Cell Structure & Function
160 likes | 171 Vues
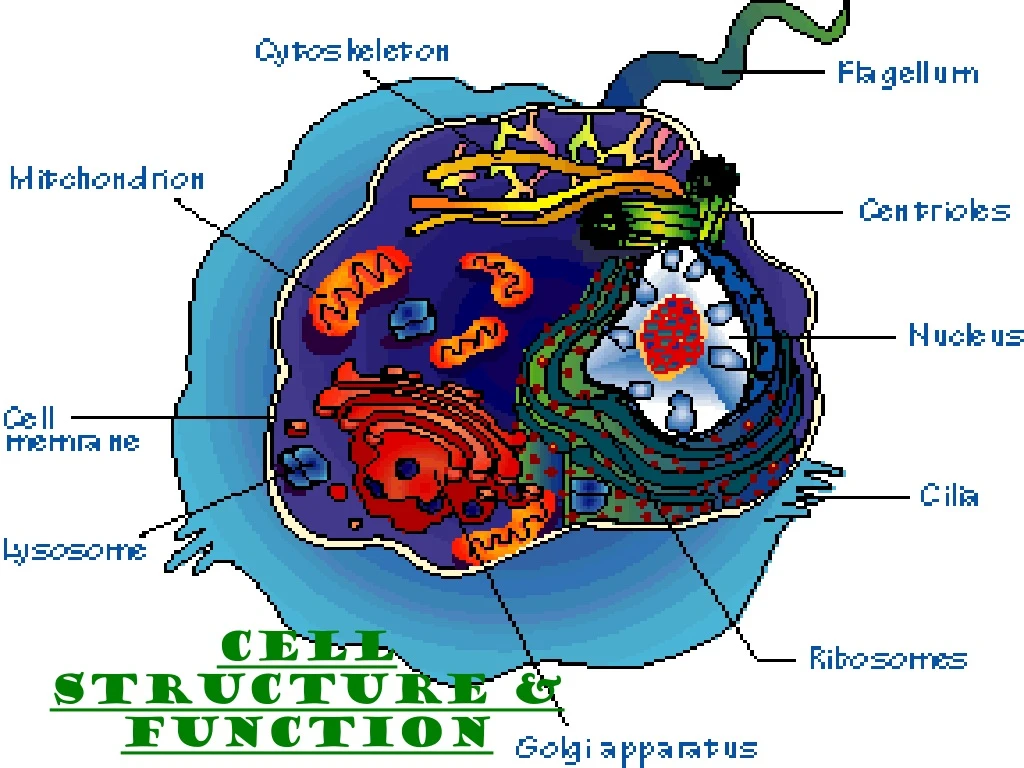
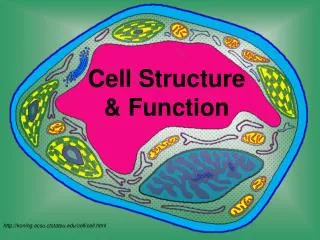
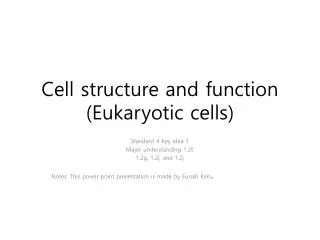
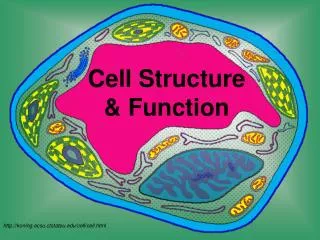
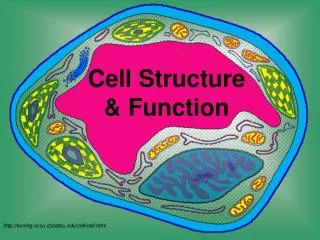
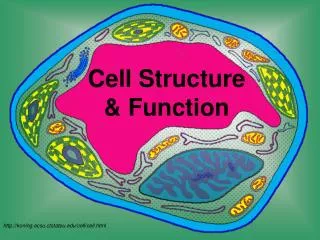
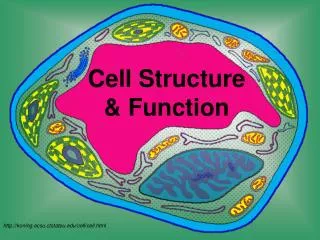
Cell Structure & Function. Discovery of Cells. A. History Of Microscopes The microscope was developed in the 1600’s, which helped scientists to discover cells. 1. Anton van Leeuwenhoeck

Cell Structure & Function
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Discovery of Cells A. History Of Microscopes • The microscope was developed in the 1600’s, which helped scientists to discover cells. • 1. Anton van Leeuwenhoeck • Was the first to try stacking several lenses together to view tiny objects. He looked at pond waterthrough his lenses. He became the first scientist to describe living cells as seen through a microscope. • 2. Robert Hooke– used the microscope to examine thin slices of cork. He called the tiny boxes he saw cells. He chose the name "cells" because the chambers he saw reminded him of roomsin a monastery which were called cells.
