The Muslim World 600-1250
450 likes | 647 Vues
The Muslim World 600-1250. Read Page 263. Bedouins- Arab Nomads Fertile- producing good crops Oases- Fertile land in desert Nomad-Wanderer Peninsula- Land projecting into water Empire- Lands ruled by a single authority Incense- Substance burned for it’s smell

The Muslim World 600-1250
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Read Page 263 • Bedouins- Arab Nomads • Fertile- producing good crops • Oases- Fertile land in desert • Nomad-Wanderer • Peninsula- Land projecting into water • Empire- Lands ruled by a single authority • Incense- Substance burned for it’s smell • Caravan- A group of desert merchants with Camels • Pilgrims- religious traveler
Stop and think • How did land and climate features influence Bedouin family life?
People relied on family to survive in harsh desert conditions.
How would an increase in trade in Arabia affect what people knew about the world?
Page 264 trade routes • Questions 1 and 2 • How did a trader get from Muscat to Alexandreia ?
Map Answers • Location- It has access to land and sea transportation routes and links three continents • Movement- Because Mecca was the hub for many trade routes, people with different ideas would meet there and exchange ideas.
Page 264 reading • Worship- Treat something like a god, take part in a religious service • Idols- Object worshipped as a god. • Monotheism-Belief in a single god.
About Muhammad • Muhammad was born into the clan of a powerful Mecca Family • Born around 580 AD in Arabian Peninsula • Orphaned at 6 • Taken in by his Uncle, Chief of his clan • Ka’bah- place for worship, sacred, center for trade • At 25, Muhammad became a merchant and trader. He managed shipments for a woman named Khadijah. • He married Khadijah 15 years later (40 years old)
Muhammad Continued • Revelation- In a cave above Mecca. He had a voice speak to him in the form of a man. The voice was the angel Gabriel. • Muhammad was told he was a messenger of Allah • One Message- There is only 1 God • Muslims- Those who surrender to god
What is a Pillar? • a tall vertical structure of stone, wood, or metal, used as a support for a building, or as an ornament or monument.
What is Faith? • Belief or Trust • Trust in God • Set of Beliefs • Loyalty
First Pillar of Islam • Shahadah • Means Faith • It is a brief prayer proclaiming the oneness of God and faith in Islam. • Children memorize the shahada, an action which introduces them into the Islamic community. The shahada simply states: • "There is no God but Allah,and Muhammad is the messenger of Allah."
Second Pillar of Faith • Salah • Daily Prayers • It requires Muslims to pray five times a day toward Mecca. • They must pray at sunset, in the evening, at dawn, at noon, and in the afternoon. • In many Islamic countries, women pray at home. • The leader of a mosque is called an imam, which means "one who walks before." The imam leads the prayer and gives sermons. However, unlike a priest or rabbi, the imam does not hold special authority. Instead, he is chosen by virtue of his dedication and sincerity.
In Muslim countries, the call to prayer is announced from a minaret atop a mosque. A mosque is where Muslims gather to pray, although it is acceptable to pray alone. Minaret Mosque
Third Pillar of Islam • Zakah • Giving to Charity
Fourth Pillar of Islam • Sawm • Fasting • It requires that Muslims fast during the month of Ramadan. • Ramadan is the ninth month of the Islamic calendar. • During this period, food and drink are not allowed between dawn and sunset. After sunset, only light snacks are allowed. • The fast represents a special time of purification and religious devotion. • Alcohol and tobacco are prohibited the entire month. Both the elderly and children are exempt from the fast.
The Festival of Eid-AI-Fitr • When the month of Ramadan ends, the festival Eid-al-fitr is celebrated. • The rejoicing begins on the first day of the tenth month of the Islamic calendar. • Although the month of Ramadan is spent fasting, families begin preparing for the celebration far in advance, sending cards to relatives and preparing gifts. • When the day finally arrives, Muslims attend special morning prayers in the local courtyard or park. • In Muslim countries, Eid-al-fitr is considered a three-day national holiday!
Fifth Pillar of Islam • Hajj • Pilgrimage • Hajj is the pilgrimage to Mecca which every Muslim is expected to make at least once. • A pilgrimage is a journey to a sacred place or shrine. Unlike the other four Pillars, the Hajj can be skipped if it involves great hardships.
