essential role in determining body plans in eukaryotic organisms.

Gene Regulation
E N D
Presentation Transcript
No lactose, high glucose levels Lac Operon Repressor doesn’t bind and RNA polymerase makes mRNA Lactose present, glucose needed Lactose binds to repressor and changes its shape Codes for enzyme lactase
TATTA Box – eukaryotes, helps rna polymerase find the promoter
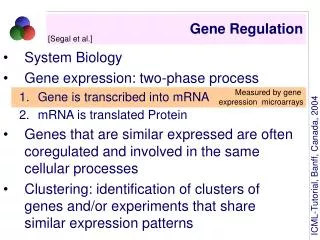
Introns produce microRNA (miRNA) = 20 bp long, • attaches to enzymes (Dicer) that destroy mRNA • Used to cure diseases: cancer, virus, Huntington’s….