Cell Structure
260 likes | 276 Vues
Explore the components of the cell's cytoplasm, including the role of cytosol, organelles like ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi complex, lysosomes, and mitochondria. Learn their structures and functions.

Cell Structure
E N D
Presentation Transcript
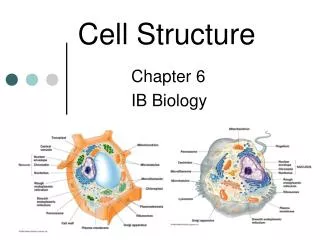
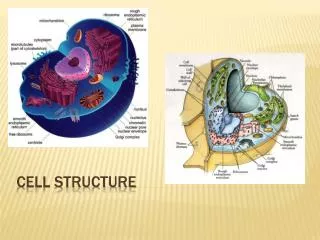
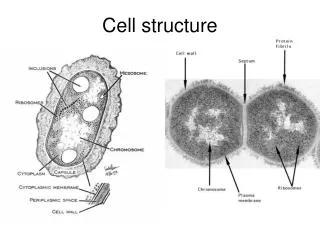
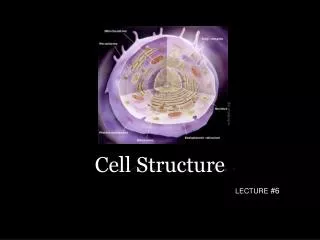
Cytoplasm • All of the cellular contents between the plasma membrane and the nucleus
Cytosol • Fluid portion of the cytoplasm • ~55% of the cell’s volume • 75%-90% water • Contains dissolved/suspended solutes: • Ions, glucose, ATP, lipids, proteins, amino acids, waste • Site of most of the chemical reactions in the cell
Organelles • Specialized structures inside cells that have characteristic shapes and specific functions
Cytoskeleton • Network of protein filaments: • Microfilaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules
Microfilaments • Thinnest • On the periphery of the cell • Contribute to shape and strength • Help generate movement • Support microvilli
Intermediate Filaments • Thicker than microfilaments, thinner than microtubules • Found in cells subject to tension • Help to hold organelles in place
Microtubules • Largest • Help determine shape • Function in movement of organelles • Function in movement of cilia and flagella
Centrosome • Near the nucleus • Pair of centrioles • Cylindrical structures composed of clusters of microtubules arranged in a circular pattern • Pericentriolar Material • Tubulins – organizing center for the growth of mitotic spindles
Cilia and Flagella • Motile projections on the cell surface • Cilia – numerous short hair-like projections on the cell surface. • Propel fluids across the surface of the cell • Flagella – longer than cilia, propel the entire cell. • Only example in the human is sperm cell
Ribosomes • Site of protein synthesis • High content of RNA • 2 sub-units • Large and small • Made in the nucleolus and assembled in the cytosol • Attached to ER or free in cytosol
Endoplasmic Reticulum • Network of folded membranes that extends through the cytoplasm • Rough ER: extends from nuclear envelope; has ribosomes attached; processes and sorts proteins that will be incorporated into the membranes • Smooth ER: extends from rough ER; no ribosomes attached; fatty acids and steroids are synthesized.
Golgi Complex (Body; Apparatus) • Packages and transports materials • Cisterns – flattened membranous sacs with bulging edges that make up the Golgi Body
Transport of Proteins by the Golgi Body • Protein is surrounded by ER membrane and buds of to form a transport vesicle • Transport vesicle moves toward Golgi Body • Vesicle fuses with Golgi Body and proteins enter • Proteins move from one cistern to another by transfer vesicles • In last cistern proteins are sorted and packaged • Proteins leave Golgi Body in secretory vesicles, other membrane vesicles or transport vesicles
Lysosomes • Membrane enclosed vesicles that contain digestive enzymes • Help to recycle cellular components • Autophagy – worn out organelles are digested • Autolysis – enzymes destroy its own cell
Tay-Sachs Disease • An inherited condition in which one lysosomal enzyme is absent. • Normally breaks down a membrane glycolipid found in nerve cells. It is not broken down, it accumulates which makes the nerve cell function less efficiently • Seizure, muscle rigidity, blindness, dementia, uncooridated. Usually die before age 5
Peroxisomes • Similar to lysosomes but smaller • Contain oxides • Enzymes that can oxidize various organic substances • Abundant in liver where there are a lot of toxic substances • Contain catalase
Proteasomes • Contain enzyme called protease • Continuously destroys unneeded, damaged or faulty proteins • Recycles amino acids
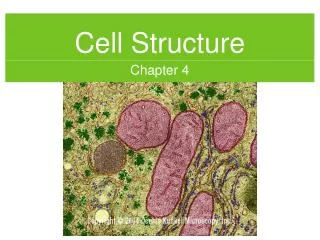
Mitochondria • Site of cellular respiration (makes ATP) • Active cells have a larger number • Double Membrane • Outer – smooth • Inner –folded • Cristae – folds • Enzymes that catalyze a series of reactions are found in the matrix
Check Point Questions • What is the difference between cytoplasm and cytosol? • What is an organelle? • Describe the structure of a ribosome, the Golgi Body and a mitochondrion.