Primate Classification
110 likes | 358 Vues
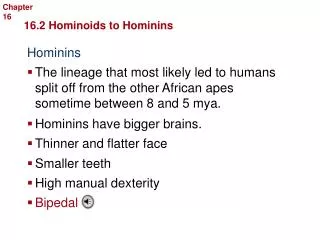
Primate Classification. P rimates – monkeys, lemurs, gorillas, chimps, humans, etc. Primates cont. Family Hominoidea (hominid) – great apes (gorilla, orangutans, chimps & bonobos), humans (living and extinct) Hominins – chimps, bonobos, and humans (living and extinct)

Primate Classification
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Primate Classification Primates – monkeys, lemurs, gorillas, chimps, humans, etc.
Primates cont. • Family Hominoidea (hominid)– great apes (gorilla, orangutans, chimps & bonobos), humans (living and extinct) • Hominins – chimps, bonobos, and humans (living and extinct) • Genus Homo – the humans
Primates • hair or fur • warm-blooded • live young • suckle • infant dependence • social life • play • observation and imitation • pecking order Common Primate Traits
Primate Family Tree Orangutan Crown lemur
Hominin Evolution • Homo habilis (2.0 – 1.6mya) • H. erectus (1.9-70kyBP) • H. neanderthalensis (300-30kyBP) • H. sapiens (200kyBP – present) • ~ 20 different homo species • Human evolution - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Scale: Millions of Years BP
Homo heidelbergensis • Africa into Europe • 500 000 – 300 000 yrs BP • primitive form of language • similar tools/fire as H. erectus • evolved into H. neandertalensis in Europe • evolved into H. sapien in Africa
Homo sapiens • Archaic – 200,000 to 35,000 years BP • Homo sapiens • Modern – 35,000 years BP to present • Anatomically modern • Homo sapiens sapiens
Modern Homo Sapiens • Multiregional Model • Humans evolved more or less simultaneously across the entire Old World from several ancestral populations. • Rapid-Replacement Model (Out of Africa) • Humans evolved only once--in Africa --and then migrated throughout the Europe and Asia, replacing their ancestors • mDNA evidence supports this