Introduction to Electrical Concepts: Charge, Voltage, Current, Joule
90 likes | 163 Vues
Learn about key electrical concepts including charge, voltage, current, and Joule, and how they relate to each other. Understand Coulomb, units of charge, and the flow of energy in a circuit in this informative guide.

Introduction to Electrical Concepts: Charge, Voltage, Current, Joule
E N D
Presentation Transcript
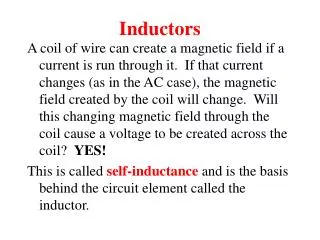
When two materials of opposite charge are connected by a conductor, the charges travel from one material to the other
Coulomb: Unit of charge. Equal to the amount of charge on 6.24*10^18 electrons. Or, the number of electrons in ~25microns of wire. [10^(-6)]m (C) This can be thought of as the amount of water a hose can carry in a small sliver of the hose.
Voltage: Difference in electric potential energy between two points in space or in a wire. Expressed in Joules per Coulomb. (J/C) Voltage can be thought of as the pressure in a hose pushing the water along. Remember Joules are a measure of “energy”.
Joule: Unit of energy. Expressed in Newton meters, i.e. the energy expended in applying one Newton of force through one meter. (J) Lift a quarter pound one meter.
Current: Motion of charges through a wire. Specifically, the number of electrons which pass through a cross section of wire per second. (C/S) Analogous to the amount of water flowing through a hose per second.
Watts: The amount of energy per second passing through a wire. (J/S)