The Atomic Model
130 likes | 274 Vues
The Atomic Model. Chem 9. The Greek Model. Democritus - A Greek Philosopher, 400 BC. Concluded that matter could not be divided into smaller and smaller pieces forever. Eventually, the smallest piece of matter would be found. He used the word "Atomos“ meaning indivisible.

The Atomic Model
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Atomic Model Chem 9
The Greek Model • Democritus- A Greek Philosopher, 400 BC. • Concluded that matter could not be divided into smaller and smaller pieces forever. • Eventually, the smallest piece of matter would be found. • He used the word "Atomos“ meaning indivisible.
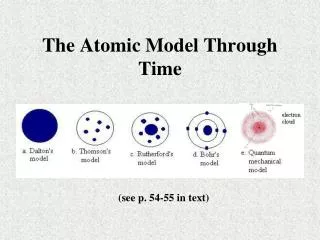
The Dalton Model: Billiard Ball Model • John Dalton - The English chemist that proposed first Atomic Theory in 1803. • All elements are composed of indivisible particles. • Atoms of the same element are exactly alike. • Atoms of different elements are different. • Compounds are formed by joining atoms of two or more elements
The Thomson Model: Chocolate Chip Cookie ModelPlum Pudding Model J. J. Thomson 1856 – 1940 – (English scientist) • discovered negative particle (an Electron) in 1887 by using a cathode ray tube • initially called electrons CORPUSLES
Robert A. Millikan (1868 – 1953) 1900 – mass of Electron approximately 1/2000 the mass of a Hydrogen atom 1916 -determined the charge carried by an electron Millikan OIL DROP EXPERIMENT
Eugene Goldstein (1850 -1930) • 1866 Eugene Goldstein found Positive particle – Protons • He named them CANAL RAYS
Sir James Chadwick 1891 - 1974 • Discovered the neutron in 1932 • Has no charge • Neutron’s mass is close to proton’s mass
Ernest Rutherford - British Physicist Gold Foil Experiment • In 1908, proved the atom had a small, • dense, positively charged Nucleus. • He said an atom is mostly empty space and • negative electrons are scattered around • the outside edge.
Niels Bohr (Danish scientist)The Planetary Model - 1913 Bohr proposed: • Electrons move in definite orbits around the nucleus, like planets moving around the sun. • That each electron moves in a specific energy level.
Quantum Mechanical Model • Erwin Schrodinger (1887-1961) • -Electrons have NO definite path in an atom. • -Only a probable location is known based • on how much energy it has. -Atomic orbitals (s,p,d,f) are NOT fixed paths as Bohr suggested
Summary • Dalton : Solid Sphere • Thomson : Pos. & neg mixed together • Rutherford: Positive nucleus, neg electrons surrounding it • Bohr: Positive nucleus, neg electrons in exact orbits • Quantum Mechanical Theory • (Electron cloud theory)