Cell Structure & Function
330 likes | 634 Vues
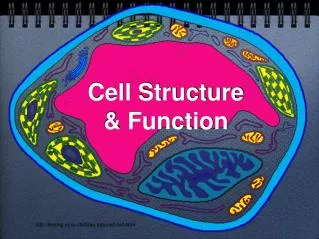
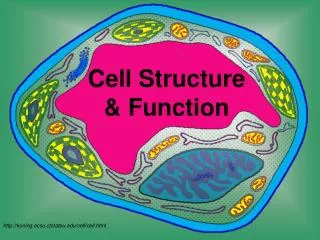
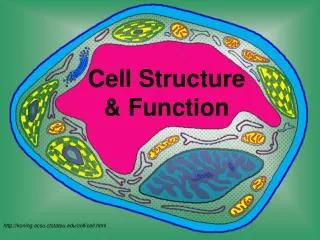
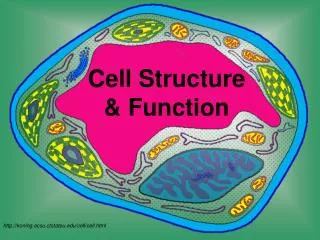
Cell Structure & Function. http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html. Definition of Cell. A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. Cell Theory. Cell Theory 1. All organisms are composed of cells.

Cell Structure & Function
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Cell Structure & Function http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html
Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions.
Cell Theory Cell Theory 1. All organisms are composed of cells. 2. Cells are basic unit of structure and function in living things 3. Cells arise only from pre-existing (OLD) cells.
Two Types of Cells Prokaryotic Eukaryotic
Prokaryote cells are smaller and simpler • Commonly known as bacteria • 10-100 microns in size • Single-celled(unicellular) or • Filamentous (strings of single cells)
These are prokaryote E. coli bacteria on the head of a steel pin.
Prokaryotes • Are generally smaller than eukaryotic cells • Have no nucleus • Carry out all of life’s processes • Ex: bacteria
Eukaryotes • Are generally larger and more complex than prokaryotes • Contain dozens of membrane bound structures that are specialized • Nucleus separates DNA from rest of cell
Exploring the Cell There are 3 major types of microscopes • 1) Light Microscope • Magnifies 40 – 1,000 times depending on objective being used • Used to magnify objects that light can pass through. • Uses slides
2) Scanning Electron Microscope • Uses electrons to illuminate objects (3D view) • Can magnify from 30,000 to 9 million times • Mostly large institutions have them • Costly to own and maintain • Can only be used to look at dead specimens
Transmission Electron Microscope • TEM- thin slices need to be made to have clear images, images are 2-D • Useful for studying internal structures
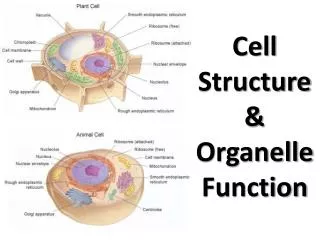
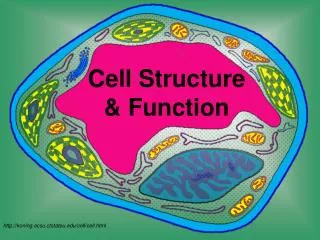
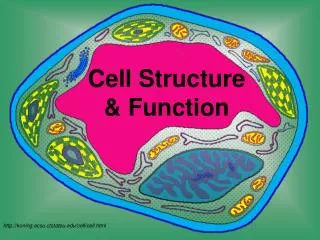
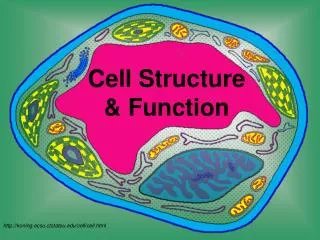
Organelles are membrane-bound cell parts • Mini “organs” that have unique structures and functions • Located in cytoplasm
Cell Structures • Cell membrane • delicate lipid and protein skin around cytoplasm • found in all cells
Nucleus • a membrane-bound sac evolved to store the cell’s chromosomes(DNA) • has pores: holes
Nucleolus • inside nucleus • location of ribosome factory • made or RNA
mitochondrion • makes the cell’s energy • the more energy the cell needs, the more mitochondria it has
Ribosomes • build proteins from amino acids in cytoplasm • may be free-floating, or • may be attached to ER • made of RNA
Endoplasmic reticulum • may be smooth: builds lipids and carbohydrates • may be rough: stores proteins made by attached ribosomes
Golgi Complex • takes in sacs of raw material from ER • sends out sacs containing finished cell products
Lysosomes • sacs filled with digestiveenzymes • digest worn out cell parts • digest food absorbed by cell
Centrioles • pair of bundled tubes • organize cell division
Cytoskeleton • made of microtubules • found throughout cytoplasm • gives shape to cell & moves organelles around inside.
“Typical” Animal Cell http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/NSC/images/cell.gif
Structures found in plant cells • Cell wall • very strong • made of cellulose • protects cell from bursting • glued to other cells next door
Vacuole • huge water-filled sac • keeps cell pressurized • stores starch
Chloroplasts • filled with chlorophyll • turn solar energy into food energy