Cell Theory • The discoveries and observations that scientists made using microscopes led to the development of the cell theory. • The cell theory states….. 1. All living things are composed of cells 2. Cells are the smallest working unit of life 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells through cell division.
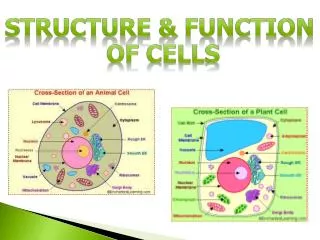
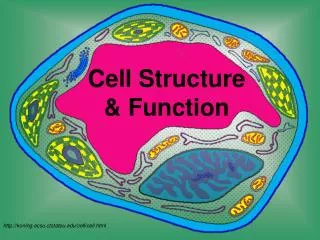
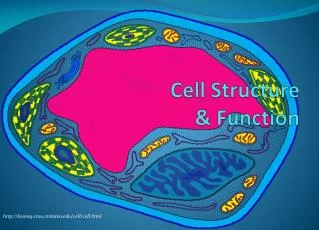
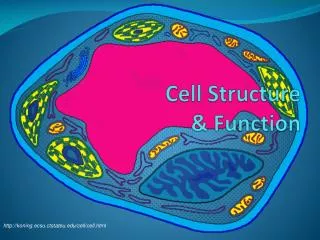
Types of Cells • All cells contain a cell boundary and DNA. • There are 2 Types of cells based on the nucleus • Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes
Prokaryotes • Prokaryotic= “before nucleus” • Prokaryotic cells lack a true nucleus and other membrane bound organelles (internal structures). • Prokaryotes do contain DNA, usually concentrated in a particular region of the cell. All prokaryotes are microscopic and single celled.
Eukaryotes • Eukaryotic= “true nucleus” • Eukaryotic cells contain a truenucleus and other membrane bound organelles. • Eukaryotic organisms may be single celled or multicellular. In multicellular organisms cells become specialized.
Cell Boundaries There are 2 types of cell boundaries. 1. Cell Membrane 2. Cell Wall
Cell Membrane • Every prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell is surrounded by the cell membrane. It helps to maintain homeostasisin the cell by functioning as a protective barrierbetween the cell and its environment. • The cell membrane is selectively permeable which means it allows only certain substances inand certain substances out. • A.K.A…… the plasma membrane. • The cell membrane is not a fixed sheet of molecules, but rather it is a fluid structure composed of three biomolecule groups, carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins.
Cell wall Cell membrane
Lipids There are two types of lipids that make up the cell membrane: phospholipids & cholesterol
Phospholipid Bilayer • Phopholipids– Phospholipids contain one non-polar end and one polar end. Each phospholipid contains 2 non-polar fatty acid tails and a polar head. • The phospholipid bilayer consists of twolayers of phospholipid molecules that surround the cell. The non-polar "tails" point toward each other and the polar heads are on the outside forming a sandwich-like membrane.
Cholesterol • Cholesterol – Found in the cell membranes of animal cellsonlyto help stabilize them. • Cholesterol is wedged between the non-polar fatty acid tails of the phospholipid bilayer.
Carbs & Proteins • Carbohydrates serve as they are “ID tags” to help identify cells • Proteins are embedded in the phospholipid bilayer. Their function is to act as channels and pumps in order to transport specific molecules or ions across the cell membrane.
A- Phospholipid Bilayer • B – Protein • Protein Channel • C – Glycoprotein • D – Carbohydrate • E. Cholesterol
Cell membrane animation http://www.susanahalpine.com/anim/Life/memb.htm
Cell Wall • Cell walls are the outer most boundary plants, fungi, and bacteria. They are not found in animal cells. • The primary function of the cell wall is toprovide structure and support. The cell wall does not regulate what comes in and out of the cell. • Cell walls of …….. 1. plants are composed of cellulose 2. fungi are composed of chitin 3. bacteria are composed of other polysaccharides