Hajj • Over two million Muslims journey to Mecca each year, and each worshipper must follow certain guidelines. First, the men are expected to shave their heads and wear a piece of white garment around the waist and over the shoulder. Women wear the clothing of their native countries, though they must keep their heads covered at all times.
First, the pilgrims walk counter-clockwise seven times around the Ka'bah, either kissing or touching the stone. • Next, they run seven times between the hills of As-Safa and Al-Marwah • After spending the night at the village of Mina, pilgrims take the next step, the wakuf, together. • They meet at the plain of Arafat, about six miles from Mecca. From noon to sunset, they pray quietly. • Next, they climb a small mountain called the Mount of Mercy, and they ask God's forgiveness for their sins. They spend the night at Muzdalifah.
Afterwards, they return to the village of Mina where the ritual of "stoning the devil" takes place. • Followers gather pebbles which they throw at three pillars. This is symbolic of Abraham throwing stones at the Devil who had disturbed his prayers. • On the tenth day, animal sacrifices, sheep or goat, are carried out. • Finally, the pilgrimage again goes seven times around the Ka'bah. • Muslims conduct a four-day celebration upon returning home from Mecca. The Eid al-Adha, or Festival of Sacrifice, marks the end of the pilgrimage and acknowledges the great accomplishment. • Now the male pilgrim has the right to call himself a hajji while the woman is called a hajjah.
A personal Hajj • http://youtu.be/q7q_LcqbvKI
About Islam • http://youtu.be/7GtFf1XFq5I
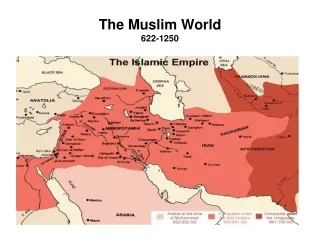
Islam Expands • After Muhammad died in 632, they elected Abu-Bakr • He was a Caliph- a successor or deputy • He used the Qu’ran and Muhammad’s actions to guide their people. • 3 other Caliphs- Umar, Uthman, Ali • Reign is known as Caliphate
Jihad • Jihad means Inner struggle against Evil • OR an armed struggle against unbelievers • Tribes in Arabia gave up Islam, Abu-Bakr used Jihad to encourage them to to follow Islam.
The Caliphate • Abu-Bakr died in 634 • At that point, Muslims controlled all of Arabia • Umar- Muslim armies conquered Syria and lower Egypt. • Uthman and Ali- Continued to spread Islam. • By 750, Muslim empire stretched 6,000 miles from Atlantic Ocean to Indus River
Why did the Muslims win? • They took over Byzantine and Sassanid empires who had been fighting each other for so long, their militaries were exhausted! • The people were tired of being persecuted by Byzantine’s • Islam promoted equality and hope
Reign of Muslims • Abu-Bakr • Uman • Uthman- Murdered • Ali- Uthman’s cousin…. Eventually Murdered in 661 • Family Umayyads came to power
Umayyads • Moved Muslim capital to Damascus • Began to surround themselves with wealth, opposite of former Caliphs • Began the divison of Sunni vs. Shi’a
The Split Sunni Shi’a Means “party of Ali” Smaller group Believed that Ali, the Prophet’s son-in-law should hae succeeded Muhammad Believe that all Muslim rulers should descend from Muhammad Claimed that Sunni have distorted the meaning of passages in the Qur’an • Means “followers of Muhammad’s example” • Followed Umayyads rule • Believed 1st 4 Caliphs were “rightly guided • Claimed that Shi’a have distorted the meaning of passages in the Qur’an
Abassids take control • Take over in 750 • Murdered the remaining members of Umayyad family • One prince got away and set up a Muslim state in south Spain- Al-Andalus
Abbasids • Moved the capital to Baghdad in central Iraq in 762 • Gave them access to key trade routes, gold and information • Bureaucracy- State administrative system
Islam Bureaucracy • Treasury- Money Flow • Army Department • Diplomats to Europe, Africa, Asia • Taxes on Land, imports, exports, and non Muslim’s wealth
Abbasids lasted until 1258 (Sunni’s) • Shi’a’s had Fatimid- Claimed descendent from Muhammad’s daughter Fatima.