Solubility Rules
70 likes | 328 Vues
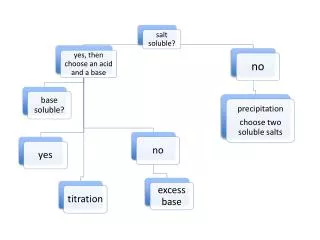
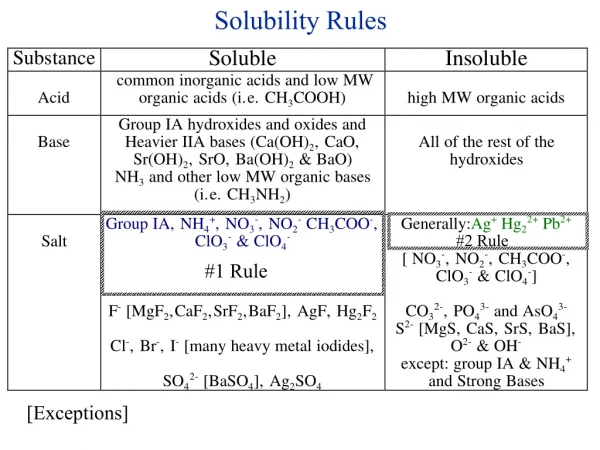
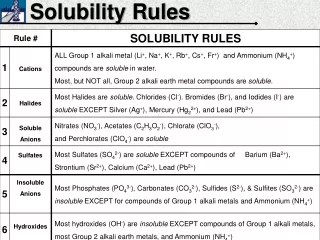
Solubility Rules. Steps for Net Ionic Equations. Write the chemical formula equation. Decide which are strong electrolytes and put a line between the anion and the cation. Also, show the charge of the ion.

Solubility Rules
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Solubility Rules Mullis
Steps for Net Ionic Equations • Write the chemical formula equation. • Decide which are strong electrolytes and put a line between the anion and the cation. Also, show the charge of the ion. • If the species is not a strong electrolyte, draw a box around it so you will remember to leave it as a compound. • Cancel the spectator ions. Mullis
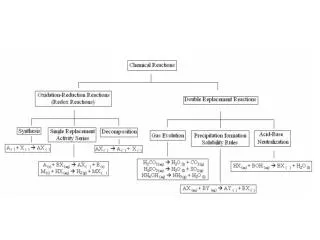
Net ionic equations (quick way) • Includes only those compounds and ions that undergo chemical change in a reaction in an aqueous solution. • Ions that do not take part in the reaction and are found in solution both before and after are spectator ions. Ex: Pb(NO3)2 + 2KCl PbCl2+ 2KNO3 All are soluble except lead(II)chloride, so: Pb2+/ NO3- + K+/Cl- PbCl2 + K+/NO3- Net ionic equation (cross out spectators on both sides): Pb2+ + 2Cl- PbCl2 Mullis
Net ionic equations (textbook way) • Includes only those compounds and ions that undergo chemical change in a reaction in an aqueous solution. • Ions that do not take part in the reaction and are found in solution both before and after are spectator ions. Ex: Zinc nitrate and ammonium sulfide make a solid precipitate, ZnS. Zn(NO3)2 (aq) + (NH4)S (aq) ZnS(s) + 2NH4NO3 (aq) Overall ionic equation: Zn2+ + 2NO3- + 2NH4 + + S2- ZnS + 2NH4+ + 2NO3- Net ionic equation (cross out spectators on both sides): Zn2+ + S2- ZnS Mullis
Net ionic equations--Examples Potassium sulfate and barium nitrate make a solid precipitate, BaSO4. K2SO4 (aq) + Ba(NO3)2(aq) BaSO4(s) + 2KNO3 (aq) Overall ionic equation: 2K++ SO42- +Ba2+ + 2NO3- BaSO4 + 2K+ + 2NO3- Net ionic equation (cross out spectators on both sides): SO42- +Ba2+ BaSO4 Mullis
HNO3 and NaOH are mixed in chemically equivalent quantities. What is the correct formula equation, overall ionic equation and net ionic equation? HNO3(aq) + NaOH(aq) NaNO3(aq) + H2O (l) Overall ionic equation: H3O+ + NO3- +Na+ + OH- Na+ + NO3- + 2H2O (l) Net ionic equation (cross out spectators on both sides): H3O+ + OH- 2H2O (l) Mullis