Introduction to Periodic Table
260 likes | 731 Vues
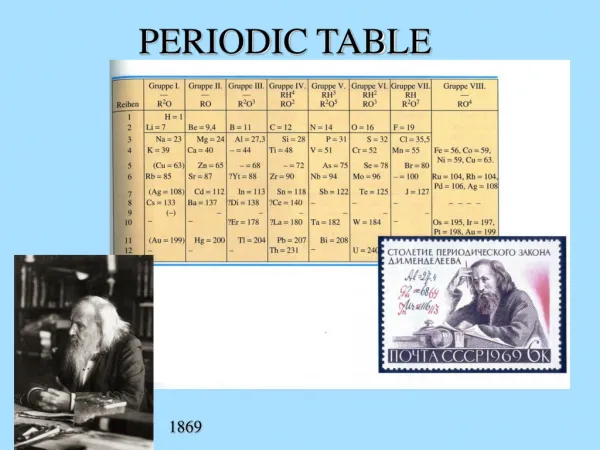
Introduction to Periodic Table. Dmitri Mendeleev. 1869 Organized the 63 known elements Put properties on cards and looked for trends Ordered elements by atomic weight, organized so there were repeating patterns both across & down. Mendeleev’s Periodic Table.

Introduction to Periodic Table
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Dmitri Mendeleev • 1869 • Organized the 63 known elements • Put properties on cards and looked for trends • Ordered elements by atomic weight, organized so there were repeating patterns both across & down
While coming up with his order, Mendeleev…. • Found errors in atomic weights of 17 known elements • Left places for undiscovered elements & predicted their properties • 3 of those were discovered in his lifetime: gallium, scandium, germanium
Henry Mosley • British chemist -1915 • Found inconsistencies with Meneleev’s Periodic Table • Arranged elements by atomic number • Inconsistencies disappeared • Arranged the periodic table for today
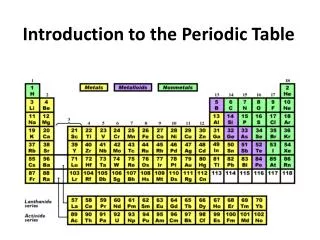
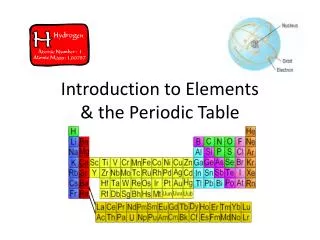
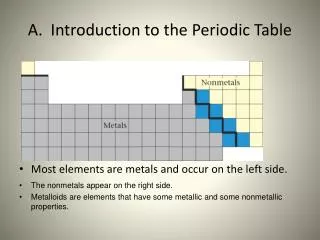
Design of the Periodic Table • Classification of Element • By looking at where a element is on the periodic table, you can tell about it’s chemical and physical properties • Columns (18) • Up and down • Called Families/Groups • Elements in Families have similar properties • Rows (7) • Side to Side • Called Periods • Elements in periods DO NOT have similar properties
1A 8A 2A 3A 4A 5A 6A 7A • The first two and last six columns are numbered 1A-8A, relates to the # of electrons in their OUTER shell.
Properties of the metals • Left side of PT • Physical Properties • Luster- Shininess • Ductile – Draw into wire • Malleable- hammered into sheets • Good Conductor of heat and electricty • Chemical Properties • Corrosive- wearing down due to chemical reaction • Easily lose electrons
Alkali Metals • Group 1/ 1st Column • Very reactive • Form +1 ions • Soft metals – cut with butter knife • Low density • Never found unreacted in nature • Cations • Examples: H, Li, Na
Alkali and a Halogen Missing Electron Extra Electron
Alkaline Earth Metals • Group 2/Second Column • Reactive (not explosive) • Rarely found unreacted in nature • Form 2+ ions • Cations • Examples: Be, Mg, Ca, etc
Transition Metals • Groups 3B-12B on the Periodic Table • Middle section of PT • Much less reactive than Alkali or Alkaline Earth Metals • often unreactive • Only 1 that is a liquid at room temp • Mercury – Hg • Examples: Cr, Co, Ni, Fe, Cu, Ag, Au
Properties of rare Earth metals • Lanthanides • Rare Elements • Actinides • Radioactive • Not often found in compounds • Some are not found in nature at all • Properties: • Silver, silvery-white, or gray metals. • The metals have a high luster, but tarnish readily in air. • High electrical conductivity. Lanthanides - part of period 6 Actinides - part of period 7
Properties of Metalloids • “Stairstep” between metals and nonmetals • Properties • Can have both metals and non metals traits • Sometimes called semiconductors • Technology • Can be shiny or dull, malleable or not… • Example: Fe, Cu
Properties of non-metals • Right Side of PT • Physical Properties • Dull • Brittle • Good insulator • Poor conductors • Solid, Liquid, & Gas • Chemical Properties • Tend to gain electrons
Halogens • Group 17 • Very reactive • “Salt-formers” • Form -1 ions • Anions Examples: Chlorine Bromine Iodine
Properties of Noble Gases • Group 18 • Unreactive, inert, “noble” • Low Boiling Point • Gases at room temp • Have a 0 charge, no ions • Examples: He, Ne, Ar, Kr, etc
Diatomic Gases • Group of gases • Paired when found in nature • H O N Cl Br I F H2 O2 N2 Cl2 Br2 I2 F2