Bacteria: Kingdoms, Classification, and Impact
220 likes | 294 Vues
Explore the world of bacteria with a focus on their classification, structures, movement, benefits, harmful effects, pathogens, and ways to control them. Discover the significance of bacteria and Archaea in different environments.

Bacteria: Kingdoms, Classification, and Impact
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Bacteria Classification By: Erin Kelly, Dan Schmid, and Ally Swartz
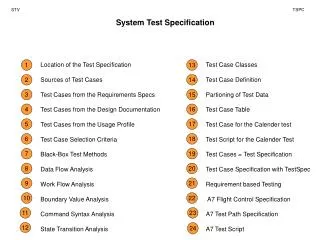
Overview • The two kingdoms of bacteria • Prokaryotic cell • Positives and negatives of bacteria • Ways to control bacteria • Classification of cells • Structure and the way they move
ek Kingdom of prokaryotes • Bacteria and Archaea are the two domains Locations • Bacteria lives almost everywhere • Archaea live in harsh enviorments
ek • Cell wall- provides structural support and protection • Cell membrane- provides support and protection for cell • Peptidoglycan- gives strength to the outer structure of organism. • Ribosome- protein factory
ek • Flagellum- allows cell to move • DNA- long term information source • Phili- attach bacterial cells to other cells
How bacteria benefits us • Waste decomposition • Creates Amino and Nucleic acids • Nutrient builders • Pollution fighters DS
How Bacteria is harmful to us • Causes diseases by killing living cells • Can cause tissue damage • Releasetoxins • Releases chemicals that upset Homeostasis DS
Pathogens • Type ofbacteria • Bloodborne, airborne, and foodborne • Five main types: • Viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoa and worms DS
Ways to control bacteria • Physical removal • Disinfection • Food storage • Food processing • Sterilization DS
Bacteria and Archaea • Bacteria or Archaea—two of the three domains of life • Bacteria domain corresponds to kingdom Eubacteria; Archaea corresponds to Archaebacteria • Bacteria usually surrounded by a cell, protects from injury, determines its shape; some have a second membrane or flagella • Archaea + Bacteria equally small, lack nuclei, contain cell walls • Archaea key genes of DNA sequence alike those of eukaryotes rather than bacteria; lacks peptidoglycan + membranes contain diff. lipids
Size and Function • Range in size from 1—5 micrometers • Much smaller than most eukaryotic cells • Stores energy in the form of fuel molecules such as sugars • Some species can change method of energy capture/release (depending on environment conditions) • Grow up to double their size • Replicates DNA after growing and divides in ½ . . . producing two identical cells • When growth conditions unfavorable, many form an endospore (thick, internal wall enclosing DNA
Shapes of Bacteria • Variety of shapes • Bacilli: rod-shaped • Cocci: spherical • Spirilla: spiral and corkscrew-shaped
Movement of Cells • Some don’t move at all • Others propelled by flagella • Some glide slowly along the slime-like material they secrete • During favorable conditions, prokaryotes can grow +divide at very fast rates • Exchange genetic information during Conjugation—where genetic material moves from 1 cell to the other
Where does the bacteria archea live? A. Harsh environments B. Tundra's C. Desert D. Bodies of water Answer A. Harsh environments
What is the function of the cell membrane? A. Send and receives messages B. Protein factory C. Provides support and protection for cell D. Stores information Answer: C. Provides support and protection for cell
ABC question one for bacteria • Which of the following is not a type of bacteria or pathogen • A: Virus • B: airborne • C: Worms • D: Gasborne Answer : D, gasborne DS
ABC question two bacteria • How many main types of bacteria are there • A: 7 • B: 3 • C: 5 • D: 4 Answer: c, 5 DS
What's the thick, internal wall many Prokaryotic cells form that encloses its DNA? A. Conjugation B. Endospore C. Binary fission D. Peptidoglycan Endospore
What's the range of Prokaryotic cell sizes? A. 5-10 micrometers B. 2-4 millimeters C. 1-5 micrometers D. 1-5 millimeters 1-5 micrometers
Overview • The two kingdoms of bacteria • Prokaryotic cell • Positives and negatives of bacteria • Ways to control bacteria • Classification of cells • Structure and the way they move