Eukaryotic Cell Structure
250 likes | 593 Vues
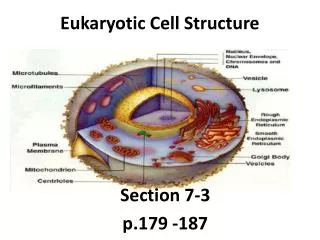
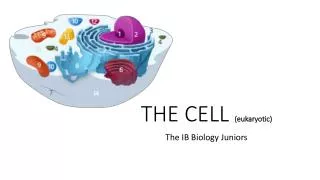
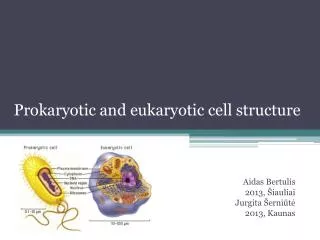
Eukaryotic Cell Structure. Section 7-3 p.179 -187. Group work vs. Cell Parts?. Cellular Boundaries. Plasma membrane Cell wall Fairly rigid structure located outside the plasma membrane that provides additional support + protection Composed of cellulose Is not selectively permeable.

Eukaryotic Cell Structure
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Eukaryotic Cell Structure Section 7-3 p.179 -187
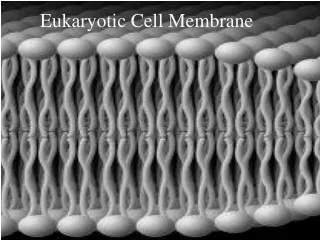
Cellular Boundaries • Plasma membrane • Cell wall • Fairly rigid structure located outside the plasma membrane that provides additional support + protection • Composed of cellulose • Is not selectivelypermeable
The Nucleus + Cell Control • The nucleus is the leader of the eukaryotic cell because… • It contains the directions to make proteins • Proteins are needed by every part of the cell • Chromatin • Strands of DNA • When a cell divides, chromatin condenses into chromosomes
The Nucleus + Cell Control • Nucleolus • Organelle within the nucleus that makes ribosomes
The Nucleus + Cell Control • Ribosomes • Sites where the cell produces proteins according to the directions of DNA • Not membrane bound • Made of RNA + proteins • To make proteins, ribosomes leave the nucleus + enter the cytoplasm • Clear, gelatinous fluid inside a cell • To get to the cytoplasm, ribosomes + translated RNA must leave the nucleus through pores in the nuclear envelope(membrane)
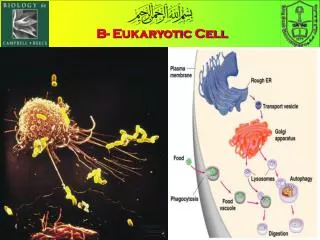
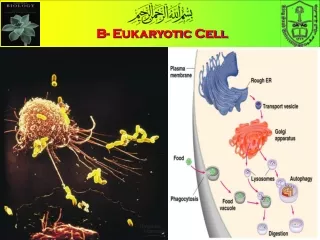
Assembly, Transport, + Storage • Endoplasmic Reticulum • Site of cellular chemical reactions • Large surfacearea for work – folds like an accordion to fit in cell
Assembly, Transport, + Storage • Rough ER • Carries out proteinsynthesis • Proteins made can be used in the plasmamembrane, released from the cell, or transported to other organelles • Smooth ER • Noribosomes • Produces + stores lipids
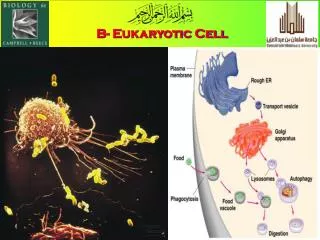
Assembly, Transport, + Storage • Golgi apparatus • Flattened stack of tubular membranes that modifies the proteins • Sorts proteins into packages called vesicles to be sent to the correct destination
Assembly, Transport, + Storage • Vacuole • Membrane-bound compartments used for temporary storage • Used to store: • Food • Enzymes • Othermaterials • Usually not found in animal cells
Assembly, Transport, + Storage • Lysosomes • Organelles that contain digestive enzymes • Can digest: • Excess or worn out organelles • Foodparticles • Engulfed viruses or bacteria • Examples: • Frog + Human Hand
Energy Transformers • Chloroplasts • Cell organelles that capture light energy + convert it to chemical energy • Has a double membrane • Made of thylakoids arranged in stacks called grana surrounded by a fluid called the stroma
Energy Transformers • Belongs to a group known as plastids, which may store: • Starches • Lipids • Otherpigments • Named according to their pigment • Contain the pigment chlorophyll, which gives plant stems + leaves their green color
Energy Transformers • Mitochondria • Organelle in plant + animal cells that transform energy for the cell • Has a double membrane • Inner membrane is folded for a large surface area for chemical reactions to take place • Energy-storing molecules are produced here • May vary in numbers depending on function of cell • Example: a liver cell = 2000 mitochondria/cell
Organelles for Support + Locomotion • Cytoskeleton • Forms the framework of a cell • Composed of microtubules + microfilaments • Maintains shape of cell, support of organelles, + allows materials to move within the cell
Organelles for Support + Locomotion • Centrioles • Organelles found in the cells of animals + protists • Occur in pairs and are made up of microtubules • Play a role in cell division
Organelles for Support + Locomotion • Cilia • Short, numerous projections (look like hairs) • Motion – oars in a row boat/swimmer doing breaststroke
Organelles for Support + Locomotion • Flagella • Longer projections (looks like a tail) • Motion – whips back + forth