DC Circuits: Emf, Voltage, and Resistors in Parallel and Series
210 likes | 259 Vues
Learn about electromotive force (emf), terminal voltage, resistors in parallel and series, and Kirchhoff’s rules in this comprehensive guide. Discover how to calculate circuit parameters and understand capacitors in series and parallel configurations.

DC Circuits: Emf, Voltage, and Resistors in Parallel and Series
E N D
Presentation Transcript
DC circuits Physics Department, New York City College of Technology
Electromotive force (emf) Terminal voltage Resistors in parallel and in series Kirchhoff’s rules Junction rule Loop rule Capacitors in series and in parallel RC cuicuits Key words
emf • Electromotive force (emf) refers to the potential difference between the terminals of a source when no current flows out. Its symbol is .
Terminal voltage • Terminal voltage is the potential difference between the terminals of a source when current flows, and is calculated as • is the emf • r is the internal resistance of the battery
Example #1 • A 65-Ω resistor is connected to the terminals of a battery whose emf is 12V and whose internal resistance is 0.5Ω. Calculate (a) the current in the circuit, (b) the terminal voltage of the battery, and (c) the power dissipated in the resistor R and in the battery's internal resistance r.
Example #1—continued (a) (b) (c)
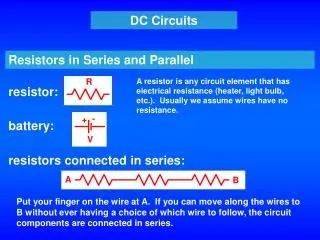
Resistors in series • The equivalent resistance for resistors in series is
Resistors in parallel • The equivalent resistance for resistors in parallel is
Voltage drop along wire • Disc 18, #1 • Disc 18, #2 • Disc 18, #6
Series/parallel resistors • Disc 17, #23 • Disc 17, #24
Example #2 • Two 100Ω resistors are connected (a) in parallel, and (b) in series, to a 24V battery. What is the current through each resistor and what is the equivalent resistance of each circuit?
Kirchhoff’s rules • The junction rule: at any junction point, the sum of all currents entering the junction must equal the sum of all currents leaving the junction. It is based on the conservation of electric charge. • The loop rule: the sum of the changes in potential around any closed path of a circuit must be zero. It is based on the conservation of energy.
Example #3 • Calculate the currents I1, I2, and I3.
Capacitors in series and in parallel • The equivalent capacitance for capacitors in series is • The equivalent capacitance for capacitors in parallel is
In the charging process, In the discharging process, The time constant is R ε C Switch RC circuits
RC charging curve • Disc 18, #28