Body Organization
1.02k likes | 1.22k Vues
2. Body Organization. Multimedia Directory. Slide 22 Muscle Contraction Animation Slide 33 Neuron Animation Slide 41 Cardiovascular System Animation Slide 44 Lymphatic System Animation Slide 46 Respiratory System Animation Slide 48 Digestive System Animation

Body Organization
E N D
Presentation Transcript
2 Body Organization
Multimedia Directory Slide 22 Muscle Contraction Animation Slide 33 Neuron Animation Slide 41 Cardiovascular System Animation Slide 44 Lymphatic System Animation Slide 46 Respiratory System Animation Slide 48 Digestive System Animation Slide 50 Urinary System Animation Slide 52 Female Reproductive System Animation Slide 54 Male Reproductive System Animation Slide 56 Endocrine System Animation Slide 58 Nervous System Animation Slide 60 Eye Anatomy Animation Slide 62 Ear Anatomy Animation
Body Organization At A Glance The body is organized into levels Cells Tissues Organs Systems Body
Body Organization At A Glance Each level is built from the one below it Body as a whole is composed of systems A system is composed of organs An organ is composed of tissues A tissue is composed of cells
Body Organization Combining Forms • abdomin/o abdomen • adip/o fat • anter/o front • brachi/o arm • cardi/o heart • caud/o tail • cephal/o head • cervic/o neck
Body Organization Combining Forms • chondr/o cartilage • crani/o skull • crin/o to secrete • crur/o leg • cyt/o cell • dermat/o skin • dist/o away from • dors/o back of body
Body Organization Combining Forms • enter/o small intestine • epitheli/o epithelium • gastr/o stomach • glute/o buttock • gynec/o woman • hemat/o blood • hist/o tissue • immun/o protection
Body Organization Combining Forms • infer/o below • laryng/o larynx • later/o side • lumb/o loin • lymph/o lymph • medi/o middle • muscul/o muscle • nephr/o kidney
Body Organization Combining Forms • neur/o nerve • ophthalm/o eye • ot/o ear • pelv/o pelvis • peritone/o peritoneum • pleur/o pleura • poster/o back • proct/o rectum and anus
Body Organization Combining Forms • proxim/o near to • pub/o genital region • pulmon/o lung • rhin/o nose • spin/o spine • super/o above • thorac/o chest • ur/o urine
Body Organization Combining Forms • vascul/o blood vessel • ventr/o belly • vertebr/o vertebra • viscer/o internal organ
Body Organization Suffixes • -ac pertaining to • -al pertaining to • -ar pertaining to • -ary pertaining to • -atic pertaining to • -iac pertaining to • -ic pertaining to • -ior pertaining to
Body Organization Suffixes • -logy study of • -ose resembling
Body Organization Prefixes • endo- within • epi- above • hypo- under • peri- around • retro- behind
Levels of Body Organization Cells form tissues Tissues form organs Organs form systems Systems form whole body
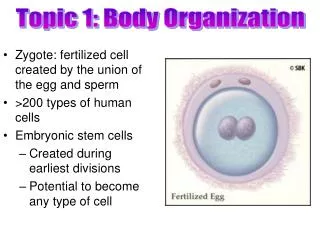
Cells Cyt/o + -logy = cytology • cyt/o + -logy = cytology • The study of cells and their function
Cells • Fundamental unit of life • Has all properties of being alive • Responds to stimuli • Engages in metabolic activity • Reproduces itself • All tissues and organs in body formed of cells
Cells • Individual cells perform functions for body • Reproduction • Hormone secretion • Energy production • Excretion
Cells • Special cells carry out very specific functions • Muscle contraction • Electrical impulse transmission
Cells • Cells come in different sizes and shapes • But all cells,at some point of their life cycle, have • Nucleus • Cytoplasm • Cell membrane
Muscle Contraction Animation Click on the screenshot to view an animation showing muscle contraction. Back to Directory
Figure 2.1Examples of four different types of cells from the body illustrating the differences in shape.
Tissues hist/o + -logy = histology • hist/o -logy = histology • The study of tissue • Formed when like cells are grouped together to perform an activity • Four types of tissue • Muscle tissue • Epithelial tissue • Connective tissue • Nervous tissue
Muscle Tissue • Produces movement in body by contracting • Composed of individual muscle cells called muscle fibers
Muscle Tissue • Three basic types of muscles • Skeletal muscle • attached to bones • Smooth muscle • internal organs like intestine and uterus • Cardiac muscle • only in the heart
Figure 2.2This figure shows the appearance of different types of tissues and their location within the body.
Epithelial Tissue • Known as epithelium • Found as lining for internal organs and covering for the skin • Close-packed cells that function to: • Form a protective barrier – skin • Absorb – lining of intestine • Secrete – sweat glands • Excrete wastes – kidney tubules
Figure 2.2This figure shows the appearance of different types of tissues and their location within the body.
Connective Tissue • Supports and protects • Function depends on location • Many different forms • Adipose • Bone • Cartilage • Tendons
Figure 2.2This figure shows the appearance of different types of tissues and their location within the body.
Nervous Tissue • Composed of cells called neurons • Forms the brain, spinal cord, and nerves • Allows for conduction of electrical impulses between brain and rest of the body
Neuron Animation Click on the screenshot to view an animation showing neurons. Back to Directory
Figure 2.2This figure shows the appearance of different types of tissues and their location within the body.
Organs • Composed of several types of tissue • Work together as a unit • Perform special functions • Example: stomach contains: • Muscle fibers • Nerve tissues • Epithelial tissue
Systems • Composed of several organs working together in coordinated manner • Perform complex functions • Example: stomach plus other digestive organs including mouth, esophagus, liver, pancreas, small intestine, and colon work together to break down, digest, and absorb food
Integumentary System • Two-way barrier and temperature regulation • Organs • Skin • Hair • Nails • Sweat glands • Sebaceous glands
Musculoskeletal System – Skeleton • Supports and protects body, forms blood cells, stores minerals • Organs • Bones • Joints
Musculoskeletal System – Muscles • Produce movement • Organs • Muscles
Cardiovascular System • Pumps blood to transport nutrients, oxygen, and wastes • Organs • Heart • Arteries • Veins
Cardiovascular System Animation Click on the screenshot to view an animation of the cardiovascular system. Back to Directory
Blood (Hematic System) • Transports oxygen, protects, and controls bleeding • Organs • Plasma • Erythrocytes • Leukocytes • Platelets
Lymphatic System • Protects body • Organs • Lymph nodes • Lymphatic vessels • Spleen • Thymus gland • Tonsils
Lymphatic System Animation Click on the screenshot to view an animation of the lymphatic system. Back to Directory
Respiratory System • Obtains oxygen and removes carbon dioxide • Organs • Nasal cavity • Pharynx • Larynx • Trachea • Bronchial tubes • Lungs
Respiratory System Animation Click on the screenshot to view an animation of the respiratory system. The animation may take a moment before playing. Back to Directory
Gastrointestinal System • Ingest, digest, and absorb nutrients • Organs • Oral cavity • Pharynx • Esophagus • Stomach • Small intestine • Colon • Liver & gallbladder • Pancreas
Digestive System Animation Click on the screenshot to view an animation of the digestive system. Back to Directory
Urinary System • Filters waste and removes from body • Organs • Kidneys • Ureters • Urinary bladder • Urethra
Urinary System Animation Click on the screenshot to view an animation of the urinary system. The animation may take a moment before playing. Back to Directory