TECHNOLOGY AS A DYNAMIC SYSTEM
340 likes | 476 Vues
TECHNOLOGY AS A DYNAMIC SYSTEM. ENGR-FET-5 – Students will describe the essential systems and processes involved with invention, innovation, and entrepreneurship .

TECHNOLOGY AS A DYNAMIC SYSTEM
E N D
Presentation Transcript
ENGR-FET-5 – Students will describe the essential systems and processes involved with invention, innovation, and entrepreneurship. ENGR-STEM-4 – Students will apply principles of science, technology, engineering, mathematics, interpersonal communication, and teamwork to the solution of technological problems.
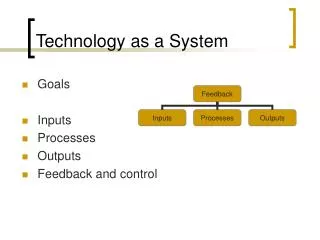
Learning Objectives- • Explain how technology is a system • Identify the major components of a technological system • List the inputs to a technological system • List the steps in the problem-solving/design process • Name positive and negative technological outputs • Explain feedback and control
What are inputs? • Resources that are used to make the system operate…the elements that are changed by the technological processes or are used by technology to change other inputs
People as Inputs: • Most important input to any technological system WHY??? 1. Human needs and wants give rise to systems 2. People bring to the systems specific knowledge, attitudes and skills 3. Human ethics and values control and direct the systems
Types of Workers: • Skilled-tasks require extensive training • Technicians-skilled workers in laboratories and product-testing facilities • Semi-Skilled-tasks require a limited amount of training-run machines, assemble products • Unskilled-tasks require minimum training
Materials as Inputs:The substances from which artifacts are made • Types of Materials/Classifications of Materials: • Organic vs Inorganic-living vs non living • Natural vs Synthetic-naturally occurring on earth vs human made • Physical State-Gases, Liquids, Solids
Tools/Machines as Inputs: Tools – • Artifacts we use to expand what we are able to do • Include hand tools and machines • Hand tools – expand muscle power and includes things like hammers and screwdrivers • Machines – amplify the speed, amount or direction of a force.
Common Hand Tools Measuring Measuring Drilling Polishing Types of Hand Tools Pounding Gripping Cutting
Lever Mechanisms • Two Parts-to move applied load • Lever Arm • Fulcrum • Three Classifications-based on the way force is applied to move load • First Class • Second Class • Third Class
Lever Diagrams… Movement Force Movement Force Load Load First Class Second Class Movement Force Load Third Class
Inclined Plane Mechanisms • Sloped surfaces which are used to make a job easier to do-it’s easier to move up a slope than a vertical surface • Principle 3 Inclined Plane Mechanisms: • Inclined plane • Wedge • Screw
Energy as Inputs:The ability to do work • Technological systems require that energy be converted, transmitted and applied. • 7 major types: • Chemical-energy stored in a substance and released by chemical reactions • Electrical-energy created by moving electrons • Thermal-energy that comes from the increased molecular action caused by heat • Radiant-energy produced by the sun, fire and other matter, which includes light, radio waves • Mechanical-energy produced by moving water, animals, people and machines • Acoustical- energy associated with audible sound • Nuclear-produced by splitting atoms or uniting atomic mater
Sources of Energy 3 Sources: • Exhaustible – Limited by the quantity found on earth • Coal • Petroleum • Natural Gas • Renewable-from living matter that can be used up but replaced • Wood and plant matter • Human and animal muscle power • Inexhaustible-always with us and will continue to be so • Wind • Sun
Information as Inputs • Data-raw facts and figures collected by people and machines • Information-data that has been sorted and categorized for human use • Knowledge-information that is learned and applied by people
Finances as Inputs:The money and credit necessary for the economic system to operate • Single Ownership-Sole Proprietorship • Equity Financing-money is raised by selling a portion of the company • Debt Financing-Money is borrowed from other sources
Time as Inputs • How much time will it take to accomplish a task
Input Activity: • On a separate piece of paper select a product that is made from exhaustible materials or a task that uses an exhaustible energy source. • Describe how that product could be made or the task could be completed using renewable materials or renewable energy sources.
Processes The conversion of ideas or activities through the use of machines, resources and labor into useful products
Problem Solving/Design Process • Major Steps: • Identify the problem • List Criteria and Constraints • Brainstorm solutions • Detail the best solution • Model the solution • Communicate final solution • MARS ROVER LEARN FROM YOUR MISTAKES Mistakes are springboards to success
Production Processes:Actions that are completed to perform the function of the technological system • Harvesting • Prevent or treat illnesses • Convert materials into products • Transform information into messages • Convert a form of energy
Activity-Manufacturing of the pencil • Write down all the production processes you think are used to make a common wooden pencil
Questions: • How do you get the hole in the pencil? a) Drilling b) Carving a groove in two slats c) Hammering d) All of the above • Why label a pencil? a) To show the colour b) To show the brand name c) To show the hardness d) All of the above • What environmental safeguards do manufacturers have in place? a) Reforestation b) Recycling of materials c) Waste management d) All of the above • Black lead pencils are made from graphite and clay? True or False • Coloured pencils are a mixture of white clay, pigments and waxes? True or False • The type of wood used is important so it doesn’t break or splinter? True or False
Management Processes:All the actions people use to ensure that the production processes operate efficiently and appropriately. • Involve 4 functions: • Planning: setting goals and developing courses of action to reach the goals • Organizing: Dividing the tasks into major segments so that the goals can be met and resources assigned to complete each task • Actuating: Starting the system to operate by assigning and supervising work • Controlling: comparing system output to the goal
Output • Is simply what the system produces • Types of Outputs: • Products • Structures • Media Messages • Relocated People and Cargo
SUMMARY: • What are the five steps of the problem solving method? • Explain what goes on during a brainstorming session. • If you test and adjust your solution, are you following an open-loop or closed-loop system? Why? • When you are solving a technological problem, why is it important to build a model of your solution? 1