Mengidentifikasi Sudut
480 likes | 1.16k Vues
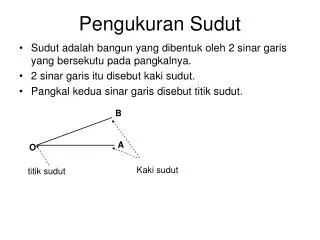
SUDUT DAN BIDANG. Mengidentifikasi Sudut. ANGLE AND PLANE. Identify Angle. SUDUT DAN BIDANG. Menentukan kedudukan garis, dan besar sudut yang melibatkan titik, garis dan bidang dalam dimensi dua. Standar Kompetensi:. Kompetensi Dasar:.

Mengidentifikasi Sudut
E N D
Presentation Transcript
SUDUT DAN BIDANG Mengidentifikasi Sudut
ANGLE AND PLANE Identify Angle
SUDUT DAN BIDANG Menentukan kedudukan garis, dan besar sudut yang melibatkan titik, garis dan bidang dalam dimensi dua Standar Kompetensi: Kompetensi Dasar: • Mengidentifikasi sudut.2. Menentukan keliling bangun datar dan luas bangun datar.3. Menerapkan transformasi bangun datar. SUDUT DAN BIDANG
ANGLE AND PLANE Determining position of line, and angle that involves point, line and plane in two-dimension. Standard Competence: Base Competence: • Identifying angle.2. Identifying the circumference of flat shape and width of flat shape.3. Applying transformation of flat shape. SUDUT DAN BIDANG
B’ B’ B B Dinamai sudut BAB’ atau BAB’ atau A atau α Dinamai sudut BAB’ atau BAB’ atau A atau α Macam-macam satuan sudut Pengertian Sudut Didalam taksonomi belajar menurut Gagne, sudut adalah suatu konsep dasar, maka dari beberapa cara untuk mendefinikan tentang pengertian sudut, dapat melalui salah satu pendekatan melalui rotasi garis sebagai berikut : α SUDUT DAN BIDANG
B’ B’ B B Dinamai sudut BAB’ atau BAB’ atau A atau α Mentioned as angle BAB’ orBAB’ or A orα Kinds of Angle Unit Definition of Angle In taxonomy study, according to Gagne, angle is a base concept, so from several ways to define about angle, is that by one approach through line rotation as follows : α SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Y C θ θ A X Sudut θ tidak dlm kedudukan baku Sudut θ dalam kedudukan baku Macam-macam satuan sudut Sudut Dalam Kedudukan Baku Sisi AB disebut sisi permulaan dari sudut θ Sisi AC disebut sisi batas dari sudut θ SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Y C θ θ A X Angleθis not in base position Angleθis in base position Kinds of Angle Unit Angle in Base Position Side AB is called beginning side from angleθ Side AC is called limit side from angleθ SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Seksagesimal Besar Sudut Radial Sentisimal Macam-macam satuan sudut Besar Sudut SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Seksagesimal Angle Size Radial Sentisimal Kinds of angle unit Angle Size SUDUT DAN BIDANG
1 radian r Macam-macam satuan sudut Sistem Radial Sebagai motivasi diceriterakan bahwa untuk pengukuran sudut elevasi penembakan meriam dalam kemiliteran zaman dulu diperlukan ukuran sudut yang tidak menggunakan ukuran derajat, namun ukuran lain yang lazim kita kenal dengan istilah sistem radian Dalam sistem radian yang dimaksud besar sudut satu radian adalah besar sudut pusat dari suatu lingkaran yang panjang busur dihadapan sudut tersebut adalah sama dengan jari-jari lingkaran tersebut. Sehingga diperoleh hubungan: 1800 = π radian 1 radian radian SUDUT DAN BIDANG
