Scientific Method
130 likes | 259 Vues
The scientific method is a systematic approach used to explore questions about our world. It generally starts with formulating a question based on observations. Following this, a hypothesis is proposed, and an experiment is conducted to test this hypothesis. Results are then analyzed to draw conclusions, which are communicated effectively. Key components include identifying variables such as independent, dependent, and controlled variables. This method ensures that findings are based on reliable data, helping to advance knowledge in various scientific fields.

Scientific Method
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Scientific Method What is it? How does it work? Mrs. Miller
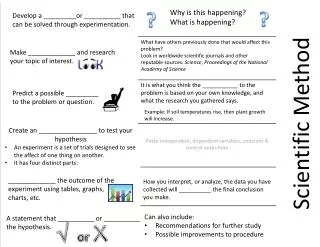
What is the scientific method? • A process used to find answers to questions about the world around us. • There are several versions of the scientific method, some have more steps than others. • All versions begin with a question to be answered, and provide an organized method for conducting and analyzing an experiment.
What steps do I follow? • Question • Hypothesis • Experiment • Analyze Data • Conclusion • Communicate Results
Question • Based on observations you have made that addresses a problem you want to investigate. • What do you want to know or explain? • Must be testable. Examples: Does salt effect the rate in which water boils? Does the type of soda effect the reaction of Mento’s candy? • Does your question make sense? Is it confusing?
Hypothesis Prediction • What do you think will happen? • Possible answer to your question. • Guess the outcome of the experiment. • Educated guess based on observations and your prior knowledge of the topic. • Rewrite your prediction using an If…Then…format. (If…comes from the question, Then…comes from your prediction) • Examples: Ifsalt effects the rate in which water boils, then the water with salt will boil faster than water without salt. Ifcaffine effects the reaction of soda and mentos, thencaffine-free soda will have a smaller explosion. Hypothesis
Experiment Materials & Procedures • List ALL materials needed to test hypothesis. • What steps will you follow to find the answer? Do not use personal pronouns such as I, me, we, etc. • BE SPECIFIC! Label steps using 1, 2, 3, etc. • Would someone else be able to follow your directions? • How will you collect your data? How will you measure results? • Address any safety issues or concerns. • Gather materials • Follow steps in your procedures • Record observations • Collect Data Perform Experiment
Analyze Data • How can you study the data you collected? • Is your data quantitative or qualitative? • Make a graph. • Is the data reliable? Be careful not to make inferences about the data.
Conclusion • Did your results support your hypothesis? • My hypothesis was correct/incorrect because…(use data to support explanation) • Explain any unexpected results.
Communicate Results • Write a summary of what you learned during your experiment and address your results. • Be sure to write in complete sentences. • This can usually be done in 3 paragraphs: • Attention grabber, why you chose the topic, state hypothesis • Summarize the procedures and explain the data collected • Conclusion. What did you learn? Does this lead you to another question?
Variables • Any factor, trait, or condition that can affect the outcome of an experiment • Experiments usually have 3 types: independent, dependent, and controlled
Controlled Variables Meaning • Things to remain constant • What I keep the same • Same size soda bottle • Same amount of Mento’s candy • Same temperature Examples • Same amount of water • Same starting temperature • Same heating surface
Independent Variable Meaning • Something changed by the scientist • What I change • Manipulated variable • Change the type of soda • Caffine-free vs. caffine Examples • Add salt
Dependent Variable Meaning • Response to change • What I observe or measure • Responding variable • Height of the reaction explosion Examples • How fast the water boils