Significant Signals
80 likes | 192 Vues
This article explores the fundamental concepts of significant signals, including impulse and delta functions. It provides definitions, visualizations, and key properties related to signal analysis, such as time shifting, scaling, and convolution. The classification of signals into periodic, aperiodic, even, and odd categories is discussed, alongside the concepts of signal energy and average power under Dirichlet conditions. Additionally, it covers Fourier series and transforms, sampling theorems, and essential properties of these mathematical tools, serving as a comprehensive guide for students and enthusiasts alike.

Significant Signals
E N D
Presentation Transcript
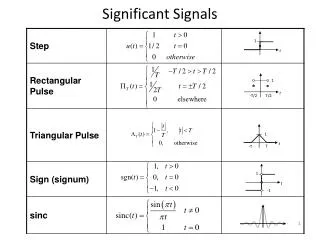
1 t 1 t -1 1 t -T/2 T/2 1 t T -T Significant Signals
Impulse Delta Function • Definition • Visualization • Properties Derivative: Time Shift: Time Scaling: Convolution: Relationship:
Signal Classification • Periodic Signals • Aperiodic Signals • Even & Odd Signals • Even: • Odd: • Signal Energy of a deterministic signal • Signal Average Power
Dirichlet Conditions Fourier Series • x(t) has a finite number of minima and maxima over one period • x(t) has a finite number of discontinuities over one period Fourier Transform • x(t) has a finite number of minima and maxima in any interval on the real line • x(t) has a finite number of discontinuities over any interval on the real line
Fourier Series(Periodic Functions) • Exponential Form • Real Coefficient Trigonometric Form • Complex Coefficient Trigonometric Form
Sampling Theorem • If, signal x(t) is bandlimited to W • i.e., X( f ) = 0 for | f |≥ 0 • x(t)is sampled at multiples of some sampling interval Ts • Where Ts ≤ 1/(2W) • Yields sequence • Possible to reconstruct the original signal x(t) from the sampled values by the reconstruction formula Where is any arbitrary number that satisfies f W -W