Efficient Mesostructure Reconstruction from Specularity Using Coded Illumination Techniques
200 likes | 322 Vues
This paper presents a novel approach to acquiring mesostructure normal maps through coded illumination, emphasizing efficiency and cost-effectiveness. By leveraging specularity and binary light patterns, we propose a method that operates in O(log N) time complexity, allowing for faster processing compared to traditional O(N) methods. This technique is particularly effective for capturing sharp specular highlights, despite its limitations to specular mesostructures. The setup utilizes inexpensive and controllable light sources, paving the way for future enhancements in 3D reconstruction and illumination techniques.

Efficient Mesostructure Reconstruction from Specularity Using Coded Illumination Techniques
E N D
Presentation Transcript
MesostructurefromSpecularityUsingCodedIllumination Yannick Francken, Tom Mertens, Jo Gielis, Philippe Bekaert Expertise Centre for Digital Media Hasselt University (Belgium) {yannick.francken, tom.mertens, philippe.bekaert}@uhasselt.be jo.gielis@student.uhasselt.be
Goal Acquire mesostructure’s normal map Mesostructure Normal map
Previous Work Shape from shading [Horn75, Zhang99]
Previous Work … Shape from shading [Horn75, Zhang99] Photometric stereo [Woodham89, Ikeuchi92]
Previous Work Shape from shading [Horn75, Zhang99] Photometric stereo [Woodham89, Ikeuchi92] Structured light [Boyer87, Scharstein03]
Previous Work … • Shape from shading [Horn75, Zhang99] • Photometric stereo [Woodham80, Ikeuchi92] • Structured light [Boyer87, Scharstein03] • Mesostructure scanning • Mesostructure from Specularity[Chen06]
Previous Work • Shape from shading [Horn75, Zhang99] • Photometric stereo [Woodham80, Ikeuchi92] • Structured light [Boyer87, Scharstein03] • Mesostructure scanning • Mesostructure from Specularity[Chen06] • Rapid Acquisition of Specular and Diffuse Normal Maps from Polarized Spherical Gradient Illumination [Ma07]
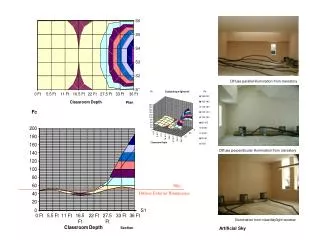
Previous Work Mesostructure from specularity[Chen06] Setup Image captures
Previous Work Mesostructure from specularity[Chen06] Law of reflection Detecting specularities V = 2(NTL)N - L L V N
Observation A specularity is caused by onelight source 1011 1100 10 100 1001 1 1101 1010 1001 1110 1000 1111 O(log N) instead of O(N) image captures!
Setup M x N light sources log2M + log2N + 1 patterns • Screen-camera setup • Screen as cheap controllable light source [Zongker96, Tarini05, Clark05, Funk06] • Calibration [Hartley04, Tarini05, Francken06, Funk06] • Binary coded light patterns • Gray code
Limits Only specularmesostructures Sharp specular highlights
Limits • Only specularmesostructures • Sharp specular highlights • Limited cone of normals • Planar display
Limits • Only specularmesostructures • Sharp specular highlights • Limited cone of normals • Planar display • Self shadowing
Conclusion • Efficient • O(log N) instead of O(N) • Longer exposure times less noise • Inexpensive setup • Only controllable binary light source
Future Work Smoothness constraints Using specularand diffuse components Surface adaptive patterns Colored patterns instead of binary Hemispherical light source
Questions? yannick.francken@uhasselt.be http://research.edm.uhasselt.be/~yfrancken • Summary • Efficient • O(log N) instead of O(N) • Longer exposure times less noise • Inexpensive setup • Only controllable binarylight source