1 radian r Kinds of angle unit Radial System As motivation, it is told that in measuring elevation angle, Merriam shoot in military was needed angle size and didn’t use degree measurement, unless the other normal measurement we know as radiant system In radiant system the center angle size is of a circle that the length of busur in front of the angle is equal to radius of that circle. Then gotten a relation: 1800 = π radian 1 radian radian SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Macam-macam satuan sudut Sistem Sentisimal • Pada instrumen-instrumen untuk keperluan astronomi, peneropongan bintang, teodolit dikenal satuan sudut yang sedikit berlainan dengan kedua ukuran di atas, sistem ini kita kenal dengan nama sistem sentisimal. Pada sistem ini satu putaran penuh adalah 400g (dibaca “400 grad”). • Sehingga besar sudut ½ putaran adalah 200g besar sudut ¼ putaran adalah 100gbesar sudut 1/400 putaran adalah 1g Untuk ukuran sudut yang lebih kecil dikenal : • 1g = 10dgr = 10 (dibaca : “10 decigrad”) • 1dgr = 10cgr = 10 (dibaca : “10 centigrad”) • 1cgr = 10 mgr = 10 (dibaca : “10 miligrad”) • 1mgr = 10 dmgr = 10(dibaca : “10 decimiligrad”) SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Kinds of Angle Unit Centesimal System • The instruments for astronomy, peneropongan bintang, teodolit known as different angle unit with both measurement above, this system is known centesimal system. A full rotation is 400g in this system (read “400 grad”). • So the angle size ½ rotation is 200g Angle size ¼ rotation is 100g Angle size 1/400 rotation is 1g For the smaller angle size known as : • 1g = 10dgr = 10 ( read : “10 decigrad” ) • 1dgr = 10cgr = 10 (read : “10 centigrad”) • 1cgr = 10 mgr = 10 (read : “10 miligrad”) • 1mgr = 10 dmgr = 10(read :“10decimiligrad”) SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Konversi Sudut Konversi satuan sudut Satuan derajad = satuan radian = grad 3600 = 2 radian = 400g 1 radian = 57,3250 = 63,694g 10 = 0,0174 radian = 1,11g 1g = 0,90 = 0,0157 radian 1° = 60’ = 3600” detik Contoh:Ubahlah 300 kedalam satuan radian dan grade!ab:300 = 30 x 0,0174 radian = 0,522 radian300 = 30 x 1,11 g = 33,3 g SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Angle Conversion Conversion of angle size Degree Unit = radian unit = grad 3600 = 2 radian = 400g 1 radian = 57,3250 = 63,694g 10 = 0,0174 radian = 1,11g 1g = 0,90 = 0,0157 radian 1° = 60’ = 3600” second Example:Change 300 into radian unit and grade!Answer:300 = 30 x 0,0174 radian = 0,522 radian300 = 30 x 1,11 g = 33,3 g SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Luas dan keliling bangun datar A. Luas daerah bidang beraturan 1. Luas segitiga: A L = ½ A x t Dimana, A = luas alas, t = tinggi C B Contoh: A Hitunglah luas dan keliling bangun disamping. 12 13 C B Jawab:AB = = = = = 24 SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Width and Circumference of flat shape A. The width place arranged plane 1. Triangle Width: A L = ½ A x t Where, A = base wide, t = tall C B Example: A Calculate the width and circumference plane beside. 12 13 C B Answer:AB = = = = = 24 SUDUT DAN BIDANG
A b c t C B a Luas dan keliling bangun datar Lanjutan! Luas segitiga: Keliling segitiga:K = AB + BC+ AC = 13 cm + 12 cm +5 L = == 84 = Jadi,luas segitiga tersebut adalah 84 cm2 dan kelilingnya 56 cm 1.1 Jika segitiga memiliki sisi a, b, c dan tinggi segitiga yang tegak lurus alas adalah t maka: Atau L = Dengan s = Keliling (K)= a + b + c Luas segitiga (L) = SUDUT DAN BIDANG
A b c t C B a The width and circumference of flat plane Next! Triangle width: Triangle circumference:K = AB + BC+ AC = 13 cm + 12 cm +5 L = == 84 = So, the triangle width is 84 cm2 and the circumference is 56 cm 1.1 If the triangle has side a, b, c and triangle high that base right stand is t, then: Or L = With s = Circumference (K)= a + b + c Triangle width (L) = SUDUT DAN BIDANG
