PROTISTS
210 likes | 466 Vues
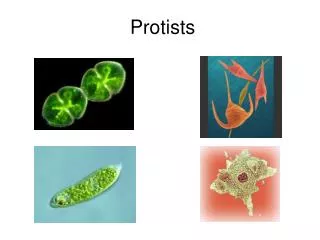
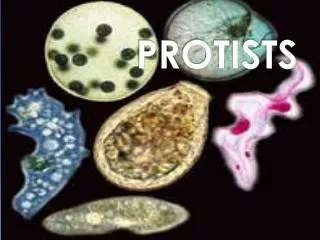
PROTISTS. CHAPTER 19. KINGDOM PROTISTA (most diverse kingdom). All are eukaryotic Unicellular or multi-cellular Microscopic or very large Heterotrophic or autotrophic Plant-like, animal-like or fungus-like . ORIGIN OF PROTISTS. ALGAE. Plant-like protists Autotrophs

PROTISTS
E N D
Presentation Transcript
PROTISTS CHAPTER 19
KINGDOM PROTISTA (most diverse kingdom) • All are eukaryotic • Unicellular or multi-cellular • Microscopic or very large • Heterotrophic or autotrophic • Plant-like, animal-like or fungus-like
ALGAE • Plant-like protists • Autotrophs • Lack true leaves, roots and stems • Most are aquatic • Produce much of the earth’s oxygen • Basis of the aquatic food chain
Spirogyra Volvox Mixed green algae
FUNGAL PROTISTS • Unlike fungi, fungus-like protists are able to move and lack chitin in their cell walls. • Decompose dead materials (saprobes) • Make nutrients available to living organisms Slime molds
PROTOZOA (singular: protozoan) • Animal-like protists • All are unicellular heterotrophs • Move by means of cilia, flagella, pseudopodia • Reproduce asexually (some sexually) • Some are parasitic • sporozoans
AMOEBAS • Protozoans with pseudopodia • “False foot” • Extensions of cytoplasm • Aid in movement & feeding • Shapeless • Most live in salt water • Some have shells • Foraminiferans • radiolarians • Most reproduce asexually • Some form cysts • Survive unfavorable conditions
FLAGELLATES • Protozoans with one or more flagella • Some are parasitic • African Sleeping Sickness
CILIATES • Protozoans with cilia • Salt or fresh water • Includes: • Paramecium • Vorticella • Stentor
SPOROZOANS • Parasitic protozoans • Malaria • Sleeping sickness • Trichimonas • Most produce spores • Reproductive cell • Produces a new organism Plasmodium (causes Malaria)
FUNGUS-LIKE PROTISTS • Slime molds • Grow on rotting leaves or decaying tree stumps & logs • Water molds • Live in water or moist places • Appear as fuzzy, white growths • Downy mildews • Live in water or moist places • Cause plant diseases
DIATOMS ALGAE • Photosynthesizing protists • Fresh or salt water • Contain chlorophyll • Produce more than half the earth’s oxygen • Include: • Red algae • Green algae • Brown algae • Diatoms - contain silica • Euglenoids • Dinoflagellates
RED ALGAE BROWN ALGAE