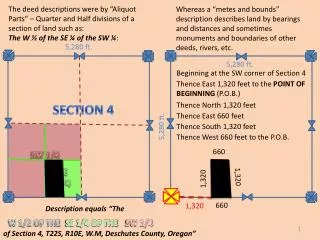
Section 18-4
300 likes | 549 Vues
Section 18.4 Neutralization. Write chemical equations for neutralization reactions. Explain how neutralization reactions are used in acid-base titrations. Compare the properties of buffered and unbuffered solutions.

Section 18-4
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Section 18.4 Neutralization • Write chemical equations for neutralization reactions. • Explain how neutralization reactions are used in acid-base titrations. • Compare the properties of buffered and unbuffered solutions. In a neutralization reaction, an acid reacts with a base to produce a salt and water. Section 18-4
Acids Neutralize Bases Neutralization reactions ALWAYSproduce a saltandwater. HCl + NaOH HCl + NaOH NaCl+H2O H2SO4 + 2NaOH Na2SO4+2H2O H2SO4 + 2NaOH 2HNO3 + Mg(OH)2 2HNO3 + Mg(OH)2 Mg(NO3)2+2H2O
Bases Neutralize Acids Milk of Magnesia contains magnesium hydroxide, Mg(OH)2, which neutralizes stomach acid, HCl. 2 HCl + Mg(OH)2 MgCl2 + 2 H2O
Reactions Between Acids and Bases (cont.) Section 18-4
Reactions Between Acids and Bases (cont.) • Titrationis a method for determining the concentration of a solution by reacting a known volume of that solution with a solution of known concentration. Section 18-4
Reactions Between Acids and Bases (cont.) • In a titration procedure, a measured volume of an acid or base of unknown concentration is placed in a beaker, and initial pH recorded. • A buret is filled with the titrating solution of known concentration, called a titrant. Section 18-4
Reactions Between Acids and Bases (cont.) • Measured volumes of the standard solution are added slowly and mixed into the solution in the beaker, and the pH is read and recorded after each addition. • The process continues until the reaction reaches the equivalence point, which is the point at which moles of H+ ion from the acid equals moles of OH– ion from the base. • An abrupt change in pH occurs at the equivalence point. Section 18-4
Standard solution : solution whose concentration is accurately known Known volume, unknown concentration
Reactions Between Acids and Bases (cont.) Section 18-4
Reactions Between Acids and Bases (cont.) • Chemical dyes whose color are affected by acidic and basic solutions are called acid-base indicators. Section 18-4
Reactions Between Acids and Bases (cont.) • An end point is the point at which an indicator used in a titration changes color. • An indicator will change color at the equivalence point. Section 18-4
Salt Hydrolysis • In salt hydrolysis, the anions of the dissociated salt accept hydrogen ions from water or the cations of the dissociated salt donate hydrogen ions to water. Section 18-4
Salt Hydrolysis (cont.) • Salts that produce basic solutions • KF is the salt of a strong base (KOH) and a weak acid (HF). KF(s) → K+(aq) + F–(aq) Section 18-4
Weak Acid/Strong Base Titration A solution that is 0.10 M CH3COOH is titrated with 0.10 M NaOH Endpoint is above pH 7
Salt Hydrolysis (cont.) • Salts that produce acidic solutions • NH4Cl is the salt of a weak base (NH3) and strong acid (HCl). • When dissolved in water, the salt dissociates into ammonium ions and chloride ions. NH4Cl(s) → NH4+(aq) + Cl–(aq) Section 18-4
Strong Acid/Weak Base Titration A solution that is 0.10 M HCl is titrated with 0.10 M NH3 Endpoint is below pH 7
Salt Hydrolysis (cont.) • Salts that produce neutral solutions • NaNO3 is the salt of a strong acid (HNO3) and a strong base (NaOH). • Little or no salt hydrolysis occurs because neither Na+ nor NO3– react with water. Section 18-4
Strong Acid/Strong Base Titration Endpoint is at pH 7 A solution that is 0.10 M HCl is titrated with 0.10 M NaOH
Strong Acid/Strong Base Titration A solution that is 0.10 M NaOH is titrated with 0.10 M HCl Endpoint is at pH 7 It is important to recognize that titration curves are not always increasing from left to right.
Buffered Solutions • Buffersare solutions that resist changes in pH when limited amounts of acid or base are added. • Ions and molecules in a buffer solution resist changes in pH by reacting with any hydrogen ions or hydroxide ions added to the buffered solution. Section 18-4
Buffered Solutions (cont.) • A buffer is most effective when the concentrations of aconjugate acid-base pair are equal or nearly equal. Section 18-4
Buffered Solutions (cont.) • Additional H+ ions react with the base of the conjugate acid-base pair and additional OH- ions react with the acid, but the pH of the solution changes little. • The amount of acid or base that a buffer solution can absorb without a significant change in pH is called the buffer capacity. Section 18-4
Titration of an Unbuffered Solution A solution that is 0.10 M CH3COOH is titrated with 0.10 M NaOH
Titration of a Buffered Solution A solution that is 0.10 M CH3COOH and 0.10 M NaCH3COO is titrated with 0.10 M NaOH
Comparing Results Buffered Unbuffered
Comparing Results Unbuffered Buffered • In what ways are the graphs different? • In what ways are the graphs similar?
A B C D Section 18.4 Assessment In a neutralization reaction, an acid and base react to form: A.salt and oxygen gas B.salt and ammonia C.salt and water D.precipitate and water Section 18-4
A B C D Section 18.4 Assessment Solutions that resist changes in pH are called ____. A.titrants B.salts C.conjugate pairs D.buffers Section 18-4