Introduction to the Periodic Table
330 likes | 664 Vues
Introduction to the Periodic Table. Atomic Number ● Symbol ● Atomic Weight. I am Dmitri Mendeleev!. I made the PERIODIC TABLE !. What is the PERIODIC TABLE?. Shows all known elements in the universe. Organizes the elements by chemical and physical properties .

Introduction to the Periodic Table
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Introduction to the Periodic Table Atomic Number ● Symbol ● Atomic Weight
I am Dmitri Mendeleev! I made the PERIODIC TABLE !
What is the PERIODIC TABLE? • Shows all known elements in the universe. • Organizes the elements by chemical and physical properties.
What does it mean? Atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus. Atomic weight is the weight of the nuclues- equals the number of the protons and neutrons.
Using your textbook, locate the elements below and identify their atomic numbers, symbol, and atomic weight. Be prepared to share your findings! • Sodium • Oxygen • Copper
Common Elements • You will need to know these common elements: • 1. H 7. C 13.Au 19. Pb • 2. Na 8. N 14. Sn 20. F • 3. K 9. O 15. Al 21. Ni • 4. Ca 10. He 16. Pt 22. P • 5. Fe 11. Cl 17. Hg 23. Mg • 6. Cu 12. S 18. Ne 24. I • 25. Zn
Introduction to the Periodic Table • The periodic table shows all of the known elements in order of increasing atomic number.
The Modern Periodic Table • Group : Each vertical column • Also called a family • Have similar physical and chemical properties • Identified by a number (1-18)
The Modern Periodic Table • Periods : horizontal rows (7 of them) • physical and chemical properties change somewhat regularly across a period
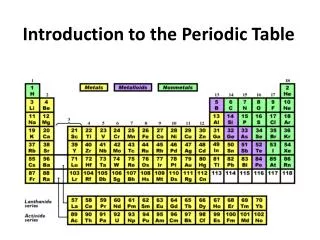
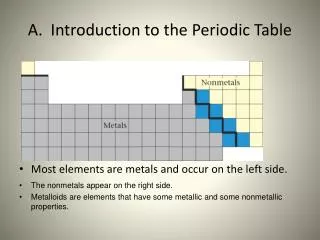
Introduction to the Periodic Table • Most elements are metals and occur on the left side. • The nonmetals appear on the right side. • Metalloids appear on the stair steps
Metals • All metals are solid, with the exception of mercury • Most have high melting points • Easily lose electrons • Have luster (reflect light) • Good conductor of heat and electricity • Malleable • Ductile
Nonmetals - tend to gain e- Gases or brittle solids Poor conductors of heat and electricity Many essential for life C, S, N, O, I Metalloids - An element that has some characteristics of metals and some characteristics of nonmetals -located along the stair-step line at the right side of the table -tend to be semiconductors of electricity Nonmetals & Metalloids
Group 1 Alkali Metals • They are so reactive to oxygen and water that they do not occur in nature in their pure state and must be stored in a specific way. • Note: This group does NOT include Hydrogen
Alkali metals (cont.) • Their reactivity increases as you go down the group. • Ex. Francium (Fr) more reactive than Sodium (Na) • Soft: Can cut these metals with a knife
Group 2 - Alkaline Earth Metals • Second column on the periodic table • They are not as soft as the Group 1 metals. • They are too reactive to occur in nature in their pure state, but NOT as reactive as alkali metals. • Their reactivity increases as you go down the column.
Intro to the PT • Groups 3 – 12 on the periodic table • Called the transition metals
Transition Metals • The lower middle section of the P.T. • These metals have multiple charges which means that they can bond in multiple ways.
Noble Gases - The elements in Group 18 are gases at room temperature and generally unreactive. -They are the most stable elements on the periodic table.
How do I find the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons in an element using the periodic table? • # of PROTONS= ATOMIC NUMBER • # of ELECTRONS= ATOMIC NUMBER • # of NEUTRONS= ATOMIC _ ATOMIC WEIGHT NUMBER