I Luas dan keliling bangun datar 2. LUAS PERSEGI • Rumus untuk luas setiap persegi adalah: • Luas = panjang sisi x panjang sisi • L = s x s • L = s2 • Keliling (K) = 4 x sisi SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Width and the circumference of flat plane 2. Square Width • The formula of width in every square is: • Width = side length X side length • L = s x s • L = s2 • Circumference (K) = 4 x side SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Luas dan keliling beliling bangun datar 3.Luas dan keliling lingkaran Rumus untuk luas setiap lingkaran adalah: Luas = πx jari-jari x jari-jari = π x r x r = πr2 Keliling lingkaran = 2 r Dengan π = 3,14 Atau π = SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Width and circumference of flat plane 3.Width and circumference of circle Width Formula in every circle is: Width = πx radius x radius = π x r x r = πr2 Circle circumference = 2 r by π = 3,14 or π = SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Luas dan keliling bangun datar 4. Luas dan keliling persegi panjang Persegi panjang ABCDA p B C D Luas ABCD = p x Keliling ABCD = (2 x p) + ( 2 x ) Contoh:Persegi panjang ABCD dengan panjang 8 cm dan lebar 6 cm. Tentukan luas dan keliling persegi panjang tersebut ! Jawab:Luas persegi panjang = p x = 8 x 6 = 48 Keliling persegi panjang = (2 x p) + (2 x ) = (2 x 8) + ( 2 x 6) = 16 + 12 = 28 SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Width and Circumference of flat plane 4. Width and circumference of rectangular Rectangular ABCDA p B C D Width ABCD = p x Circumference ABCD = (2 x p) + ( 2 x ) Example:Rectangular ABCD, the length is 8 cm and wide is 6 cm. Determine the width and circumference of that rectangular! Answer:Rectangular width = p x = 8 x 6 = 48 Rectangular circumference = (2 x p) + (2 x ) = (2 x 8) + ( 2 x 6) = 16 + 12 = 28 SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Luas dan keliling bangun datar 5. Luas dan keliling Jajargenjang Misal: Jajargenjang memiliki sisi a dan b serta tinggi t b t a Luas Jajargenjang (L)= a x t Keliling Jajargenjang (K)= 2 (a + b) Contoh:Jajargenjang seperti gamabar dibawah . Tentukan luas dan kelilingnya! Jawab: 7 5 4 Luas = 7 cm x 4 cm = 28 cm2Keliling = 2 ( 7 cm + 5 cm) = 2 x 12 cm = 24 cm SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Width and circumference of flat shape 5. Width and circumference of parallelogram Example: Parallelogram has sides a and b and tall t b t a Parallelogram width (L)= a x t Parallelogram circumference (K)= 2 (a + b) Example:Find the width and the circumference of Parallelogram in the picture below! Answer: 7 5 4 Width = 7 cm x 4 cm = 28 cm2Circumference = 2 ( 7 cm + 5 cm) = 2 x 12 cm = 24 cm SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Luas dan keliling bangun datar 6. Luas dan keliling layang-layang Layang-layang ABCD D A C B Luas (L)= ½ (a x b) a b keliling = AB +BC + CD+ DA Contoh: Hitunglah luas layang- layang seperti dibawah jika panlang diagonal AC = 10 cm dan BD= 8 cm. D Jawab: Luas = ½ ( AC x BD) A C = ½ ( 10 cm x 8 cm ) = 40 cm2 B SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Width and circumference of flat shape 6. Width and circumference of kites Kite ABCD D A C B Width (L)= ½ (a xb) a b Circumference= AB+BC+CD+DA Example: Find the width of kite below, if the diagonal line is AC = 10 cm and BD= 8 cm. D Answer: Width = ½ ( AC x BD) A C = ½ ( 10 cm x 8 cm ) = 40 cm2 B SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Luas dan keliling bangun datar 7. Luas dan Keliling Trapesium A B Luas = ½ ( AB + CD) . t t Keliling = AB + BC + CD + DA C D Contoh: Hitunglah luas trapesium pada gambar berikut! D E C 8 