Cell Structures
440 likes | 638 Vues
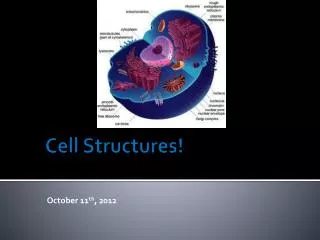
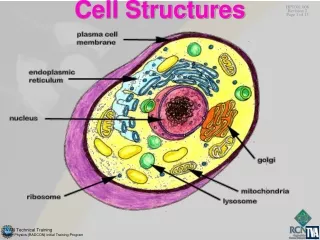
Cell Structures. Cell Structures. Barriers…. Cell Wall Plants & prok . (not animals) Structural (plant support) & protective role Cellulose in plants Freely permeable. Cell walls of onion skin…. Barriers…. Cell Membrane (plasma membrane) In ALL cells Support/protection

Cell Structures
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Barriers… • Cell Wall • Plants & prok. (not animals) • Structural (plant support) & protective role • Cellulose in plants • Freely permeable
Barriers… • Cell Membrane (plasma membrane) • In ALL cells • Support/protection • Regulates movement in/out of: • Water • Nutrients • Waste products
Barriers… • Nuclear Envelope (nuclear membrane) • Surrounds nucleus • Thousands of pores • Material move in/out, incl. RNA
Fluids… • Cytoplasm (cytosol) • Bet. cell mem. and nuclear env., site of most chemical activity • Nucleoplasm • Semi-fluid medium of nucleus • Protoplasm • Term used for all substances inside cell
The Control Center The Nucleus
The Nucleus… • Controls most cell processes • Contains Chromatin • DNA bound to proteins • During cell division, condenses to Chromosomes… • Has a Nucleolus • Small, dense region • Assembly of Ribosomes • Nuclear Envelope (or membrane)
Little Organsassist the cell in conducting reproductive, respiratory, and structural needs Organelles of the cytoplasm
Cytoskeleton… • Protein filaments • Maintains cell shape • Involved in cell movement
Mitochondrion… • Uses energy from food • Makes high-energy compounds (ATP) needed for Rx elsewhere.
Ribosomes… • Small, made of RNA (is an RNA molecule) • Assembly of proteins • Free in cytoplasm or attached to Rough ER
Endoplasmic Reticulum… • Large, assists with other organelle movement • Two types: • Rough ER (RER) • Ribosomes stud surface • Aids in synthesis and modif. of proteins • Found wrapped around nucleus, extending into cytosol • Smooth ER (SER) • No ribosomes, attached to distal RER • Synthesis of lipids, phospholipids, steroids (Plentiful in testes, ovaries, skin oil glands)
Golgi Apparatus… • Receives proteins from rough ER • Enzymes attach carbs and lipids to the proteins • Can store proteins until needed • Proteins then sent to final destination(within cell or outside – exocytosis) • PACKAGING and SHIPPING
Vacuoles… • Saclike structure • Stores water, salts, proteins, carbs • Can be large in plant cells • Helps in plant support by keeping turgor pressure high
Vacuoles Korotnovella, an amoeba. Inside this cell we can see a nucleus near the center with a rather angular dark nucleolus, various food vacuoles, and a clear round contractile vacuole at about 10 o'clock.
Lysosomes… • Filled with enzymes (like H2O2) • Breaks down • lipids, carbs, and proteins from food • old organelles • debris and harmful invaders
Plastid 1: Chloroplasts… • In plants, not animals or fungi • Uses sunlight to make energy rich food mol. thru photosynthesis (psyn)
Plastid 2: Leucoplast • Sometimes called amyloplast; stores starch (amylose)
Plastid 3: Chromoplast • Stores pigments in plants
Centrioles • Cylindrical; group of microtubules • In animal cells, used in cell division • As “basal bodies,” form cilia and flagella
Cell membrane - Structure • A phospholipid contains- • one head; negatively charged phosphate group that is hydrophilic (water-loving) • two tails of fatty acid chains that are hydrophobic (water fearing)
The Cell Membrane • Made of a phospholipid bilayer • regulates what passes in/out • Supports and protects • Selectively permeable – only certain things pass through. • 5 nm thick
Cell membrane features • The fluid mosaic model • fluid in nature cell mobility • Within mem. are various proteins for: • enzyme activity, • cell attachment, • communicating with other cells, • Trans. of substances in and out