Spatial Data
240 likes | 585 Vues
Spatial Data. Chapter 2. What is a model?. Simplified view of the real world. GIS Data Model. The GIS Data Model: Purpose.

Spatial Data
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Spatial Data Chapter 2
What is a model? • Simplified view of the real world
The GIS Data Model:Purpose • allows the geographic features in real world locations to be digitally represented and stored in a database so that they can be abstractly presented in map (analog) form, and can also be worked with and manipulated to address some problem
Information and data • Data • Collection of facts • Information • Data with meaning and context
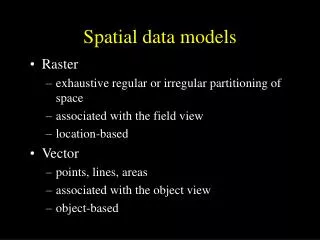
Three modes of data • Temporal • Thematic • Spatial Lat 43° Long 81°
What makes a good map? • Establish purpose • Define the scale • Select the features • How represented • Generalize • Map projection • Spatial referencing • annotate
Establish Purpose • What do we want to portray? • Happy Valley • Help orient people • Decide how to spend time
Scale • Ratio • 1:5000 • Verbal • 1 cm represents 50 m • Graphic Note that: Large Scale maps -Hamilton -1:10,000 Small Scale Maps -Canada -1:1,00,000
Spatial Entities • Points • elevations • Lines • elevations • Areas • Island and adjacent polygons • Dependent on scale • Small scale city a point • Large scale city a area
Generalization • All spatial data are a generalization of real world
Cartographic Generalization • Selection • Simplification • Displacement • Smoothing and enhancement
Topology • Objects do not change when • Stretched or bend • Independent of coordinate system • Three elements • Adjacency • Containment • Connectivity
Categorical (name): nominal no inherent ordering land use types, county names ordinal inherent order road class; stream class often coded to numbers eg SSN but can’t do arithmetic Numerical Known difference between values interval No natural zero can’t say ‘twice as much’ temperature (Celsius or Fahrenheit) ratio natural zero ratios make sense (e.g. twice as much) income, age, rainfall may be expressed as integer [whole number] or floating point [decimal fraction] Attribute data types Attribute data tables can contain locational information, such as addresses or a list of X,Y coordinates. ArcView refers to these as event tables. However, these must be converted to true spatial data (shape file), for example by geocoding, before they can be displayed as a map.
Data Acquisition • Five Essential Functions of a GIS • Data Acquisition • Preprocessing • Data Management • Manipulation and Analysis • Project Generation • Data Acquisition and Preprocessing • Biggest part-80% of time and cost • Two types data • Spatial • Non-spatial (attributes)
Collection Methods • Field data collection • Land surveys • Soil sampling • Tree inventory • Tracking wild animals • Census Data • Remote Sensing • Surveying or GPS • LIDAR • Donated, traded or bought • Paper or digital
Methods of Collecting Data • Existing data, • downloads from field • Keyboard • COGO
Methods of Gathering data • Digitizing and scanning Scanner Raster to Vector Digitizing
ESRI, Inc., Redlands, CA clear market leader with about a third of the market originated commercial GIS with their ArcInfo product in 1981 privately owned by Jack Dangermond, a legend in the field Strong in gov., education, utilities and business logistics MapInfo, Troy N.Y. Aggressive newcomer in early 1990s, but now well-established. Strong presence in business, especially site selection & marketing, and telecom Intergraph (Huntsville, AL) origins in proprietary CAD hardware/software Older UNIX-based MGE (Modular GIS Environment) evolved from CAD “new generation” GeoMedia product based on NT is now their main focus strong in design, public works, and FM (facilities management) Bentley Systems (Exton, PA) MicroStation GeoGraphics, originally developed with Intergraph, is now their exclusive and main product.. Strong in engineering; advertises itself as “geoengineering” Autodesk (San Rafael, CA) Began as PC-based CAD, but now the dominant CAD supplier First GIS product AutoCAD Map introduced in 1996 Primarily small business/small city customer base Software for GIS: The Main Players The main two “pure GIS” companies.
