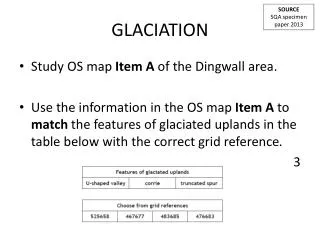
GLACIATION
420 likes | 704 Vues
GLACIATION. GLACIERS. Definition a slowly moving mass or river of ice formed by the accumulation and compaction of snow on mountains or near the poles. GLACIERS.

GLACIATION
E N D
Presentation Transcript
GLACIERS • Definition • a slowly moving mass or river of ice formed by the accumulation and compaction of snow on mountains or near the poles
GLACIERS • At any place on the land where more snow accumulates than is melted during the course of a year, the snow will gradually grow thicker. • As the snow piles up, the increasing weight of snow overlying the basal layers causes them to recrystallize, forming a solid mass of ice. • When the accumulating snow and ice become so thick that the pull of gravity causes the frozen mass to move, a glacier is born.
HOW IS A GLACIER FORMED? • Ice crystals grow & join together to form solid sheets 90% air 50% air
ALPINE GLACIER: • a glacier found in a mountain range • forms because of the continual snow build-up in mountainous areas
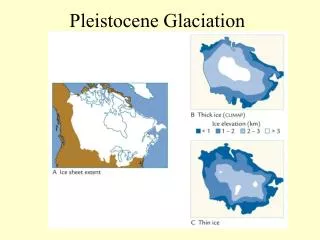
CONTINENTAL GLACIER • A continuous mass of unconfined ice, covering at least 50,000 square km • Most extensive at present as ‘ICE SHEETS’ covering Greenland and Antarctica
EROSIONAL FEATURES OF GLACIERS • Straitions
GLACIAL DEPOSITS • After eroding rock, glaciers leave “deposits” • Glacial Drift: refers to all sediments of glacial origin
TILL • material that is deposited directly by the ice
OUTWASH • sediments laid down by glacial melt water
EROSIONAL FEATURES FINGER LAKES • glaciers gouge out a strip of land in a narrow channel often where a river valley once existed
EROSIONAL FEATURES KETTLES • Are hollows formed when giant blocks of ice were buried in the till
EROSIONAL FEATURES FJORDS • Flooded U-shaped valleys
EROSIONAL FEATURES CIRQUES • Circular hollows on the upper slopes of mountains where alpine glaciers originated
EROSIONAL FEATURES ARETES • Ridges that are left when two cirques occur side by side
? horn ? cirque ? arete
DEPOSTIONAL FEATURES ERRATICS • A large, isolated boulder left behind by a glacier
ICE AGE • An extended period of sub-zero temperatures (10,000 years) where glaciers are found over large areas of land
ICE AGE • Most recent Ice Age ended 12,000 years ago (Wisconsin Ice Age)
GLOBAL DISTRIBUTION OF GLACIERS • Occupy 10% of Earth’s surface