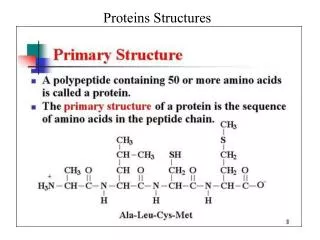
In-Depth Insights into Enzyme Structure, Function, and Kinetics
170 likes | 306 Vues
This article explores the intricate world of enzymes, focusing on their defined 3D structures and catalytic mechanisms. Highlights include enzyme-catalyzed reactions, types of enzyme assays, and the significance of the Michaelis-Menten model in enzyme kinetics. We delve into key metrics such as Km and kcat, their meanings in substrate binding, and the basis of catalytic efficiency. The paper also discusses enzyme inhibition strategies, including reversible and irreversible mechanisms, and the use of transition state analogues for inhibitor design.

In-Depth Insights into Enzyme Structure, Function, and Kinetics
E N D
Presentation Transcript
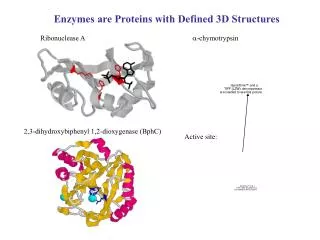
Enzymes are Proteins with Defined 3D Structures Ribonuclease A a-chymotrypsin 2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl 1,2-dioxygenase (BphC) Active site:
Enzyme Catalysis: What Enzymes Can & Can’t Do Acid-catalysed reaction Enzyme-catalysed reaction
Types of Enzyme Assay 1 Unit = activity required to convert 1 µmole S to P per minute
Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer Assay for MurG MurG N-dansyl lipid I Ex 290 nm 340 nm 0.2 M Tris pH 7.5, 10 mM MgCl2, 0.2% CHAPS 2.7 µM Fl UDPGlcNAc, 3.0 µM dansyl lipid I + 3.0 µg E. coli MurG Em 500 nm J.J. Li and T.D.H. Bugg,Chem. Commun., 182-183 (2004).
Enzyme Purification Preparation of Cell Extract SDS-PAGE gel Purification Table
Michaelis-Menten Model for Enzyme Kinetics Kinetic Model
What do Km & kcat really mean? kcat - turnover number 1st order rate constant (units s-1) for turnover at high [S] Km - Michaelis constant Measure of affinity of Substrate binding BUT not the same as Kd! kcat/Km - catalytic efficiency 2nd order rate constant (units M-1 s-1) for turnover at low [S]
Transition State Analogues for Ligase MurM Inhibitor design: mimic tetrahedral transition state: Transition state Phosphonate analogue
Inhibition by 2’-deoxyadenosine analogue IC50 = 100 µM
Enzyme Inhibition - Irreversible Inhibition e.g. serine protease inhibitor DFP
Pre-Steady State Kinetics —— Application to C-C Hydrolase MhpC Data Simulation • Single Exponential Mode • A = A0 +A1 exp (-k1t) • Double Exponential Mode • A= A0 + A1 exp (-k1t) + A2exp (-k2t) • Triple Exponential Mode • A= A0 + A1 exp (-k1t) + A2exp (-k2t) + A3exp (-k3t)
Fit with single exponential (1 step) Fit with double exponential (2 step)
pH=7.0 A1 (×103) k1 (s-1) A2 (×103) k2 (s-1) 317nm (dienol S) Wild type. 145.6 153.2 H263A 96.6 0.34 78.5 0.040 270nm (dienol P) Wild type. -131 144 -117 18 H263A -146 0.223 -55.4 0.037 Analysis of His263Ala Mutant • Kinetic Parameters • Pre-steady state Kinetic Parameters 0.04s-1 0.34s-1 H263 is involved in both ketonization and C-C cleavage !
20ms 317nm 200ms 317nm 200s 317nm 140s-1 0.02s-1 3.1s-1 Analysis of Ser110Ala Mutant • Kinetic Parameters • Pre-steady state Kinetic