Possible types of module
40 likes | 169 Vues
This document presents the detailed mechanical structure and module electronics of a silicon-tungsten (Si/W) calorimeter designed at Moscow State University in June 2002. It explores various module types, including stainless steel and tungsten components, alongside the specifics of detector board layouts. The configurations and bonding techniques involved in the detector systems are examined, highlighting innovations such as strip-line bonding vs. traditional wire bonding. The design emphasizes adaptability in pixel size and layout for enhanced detection efficiency and structural integrity.

Possible types of module
E N D
Presentation Transcript
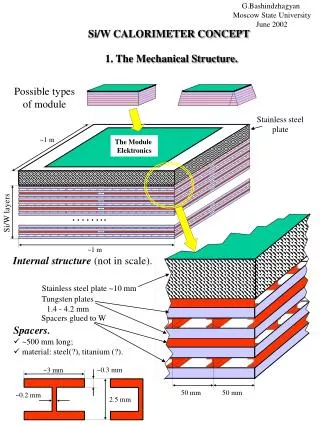
G.Bashindzhagyan Moscow State University June 2002 Si/W CALORIMETER CONCEPT 1. The Mechanical Structure. Possible types of module Stainless steel plate ~1 m The Module Elektronics …….. Si/W layers ~1 m Internal structure (not in scale). Stainless steel plate ~10 mm Tungsten plates 1.4 - 4.2 mm Spacers glued to W • Spacers. • ~500 mm long; • material: steel(?), titanium (?). ~0.3 mm ~3 mm 50 mm 50 mm ~0.2 mm 2.5 mm
G.Bashindzhagyan Moscow State University June 2002 Si/W CALORIMETER CONCEPT 2. Detector Board. • Top View. • Length: ~50 cm; • Width: 5/6/10 cm; • Pixel size: 1-2 cm2. Detector Board G10 (?) 0.2 mm 0.1 mm 0.1 mm Pixeled Si detectors Cross section (not in scale). Gold strip-lines on the kapton cable Kapton cable Elastic foam band ~2.5 mm Detector Board Silicon detectors
G.Bashindzhagyan Moscow State University June 2002 Si/W CALORIMETER CONCEPT Compare to regular wire bonding: • three contacts; • a protection is required. • The strip-line bonding: • only one contact; • no additional thickness. 3. Kapton Cable • Kapton thickness ~20 µm; • Gold strip-line thickness ~10 µm; • Gold strip-lines width ~100 µm; - The Detector Board (G10 ?); - Kapton layer; - Gold strip-line on the kapton; - Silicon sensors; - Elastic foam band. Top View. ~ 2 mm 5 (6;10) cm Gold strip-lines The holes in the kapton Kapton cable Detector Board iside the Module. Cross section. To the Module Electronics Kapton cable with gold strip-lines Elastic foam band Tungsten Si-detector ~2.5 mm Detector Board Tungsten Gold strip-line Points of bonding Gold strip-line Kapton Point of bonding Aluminum on the Si-detector Silicon detector Aluminum wire 25 µm Silicon detector
G.Bashindzhagyan Moscow State University June 2002 Si/W CALORIMETER CONCEPT 4. Silicon Detector. First option: One detector 1010cm2 size. Second Option: Four detectors 55cm2 size. A coast per 1 cm2 can be essentially less for the second option. ~10 cm ~10 cm 6” Si-Wafer Possible types of Si-detectors: Strip detector (type 1). Pixel detector. Detector size: 55 cm2; Pixel size: 1.251.25 cm2; Pixel area: 1.251.25=1.56 cm2; Number of pixels: 16. Detector size: 55 cm2; Strip width: 0.31cm; Strip area: 50.31=1.56 cm2; Number of strips: 16. Strips of both detectors connected to one strip-line on the kapton cable forming one 10cm long strip. Each detector size: 55 cm2; Area of two connected strips: 1.55 cm2; Number of strips: 32. Strip detector (type 2). Detector #1 Detector #2