Software for GIS: other players • Raster GIS • ERDAS/Imagine • long established leader • acquired by Leica Geosystems in 2001 • ER MAPPER • aggressive newcomer originating in Australia • Envi, • relative newcomer, radar specialization • acquired by Kodak in 2000 • PCI--Geomatica • long-term Canadian player • CARIS • newer Canadian entry • GRASS (Rutgers Univ.) • Classic old-timer originally developed by US Army Construction Engineering Research Lab(CERL) in Champaign, IL; • army ended dev. & support in 1996 but assumed by Baylor University. • IDRSI (Clark Univ) • pioneering, university-developed package Vector GIS • Smallworld Systems (Englewood, CO) • first to use OO (early ‘90s), but failed to compete as established vendors did same • Purchased by GE in 2000 • emphasis on FM & utilities • Manifold (CDA International Corp): • low cost, but low market share • Maptitude(Caliper Corp, Newton, MA): • another low cost one
ESRI Product Line-up: ArcGISclient products (Fall 2004) ArcReader (“adobe acrobat” for maps) & ArcExplorer (spatial data viewer) • Free viewers for geographic data. ArcGIS 9.x Desktop: two primary modules (MS NT/2000/XP only) • ArcMap: for data display, map production, spatial analysis, data editing • ArcCatalog: for data management and preview ArcToolbox, for specialized data conversions and analyses, available as a window in both Available capabilities within these modules are “tiered” • ArcView: viewing, map production, spatial analysis, basic editing • ArcEditor: ArcView, plus specialized editing • ArcInfo: ArcView & ArcEditor plus special analyses and conversions Extensions: for special apps.: Spatial Analyst, 3D Analyst, Geostatistics, Business Analyst, etc. ArcObjects: build specialized capabilities within ArcMap or ArcCatalog using VB for Applications ArcGIS Workstation (for UNIX and MS NT/2000/XP) • the old command line ArcInfo 7.1 ArcGIS Engine (MS NT/2000/XP) • Set of embeddable GIS components (ArcObjects software objects) for use in building custom applications • Runs under Windows, Unix and Linux, with support for Java, C++, COM and .NET • Replaces MapObjects which were based upon a previous generation of GIS objects Notes: ArcGIS 8 released 2000 to integrate two previous standalone products: ArcView and ArcInfo ArcGIS 9 released 2004 providing the full capability that should have been in ArcGIS 8!!! --full support for all data types (coverages, shapefiles, geodatabases) --full support for all previous geoprocessing analyses --Modelbuilder for scripting and repetitive processing --ArcEngine for building custom applications ArcView 3.3 (the predecessor to ArcGIS 8.x) the only GUI option for UNIX.
ESRI Product Line-up: ArcGISserver products (Fall 2004) SDE (Spatial Database Engine) • middleware to support spatial data storage in standard DBMS • Supports all major industry databases: • Oracle, SQL-Server, IBM DB2, Ingres ArcGIS Server • Permits the creation of server-based GIS services using any ArcGIS capability • Provides GIS capabilities to a user without a desktop GIS system: • inward focus—user goes to server ArcIMS • Software to develop Internet server-based mapping and basic analysis • Provides maps to the user without a desktop GIS system : • outward focus—gives user a map ArcGIS Services • Server based applications built and operated by ESRI or its partners and made available on the Internet for subscription • Normally charged on a “per transaction” basis, but can be flat fee • presumably built using ArcGIS Server
ArcInfo ArcEditor ArcView ArcExplorer Browser Internet ArcGIS System Consistent interface Increasing capability Clients c:\ ArcGIS Workstation $ ArcMap ArcCatalog ArcToolbox ArcMap ArcCatalog ArcToolbox ArcMap ArcCatalog ArcToolbox ArcServer Services ArcEngine/ ArcObjects Application Development & Customization ArcIMS Services ArcSDE Services ArcPad Databases Multi-user Geodatabases (in Oracle, SQL Server, IBM DBII, etc) Files (Personal Geodatabase, Shapefiles, Coverages, Grids, tins, etc) Source: ESRI with mods. Handheld/Wireless