10A B 15 Jawab: Luas = ½ ( AB + CD) CE = = = SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Find the trapezium width in the picture! D E C 8 10A B 15 Width and circumference of flat plane 7. Width and circumference of Trapezium A B Width = ½ ( AB + CD) . t t Circumference = AB + BC + CD + DA C D Example: Answer: Width = ½ ( AB + CD) CE = = = SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Segi n beraturan yang panjang = aL = a2 x ctg ½ a a Misal:Luas segi 6 beraturanL = Luas dan keliling bangun datar 8. Luas daerah segi n beraturan SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Side n arranged which has length = aL = a2 x ctg ½ a a Sample:Width of 6 side arrangedL = Width and circumference of flat plane 8. Area width side n arranged SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Luas dan keliling bangun datar 9. Luas daerah elips b Luas daerah elips jika sumbu mayor = a dan sumbu minor = b maka:L = ab a SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Width and circumference of flat plane 9. Area width of ellipse b Area width of ellipse if the axis mayor = a and axis minor = b then:L = ab a SUDUT DAN BIDANG
M I E K G C o1 o2 o3 o4 o5 o6 O 7 A Itu lo! L N B D F H J d Luas Daerah Bidang Tak Beraturan 1. Aturan Trapesoida • Luas pias ABCD = ½ (O1 + O2), demikian pula untuk pias-pias yang lain , sehingga diperoleh pias atau luas total merupakan jumlah dari luas semua pias. Luas = lebar pias . Luas = d . SUDUT DAN BIDANG
M I E K G C o1 o2 o3 o4 o5 o6 O 7 A See! L N B D F H J d Area width in irregular plane 1. Trapesoida Rule • Part width ABCD = ½ (O1 + O2), and so are the other parts, then gotten part or total width as total of all parts width. Width = part width. Width= d . SUDUT DAN BIDANG
E C d A yy y2 y3 B D F Luas Daerah Bidang Tak Beraturan 2. Aturan Mid Ordinat y1, y2, … menunjukkan ordinat ditengah ordinat terdahulu. y1 = , y2 = Luas pias ABCD= y1 x d dan Luas CDEF = y2 x d Luas pias total = y1 . d + y2 . d+ y3 . d+ …. SUDUT DAN BIDANG
E C d A yy y2 y3 B D F Area width of irregular plane 2. Mid Ordinate Rule y1, y2, … shows ordinate in the middle last ordinate. y1 = , y2 = Part width ABCD= y1 x d and width CDEF = y2 x d Total part width = y1 . d + y2 . d+ y3 . d+ …. SUDUT DAN BIDANG
M I E K G 2 C A 5 7 10 8 12 913 L N B D F H J Luas Daerah Bidang Tak Beraturan Contoh soal bidang tak beraturan Tentukan luas bidang tak beraturan disamping dengan aturan:a. Trapesoidab. Mid Ordinat Jawab:a. Aturan Trapesoida L = 2. L =2 . L = 2 . 47 = 94 SUDUT DAN BIDANG
M I E K G 2 C A 5 7 10 8 12 913 L N B D F H J Area width of irregular plane Example of irregular plane Determine irregular plane width beside by rules:a. Trapesoidab. Mid Ordinate Answer:a. Trapesoida Rule L = 2. L =2 . L = 2 . 47 = 94 SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Luas Daerah Bidang Tak Beraturan Lanjutanb. Aturan Mid Ordinat y1 = , y2 = , y3= , y4= y5= , y6 = Luas Total = y1 .d + y2. d+ y3. d + y4. d+ y5. d+ y6. d = 6 . 2 + 8,5. 2 + 8 . 2 + 10 . 2+ 10,5 . 2 + 6 . 2 = 12 + 17 + 16 + 20 + 21 + 12 = 98 SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Area width of irregular plane area Nextb. Mid Ordinate y1 = , y2 = , y3= , y4= y5= , y6 = Total width = y1 .d + y2. d+ y3. d + y4. d+ y5. d+ y6. d = 6 . 2 + 8,5. 2 + 8 . 2 + 10 . 2+ 10,5 . 2 + 6 . 2 = 12 + 17 + 16 + 20 + 21 + 12 = 98 SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Terima kasih Giatlah untuk terus berlatih..berlatih.. dan berlatih… SEKIAN SUDUT DAN BIDANG
Thank you Keep practicing!… The end SUDUT DAN BIDANG