3.1 Exponential Functions and their Graphs
110 likes | 298 Vues
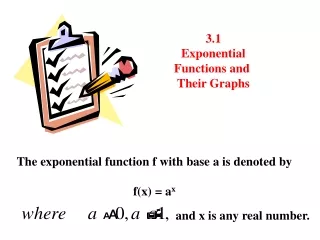
3.1 Exponential Functions and their Graphs. Students will recognize and evaluate exponential functions with base a. Students will graph exponential functions. Students will recognize, evaluate, and graph exponential functions with base e.

3.1 Exponential Functions and their Graphs
E N D
Presentation Transcript
3.1 Exponential Functions and their Graphs Students will recognize and evaluate exponential functions with base a. Students will graph exponential functions. Students will recognize, evaluate, and graph exponential functions with base e. Students will use exponential functions to model and solve real-life problems.
Example 1 Use a calculator to evaluate each function at the indicated value of x. a. b. c.
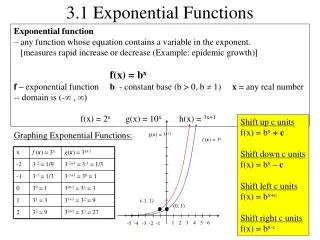
y 2 x –2 Example 2 In the same coordinate plane, sketch the graph of each function by hand. • b.
y 2 x –2 Example 3 In the same coordinate plane, sketch the graph of each function by hand. • b.
y 2 x –2 Example 4 Each of the following graphs is a transformation of • b. c. d.
Compound Interest Annually Compounded Interest: = Accumulated amount after n years P = principle (invested amount) r = the interest rate in decimal form (5% = .05) n = time in years Compounded Interest m times per year: m = # of times per year interest is compounded (i.e. m = 1 is yearly, m = 12 is monthly, m = 365 is daily) Compounded Interest continuously: e is the natural number
Example: Invest $1 for 1 year at 100% Consider how m affects the accumulated amount: Yearly m = 1 Bi-annually m = 2 Monthly m = 12 Daily m = 365 Hourly m = 8760 Example 5
y 2 x –2 Example 6 Use a calculator to evaluate the function where: • b. c.
Example 7 A total of $12000 is invested at 7% interest. Find the balance after 10 years if the interest is compounded a) quarterly b) continuously a) b)